iOS 在地图上绘制运动轨迹
2016-08-01 11:36
537 查看
iOS中的MapKit集成了google地图api的很多功能加上iOS的定位的功能,我们就可以实现将你运行的轨迹绘制到地图上面。这个功能非常有用,比如快递追踪、汽车的gprs追踪、人员追踪等等。这篇文章我们将使用Map Kit和iOS的定位功能,将你的运行轨迹绘制在地图上面。
实现
在之前的一篇文章描述了如何在地图上显示自己的位置,如果我们将这些位置先保存起来,然后串联起来绘制到地图上面,那就是我们的运行轨迹了。
首先我们看下如何在地图上绘制曲线。在Map Kit中提供了一个叫MKPolyline的类,我们可以利用它来绘制曲线,先看个简单的例子。
使用下面代码从一个文件中读取出经纬度,然后创建一个路径:MKPolyline实例。
[plain] view
plaincopy
-(void) loadRoute
{
NSString* filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@”route” ofType:@”csv”];
NSString* fileContents = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSArray* pointStrings = [fileContents componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet]];
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * pointStrings.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < pointStrings.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [pointStrings objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
// create our coordinate and add it to the correct spot in the array
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
//
// adjust the bounding box
//
// if it is the first point, just use them, since we have nothing to compare to yet.
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
// create the polyline based on the array of points.
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:pointStrings.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
// clear the memory allocated earlier for the points
free(pointArr);
}
[plain] view
plain copy
-(void) loadRoute
{
NSString* filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@”route” ofType:@”csv”];
NSString* fileContents = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSArray* pointStrings = [fileContents componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet]];
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * pointStrings.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < pointStrings.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [pointStrings objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
// create our coordinate and add it to the correct spot in the array
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
//
// adjust the bounding box
//
// if it is the first point, just use them, since we have nothing to compare to yet.
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
// create the polyline based on the array of points.
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:pointStrings.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
// clear the memory allocated earlier for the points
free(pointArr);
}
将这个路径添加到地图上
[plain] view
plaincopy
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
[plain] view
plain copy
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
显示在地图上:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (MKOverlayView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForOverlay:(id )overlay
{
MKOverlayView* overlayView = nil;
if(overlay == self.routeLine)
{
//if we have not yet created an overlay view for this overlay, create it now.
if(nil == self.routeLineView)
{
self.routeLineView = [[[MKPolylineView alloc] initWithPolyline:self.routeLine] autorelease];
self.routeLineView.fillColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.lineWidth = 3;
}
overlayView = self.routeLineView;
}
return overlayView;
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (MKOverlayView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForOverlay:(id )overlay
{
MKOverlayView* overlayView = nil;
if(overlay == self.routeLine)
{
//if we have not yet created an overlay view for this overlay, create it now.
if(nil == self.routeLineView)
{
self.routeLineView = [[[MKPolylineView alloc] initWithPolyline:self.routeLine] autorelease];
self.routeLineView.fillColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.lineWidth = 3;
}
overlayView = self.routeLineView;
}
return overlayView;
}
效果:
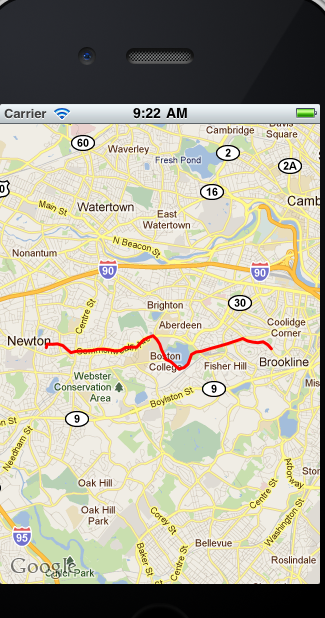
然后我们在从文件中读取位置的方法改成从用gprs等方法获取当前位置。
第一步:创建一个CLLocationManager实例
第二步:设置CLLocationManager实例委托和精度
第三步:设置距离筛选器distanceFilter
第四步:启动请求
代码如下:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
noUpdates = 0;
locations = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
locationMgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationMgr.delegate = self;
locationMgr.desiredAccuracy =kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
locationMgr.distanceFilter = 1.0f;
[locationMgr startUpdatingLocation];
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
noUpdates = 0;
locations = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
locationMgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationMgr.delegate = self;
locationMgr.desiredAccuracy =kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
locationMgr.distanceFilter = 1.0f;
[locationMgr startUpdatingLocation];
}
上面的代码我定义了一个数组,用于保存运行轨迹的经纬度。
每次通知更新当前位置的时候,我们将当前位置的经纬度放到这个数组中,并重新绘制路径,代码如下:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation *)newLocation
fromLocation:(CLLocation *)oldLocation{
noUpdates++;
[locations addObject: [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f,%f",[newLocation coordinate].latitude, [newLocation coordinate].longitude]];
[self updateLocation];
if (self.routeLine!=nil) {
self.routeLine =nil;
}
if(self.routeLine!=nil)
[self.mapView removeOverlay:self.routeLine];
self.routeLine =nil;
// create the overlay
[self loadRoute];
// add the overlay to the map
if (nil != self.routeLine) {
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
}
// zoom in on the route.
[self zoomInOnRoute];
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation *)newLocation
fromLocation:(CLLocation *)oldLocation{
noUpdates++;
[locations addObject: [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f,%f",[newLocation coordinate].latitude, [newLocation coordinate].longitude]];
[self updateLocation];
if (self.routeLine!=nil) {
self.routeLine =nil;
}
if(self.routeLine!=nil)
[self.mapView removeOverlay:self.routeLine];
self.routeLine =nil;
// create the overlay
[self loadRoute];
// add the overlay to the map
if (nil != self.routeLine) {
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
}
// zoom in on the route.
[self zoomInOnRoute];
}
我们将前面从文件获取经纬度创建轨迹的代码修改成从这个数组中取值就行了:
[plain] view
plaincopy
// creates the route (MKPolyline) overlay
-(void) loadRoute
{
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * locations.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < locations.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [locations objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:locations.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
free(pointArr);
}
[plain] view
plain copy
// creates the route (MKPolyline) overlay
-(void) loadRoute
{
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * locations.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < locations.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [locations objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:locations.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
free(pointArr);
}
这样我们就将我们运行得轨迹绘制google地图上面了。
扩展:
如果你想使用其他的地图,比如百度地图,其实也很方便。可以将百度地图放置到UIWebView中间,通过用js去绘制轨迹。
总结:这篇文章我们介绍了一种常见的技术实现:在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹。
实现
在之前的一篇文章描述了如何在地图上显示自己的位置,如果我们将这些位置先保存起来,然后串联起来绘制到地图上面,那就是我们的运行轨迹了。
首先我们看下如何在地图上绘制曲线。在Map Kit中提供了一个叫MKPolyline的类,我们可以利用它来绘制曲线,先看个简单的例子。
使用下面代码从一个文件中读取出经纬度,然后创建一个路径:MKPolyline实例。
[plain] view
plaincopy
-(void) loadRoute
{
NSString* filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@”route” ofType:@”csv”];
NSString* fileContents = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSArray* pointStrings = [fileContents componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet]];
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * pointStrings.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < pointStrings.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [pointStrings objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
// create our coordinate and add it to the correct spot in the array
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
//
// adjust the bounding box
//
// if it is the first point, just use them, since we have nothing to compare to yet.
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
// create the polyline based on the array of points.
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:pointStrings.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
// clear the memory allocated earlier for the points
free(pointArr);
}
[plain] view
plain copy
-(void) loadRoute
{
NSString* filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@”route” ofType:@”csv”];
NSString* fileContents = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSArray* pointStrings = [fileContents componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet whitespaceAndNewlineCharacterSet]];
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * pointStrings.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < pointStrings.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [pointStrings objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
// create our coordinate and add it to the correct spot in the array
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
//
// adjust the bounding box
//
// if it is the first point, just use them, since we have nothing to compare to yet.
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
// create the polyline based on the array of points.
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:pointStrings.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
// clear the memory allocated earlier for the points
free(pointArr);
}
将这个路径添加到地图上
[plain] view
plaincopy
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
[plain] view
plain copy
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
显示在地图上:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (MKOverlayView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForOverlay:(id )overlay
{
MKOverlayView* overlayView = nil;
if(overlay == self.routeLine)
{
//if we have not yet created an overlay view for this overlay, create it now.
if(nil == self.routeLineView)
{
self.routeLineView = [[[MKPolylineView alloc] initWithPolyline:self.routeLine] autorelease];
self.routeLineView.fillColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.lineWidth = 3;
}
overlayView = self.routeLineView;
}
return overlayView;
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (MKOverlayView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForOverlay:(id )overlay
{
MKOverlayView* overlayView = nil;
if(overlay == self.routeLine)
{
//if we have not yet created an overlay view for this overlay, create it now.
if(nil == self.routeLineView)
{
self.routeLineView = [[[MKPolylineView alloc] initWithPolyline:self.routeLine] autorelease];
self.routeLineView.fillColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
self.routeLineView.lineWidth = 3;
}
overlayView = self.routeLineView;
}
return overlayView;
}
效果:

然后我们在从文件中读取位置的方法改成从用gprs等方法获取当前位置。
第一步:创建一个CLLocationManager实例
第二步:设置CLLocationManager实例委托和精度
第三步:设置距离筛选器distanceFilter
第四步:启动请求
代码如下:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
noUpdates = 0;
locations = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
locationMgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationMgr.delegate = self;
locationMgr.desiredAccuracy =kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
locationMgr.distanceFilter = 1.0f;
[locationMgr startUpdatingLocation];
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
noUpdates = 0;
locations = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
locationMgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationMgr.delegate = self;
locationMgr.desiredAccuracy =kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
locationMgr.distanceFilter = 1.0f;
[locationMgr startUpdatingLocation];
}
上面的代码我定义了一个数组,用于保存运行轨迹的经纬度。
每次通知更新当前位置的时候,我们将当前位置的经纬度放到这个数组中,并重新绘制路径,代码如下:
[plain] view
plaincopy
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation *)newLocation
fromLocation:(CLLocation *)oldLocation{
noUpdates++;
[locations addObject: [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f,%f",[newLocation coordinate].latitude, [newLocation coordinate].longitude]];
[self updateLocation];
if (self.routeLine!=nil) {
self.routeLine =nil;
}
if(self.routeLine!=nil)
[self.mapView removeOverlay:self.routeLine];
self.routeLine =nil;
// create the overlay
[self loadRoute];
// add the overlay to the map
if (nil != self.routeLine) {
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
}
// zoom in on the route.
[self zoomInOnRoute];
}
[plain] view
plain copy
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation *)newLocation
fromLocation:(CLLocation *)oldLocation{
noUpdates++;
[locations addObject: [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f,%f",[newLocation coordinate].latitude, [newLocation coordinate].longitude]];
[self updateLocation];
if (self.routeLine!=nil) {
self.routeLine =nil;
}
if(self.routeLine!=nil)
[self.mapView removeOverlay:self.routeLine];
self.routeLine =nil;
// create the overlay
[self loadRoute];
// add the overlay to the map
if (nil != self.routeLine) {
[self.mapView addOverlay:self.routeLine];
}
// zoom in on the route.
[self zoomInOnRoute];
}
我们将前面从文件获取经纬度创建轨迹的代码修改成从这个数组中取值就行了:
[plain] view
plaincopy
// creates the route (MKPolyline) overlay
-(void) loadRoute
{
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * locations.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < locations.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [locations objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:locations.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
free(pointArr);
}
[plain] view
plain copy
// creates the route (MKPolyline) overlay
-(void) loadRoute
{
// while we create the route points, we will also be calculating the bounding box of our route
// so we can easily zoom in on it.
MKMapPoint northEastPoint;
MKMapPoint southWestPoint;
// create a c array of points.
MKMapPoint* pointArr = malloc(sizeof(CLLocationCoordinate2D) * locations.count);
for(int idx = 0; idx < locations.count; idx++)
{
// break the string down even further to latitude and longitude fields.
NSString* currentPointString = [locations objectAtIndex:idx];
NSArray* latLonArr = [currentPointString componentsSeparatedByCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@","]];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:0] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[latLonArr objectAtIndex:1] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(coordinate);
if (idx == 0) {
northEastPoint = point;
southWestPoint = point;
}
else
{
if (point.x > northEastPoint.x)
northEastPoint.x = point.x;
if(point.y > northEastPoint.y)
northEastPoint.y = point.y;
if (point.x < southWestPoint.x)
southWestPoint.x = point.x;
if (point.y < southWestPoint.y)
southWestPoint.y = point.y;
}
pointArr[idx] = point;
}
self.routeLine = [MKPolyline polylineWithPoints:pointArr count:locations.count];
_routeRect = MKMapRectMake(southWestPoint.x, southWestPoint.y, northEastPoint.x - southWestPoint.x, northEastPoint.y - southWestPoint.y);
free(pointArr);
}
这样我们就将我们运行得轨迹绘制google地图上面了。
扩展:
如果你想使用其他的地图,比如百度地图,其实也很方便。可以将百度地图放置到UIWebView中间,通过用js去绘制轨迹。
总结:这篇文章我们介绍了一种常见的技术实现:在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹。
相关文章推荐
- 在地图上绘制你运动的轨迹 ios
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS 在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS 之地图上绘制运动轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运动的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- iOS开发之在地图上绘制出你运行的轨迹
- ios使用地图定位记录运动轨迹
