C++中的IO类(iostream, fstream, stringstream)小结
2016-08-27 11:55
417 查看
以前学习C++的时候, 总是囫囵吞枣地理解cin, cout等东东, 最近又在刷oj, 使用到了IO类的时候, 有点感触, 所以呢, 打算记录一下。
俗话说, 一图胜过千言万语, 这不是没有道理的, 下面, 我们来看看基本IO类的继承结构:
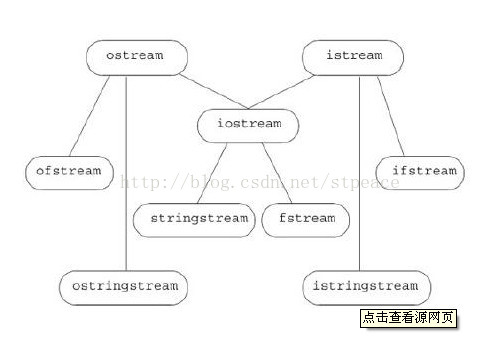
在我们写C++简单代码的时候, 最喜欢写#include <iostream> , 那么, 这实际上是在包括IO流的头文件, 而用using namespace std;则表示用标准空间, 这样才能用cin,cout, endl等东东啊。
从上图看, 实际上可以把IO类分为三类:
1. iostream类: 负责与控制台输入输出打交道, 这个我们已经很熟悉了。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:istream和ostream
2. fstream类: 负责与文件输入输出打交道, 这个我们接触过。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:ifstream和ofstream
3. stringstream类:负责与string上的输入输出打交道, 这个我们暂时还真没用过。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:istringstream和ostringstream。
下面, 我们来一一学习/复习:
1. IO类之iostream,继承了istream和ostream。
iostream类的对象, 如cin, cout, 会直接与控制台输入输出关联, 下面我们来看看最简单的程序:
最常使用的是cin和cout,这两个都是对象,cin是istream类的对象,cout是ostream类的对象,而输入的cin>>与输出时的cout<<中的左移<<与右移>>分别是istream类与ostream类的操作符重载。
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = -1;
cin >> i; // cin从控制台接收输入, 并保存在i中
cout << i << endl; // count把i的值输出到控制台
return 0;
}
很简单很好理解吧。
2. IO类值之fstream,继承了iostream。
1) ifstream类:从istream类派生。
2) ofstream类:从ostream类派生。
3) fstream类:从iostream类派生。
fstream的对象, 与文件建立关联, 我们已经很熟悉了, 直接看代码吧:
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt"); // 建立in与文件test.txt之间的额关联
if(!in)
{
cout << "error" << endl;
return 1;
}
string line;
while(getline(in, line))
{
cout << line << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3. IO类之stringstream
stringstream的对象与内存中的string对象建立关联, 往string对象写东西, 或者从string对象读取东西。
我们先看这样一个问题, 假设test.txt的内容为:
lucy 123
lili 234 456
tom 222 456 535
jim 2345 675 34 654
其中每行第一个单词是姓名, 后面的数字都是他们的银行卡密码, 当然啦, jim的银行卡最多, 有4张, 现在, 要实现如下输出, 该怎么做呢?
lucy 123x
lili 234x 456x
tom 222x 456x 535x
jim 2345x 675x 34x 654x
直接看程序吧:
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt"); // 建立in与文件test.txt之间的额关联
if(!in)
{
cout << "error" << endl;
return 1;
}
string line;
string password;
while(getline(in, line))
{
istringstream ss(line); // 建立ss与line之间的关联
int i = 0;
while(ss >> password) // ss从line读取东西并保存在password中
{
cout << password + (1 == ++i ? "" : "x") << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果ok.
下面, 我们来看看如何利用istringstream实现字符串向数值的转化:
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = -1;
string s = "101";
istringstream is(s); // 建立关联
cout << is.str() << endl; // 101, 看来is和s确实关联起来了啊
is >> a;
cout << a << endl; // 101
return 0;
}
当然, 我们也可以把数字格式化为字符串, 如下(下面这个程序有问题):
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
ostringstream os(str); // 建立关联, 但实际没有关联上啊!!!
os << "hello";
cout << str << endl; // str居然是空, 怎么不是"abc"呢? 我不理解
return 0;
}
看来, 上面的关联是不成功的, 改为:
[cpp] view
plain copy


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = -1;
ostringstream os;
os << "hello" << a;
cout << os.str() << endl; // hello-1
return 0;
}
所以, 我总结呢, istringstream的关联是ok的, 但是ostringstream不能依赖于关联, 不知道C++为啥要这样搞。
好吧, 到此为止, 总算是对三种类型的IO类有所掌握了。
getline()头文件为
[plain] view
plain copy


#include <string>
getline()的原型为:
[plain] view
plain copy


istream& getline(istream &in, string &line, char delim);
in是一个输入流,如cin、ifstream等。line是将输入流中的字符串放到这个string中,delim是结束字符,默认情况下是‘\n’,也就是说读取字符串直到遇到'\n';当没有任何字符时,返回false,可以用来判断文件是否结束。
所以,我们可以使用getline从文件中逐行读取到string中,然后将该行和istringstream绑定,逐个字符串处理。
例如,txt文件中每行的内容为:
[plain] view
plain copy


000002.jpg car 44 28 132 121
逐行读取,并对每行中的字符串逐个处理。
[plain] view
plain copy


int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string line;
std::string word;
std::ifstream fin("test.txt");
while (getline(fin, line))
{
std::istringstream stream(line);
while (stream >> word)
std::cout << word << "\n";
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
最后输出:

后面的数字可以转成int:
[plain] view
plain copy


atoi(stream.c_str());
俗话说, 一图胜过千言万语, 这不是没有道理的, 下面, 我们来看看基本IO类的继承结构:

在我们写C++简单代码的时候, 最喜欢写#include <iostream> , 那么, 这实际上是在包括IO流的头文件, 而用using namespace std;则表示用标准空间, 这样才能用cin,cout, endl等东东啊。
从上图看, 实际上可以把IO类分为三类:
1. iostream类: 负责与控制台输入输出打交道, 这个我们已经很熟悉了。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:istream和ostream
2. fstream类: 负责与文件输入输出打交道, 这个我们接触过。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:ifstream和ofstream
3. stringstream类:负责与string上的输入输出打交道, 这个我们暂时还真没用过。 注意: 实际具体又可以区分为:istringstream和ostringstream。
下面, 我们来一一学习/复习:
1. IO类之iostream,继承了istream和ostream。
iostream类的对象, 如cin, cout, 会直接与控制台输入输出关联, 下面我们来看看最简单的程序:
最常使用的是cin和cout,这两个都是对象,cin是istream类的对象,cout是ostream类的对象,而输入的cin>>与输出时的cout<<中的左移<<与右移>>分别是istream类与ostream类的操作符重载。
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = -1;
cin >> i; // cin从控制台接收输入, 并保存在i中
cout << i << endl; // count把i的值输出到控制台
return 0;
}
很简单很好理解吧。
2. IO类值之fstream,继承了iostream。
1) ifstream类:从istream类派生。
2) ofstream类:从ostream类派生。
3) fstream类:从iostream类派生。
fstream的对象, 与文件建立关联, 我们已经很熟悉了, 直接看代码吧:
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt"); // 建立in与文件test.txt之间的额关联
if(!in)
{
cout << "error" << endl;
return 1;
}
string line;
while(getline(in, line))
{
cout << line << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3. IO类之stringstream
stringstream的对象与内存中的string对象建立关联, 往string对象写东西, 或者从string对象读取东西。
我们先看这样一个问题, 假设test.txt的内容为:
lucy 123
lili 234 456
tom 222 456 535
jim 2345 675 34 654
其中每行第一个单词是姓名, 后面的数字都是他们的银行卡密码, 当然啦, jim的银行卡最多, 有4张, 现在, 要实现如下输出, 该怎么做呢?
lucy 123x
lili 234x 456x
tom 222x 456x 535x
jim 2345x 675x 34x 654x
直接看程序吧:
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt"); // 建立in与文件test.txt之间的额关联
if(!in)
{
cout << "error" << endl;
return 1;
}
string line;
string password;
while(getline(in, line))
{
istringstream ss(line); // 建立ss与line之间的关联
int i = 0;
while(ss >> password) // ss从line读取东西并保存在password中
{
cout << password + (1 == ++i ? "" : "x") << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果ok.
下面, 我们来看看如何利用istringstream实现字符串向数值的转化:
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = -1;
string s = "101";
istringstream is(s); // 建立关联
cout << is.str() << endl; // 101, 看来is和s确实关联起来了啊
is >> a;
cout << a << endl; // 101
return 0;
}
当然, 我们也可以把数字格式化为字符串, 如下(下面这个程序有问题):
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
ostringstream os(str); // 建立关联, 但实际没有关联上啊!!!
os << "hello";
cout << str << endl; // str居然是空, 怎么不是"abc"呢? 我不理解
return 0;
}
看来, 上面的关联是不成功的, 改为:
[cpp] view
plain copy

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = -1;
ostringstream os;
os << "hello" << a;
cout << os.str() << endl; // hello-1
return 0;
}
所以, 我总结呢, istringstream的关联是ok的, 但是ostringstream不能依赖于关联, 不知道C++为啥要这样搞。
好吧, 到此为止, 总算是对三种类型的IO类有所掌握了。
getline()
getline()头文件为[plain] view
plain copy

#include <string>
getline()的原型为:
[plain] view
plain copy

istream& getline(istream &in, string &line, char delim);
in是一个输入流,如cin、ifstream等。line是将输入流中的字符串放到这个string中,delim是结束字符,默认情况下是‘\n’,也就是说读取字符串直到遇到'\n';当没有任何字符时,返回false,可以用来判断文件是否结束。
所以,我们可以使用getline从文件中逐行读取到string中,然后将该行和istringstream绑定,逐个字符串处理。
例如,txt文件中每行的内容为:
[plain] view
plain copy

000002.jpg car 44 28 132 121
逐行读取,并对每行中的字符串逐个处理。
[plain] view
plain copy

int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string line;
std::string word;
std::ifstream fin("test.txt");
while (getline(fin, line))
{
std::istringstream stream(line);
while (stream >> word)
std::cout << word << "\n";
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
最后输出:

后面的数字可以转成int:
[plain] view
plain copy

atoi(stream.c_str());
相关文章推荐
- C++中的IO类(iostream, fstream, stringstream)小结
- C++中的IO类(iostream, fstream, stringstream)小结
- C++中的IO类(iostream, fstream, stringstream)
- C++中的IO类(iostream, fstream, stringstream)小结
- C++ IO流:iostream、fstream、strstream
- c++文件处理————fstream,和 io中状态标识位failbit badbit eofbit goodbit
- stream、fstream和stringstream用法小结(提纲)
- C++ 标准IO库 iostream,fstream,sstream
- c++ primer plus 第十七章 输入 输出 文件 IO iostream fstream
- C/C++文件IO输入输出操作——FILE*、fstream、windowsAPI
- C++IO库--fstream和stringstream
- C/C++文件IO输入输出操作——FILE*、fstream、windowsAPI
- 【C++】iostream, fstream, stringstream知识
- [C++][IO]fstream用法
- C++ iostream和fstream的示例
- IO类(iostream、fstream、sstream)
- C++的iostream标准库介绍
- "COM as a better C++"读后小结
- C++的iostream标准库介绍
- C++中二维数组new小结
