Netty 之 TCP粘包拆包场景
2016-09-20 14:48
387 查看
TCP编程底层都有粘包和拆包机制,因为我们在C/S这种传输模型下,以TCP协议传输的时候,在网络中的byte其实就像是河水,TCP就像一个搬运工,将这流水从一端转送到另一端,这时又分两种情况:
1)如果客户端的每次制造的水比较多,也就是我们常说的客户端给的包比较大,TCP这个搬运工就会分多次去搬运。
2)如果客户端每次制造的水比较少的话,TCP可能会等客户端多次生产之后,把所有的水一起再运输到另一端
上述第一种情况,就是需要我们进行粘包,在另一端接收的时候,需要把多次获取的结果粘在一起,变成我们可以理解的信息,第二种情况,我们在另一端接收的时候,就必须进行拆包处理,因为每次接收的信息,可能是另一个远程端多次发送的包,被TCP粘在一起的
我们进行上述两种情况给出具体的场景:
1)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,拆包的现象:
我们先写客户端的bootstrap:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class BaseClient {
static final String HOST = System.getProperty("host", "127.0.0.1");
static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8080"));
static final int SIZE = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("size", "256"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
// p.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
p.addLast(new BaseClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush("Hello Netty Server ,I am a common client");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端的handler:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private byte[] req;
private int counter;
public BaseClientHandler() {
// req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner" + System.getProperty("line.separator"))
// .getBytes();
req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
+ "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
+ "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
+ "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
+ "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
+ "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
+ " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
+ "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
+ "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
+ "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
+ "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
// }
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
String buf = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Now is : " + buf + " ; the counter is : "+ ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}
服务端的serverBootstrap:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class BaseServer {
private int port;
public BaseServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap sbs = new ServerBootstrap().group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new BaseServerHandler());
};
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture future = sbs.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Server start listen at " + port );
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} else {
port = 8080;
}
new BaseServer(port).start();
}
}
服务端的handler:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private int counter;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String body = (String)msg;
System.out.println("server receive order : " + body + ";the counter is: " + ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
照例,我们先运行服务器端:
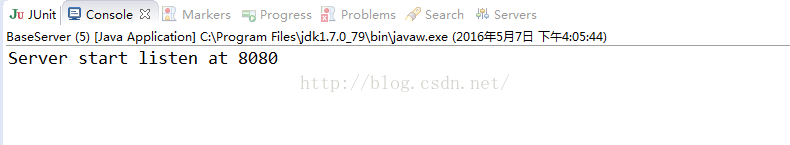
我们再运行客户端,客户端启动后,我们再看看服务器端的控制台打印输出:

我们可以看到服务器端分三次接收到了客户端两次发送的那段很长的信息
2)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,粘包的现象:
客户端和服务端的bootstrap不改变,我们修改一下,客户端发送信息的channelActive的代码:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private byte[] req;
private int counter;
public BaseClientHandler() {
req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner").getBytes();
// req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
// + "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
// + "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
// + "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
// + "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
// + "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
// + " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
// + "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
// + "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
// + "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
// + "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}
我们再次启动服务器端:
启动客户端后,依旧看服务器端的控制台:
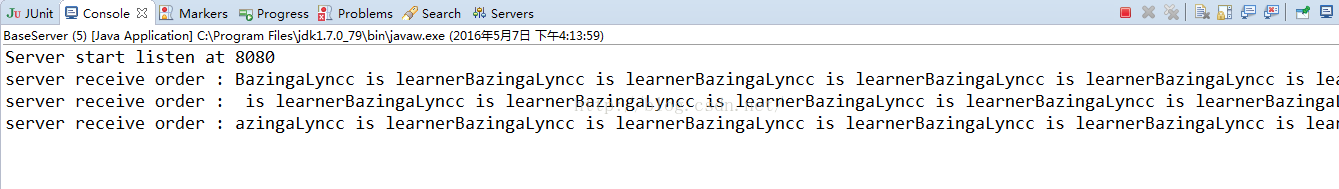
可以看出,客户端发送100次的信息,被服务器端分三次就接收了,这就发生了粘包的现象
以上就是典型的粘包和拆包的场景
1)如果客户端的每次制造的水比较多,也就是我们常说的客户端给的包比较大,TCP这个搬运工就会分多次去搬运。
2)如果客户端每次制造的水比较少的话,TCP可能会等客户端多次生产之后,把所有的水一起再运输到另一端
上述第一种情况,就是需要我们进行粘包,在另一端接收的时候,需要把多次获取的结果粘在一起,变成我们可以理解的信息,第二种情况,我们在另一端接收的时候,就必须进行拆包处理,因为每次接收的信息,可能是另一个远程端多次发送的包,被TCP粘在一起的
我们进行上述两种情况给出具体的场景:
1)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,拆包的现象:
我们先写客户端的bootstrap:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class BaseClient {
static final String HOST = System.getProperty("host", "127.0.0.1");
static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8080"));
static final int SIZE = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("size", "256"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
// p.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
p.addLast(new BaseClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush("Hello Netty Server ,I am a common client");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端的handler:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private byte[] req;
private int counter;
public BaseClientHandler() {
// req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner" + System.getProperty("line.separator"))
// .getBytes();
req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
+ "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
+ "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
+ "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
+ "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
+ "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
+ " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
+ "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
+ "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
+ "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
+ "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
// }
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
String buf = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Now is : " + buf + " ; the counter is : "+ ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}
服务端的serverBootstrap:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class BaseServer {
private int port;
public BaseServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap sbs = new ServerBootstrap().group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new BaseServerHandler());
};
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture future = sbs.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Server start listen at " + port );
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} else {
port = 8080;
}
new BaseServer(port).start();
}
}
服务端的handler:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private int counter;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String body = (String)msg;
System.out.println("server receive order : " + body + ";the counter is: " + ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
照例,我们先运行服务器端:

我们再运行客户端,客户端启动后,我们再看看服务器端的控制台打印输出:

我们可以看到服务器端分三次接收到了客户端两次发送的那段很长的信息
2)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,粘包的现象:
客户端和服务端的bootstrap不改变,我们修改一下,客户端发送信息的channelActive的代码:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private byte[] req;
private int counter;
public BaseClientHandler() {
req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner").getBytes();
// req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
// + "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
// + "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
// + "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
// + "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
// + "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
// + " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
// + "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
// + "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
// + "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
// + "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
// message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
// message.writeBytes(req);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}
我们再次启动服务器端:

启动客户端后,依旧看服务器端的控制台:

可以看出,客户端发送100次的信息,被服务器端分三次就接收了,这就发生了粘包的现象
以上就是典型的粘包和拆包的场景
相关文章推荐
- Netty 之 TCP粘包拆包场景
- 一起学Netty(六)之 TCP粘包拆包场景
- 一起学Netty(六)之 TCP粘包拆包场景
- 一起学Netty(六)之 TCP粘包拆包场景
- Netty学习(四)-TCP粘包和拆包
- Netty的TCP粘包/拆包(源码二)
- Netty通信框架提供解决TCP粘包拆包问题方案
- Netty解决半包(TCP粘包/拆包导致)读写问题
- Netty(二)——TCP粘包/拆包
- 网络通信框架Netty的TCP粘包/拆包解决方案
- Netty中处理TCP粘包和拆包
- Netty学习之TCP粘包/拆包
- Netty(三)TCP粘包拆包处理
- java netty入门(2)-TCP粘包拆包
- TCP粘包&拆包问题与Netty解决方案
- Netty中使用MessagePack时的TCP粘包问题与解决方案
- 【Netty】TCP粘包和拆包
- Netty解决TCP粘包,拆包
- Netty解决半包(TCP粘包/拆包导致)读写问题
- Netty3.10.1:关于TCP粘包问题 及 Encoder&Decoder
