数据结构与算法 1 :基本概念,线性表顺序结构,线性表链式结构,单向循环链表
2016-07-22 21:45
811 查看
【本文谢绝转载】
数据结构
起源:
计算机从解决数值计算问题到解决生活中的问题
现实生活中的问题涉及不同个体间的复杂联系
需要在计算机程序中描述生活中个体间的联系
数据结构主要研究非数值计算程序问题中的操作对象以及它们之间的关系
不是研究复杂的算法
基本概念
数据 – 程序的操作对象,用于描述客观事物
数据的特点:
可以输入到计算机
可以被计算机程序处理
数据是一个抽象的概念,将其进行分类后得到程序设计语言中的类型。如:int,float,char等等
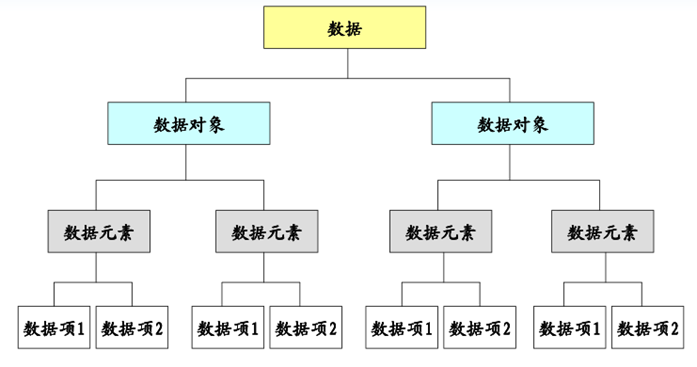
数据元素:组成数据的基本单位
数据项:一个数据元素由若干数据项组成
数据对象 – 性质相同的数据元素的集合
兑现代码:
数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系
数据元素之间不是独立的,存在特定的关系,这些关系即结构
数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系
如:数组中各个元素之间存在固定的线性关系
编写一个“好”的程序之前,必须分析待处理问题中各个对象的特性,以及对象之间的关系。
基本概念总结:
逻辑结构
指数据元素之间的逻辑关系。即从逻辑关系上描述数据,它与数据的存储无关,是独立于计算机的。逻辑结构可细分为4类:

物理结构

数据的运算

算法概念概念:
算法是特定问题求解步骤的描述
在计算机中表现为指令的有限序列
算法是独立存在的一种解决问题的方法和思想。
对于算法而言,语言并不重要,重要的是思想。
算法和数据结构区别:
数据结构只是静态的描述了数据元素之间的关系
高效的程序需要在数据结构的基础上设计和选择算法
程序=数据结构+算法
总结:
算法是为了解决实际问题而设计的
数据结构是算法需要处理的问题载体
数据结构与算法相辅相成
算法特性:
算法特性
输入
算法具有0个或多个输入
输出
算法至少有1个或多个输出
有穷性
算法在有限的步骤之后会自动结束而不会无限循环
确定性
算法中的每一步都有确定的含义,不会出现二义性
可行性
算法的每一步都是可行的
算法效率的度量
1、事后统计法
比较不同算法对同一组输入数据的运行处理时间缺陷 ,为了获得不同算法的运行时间必须编写相应程序,运行时间严重依赖硬件以及运行时的环境因素,算法的测试数据的选取相当困难。
事后统计法虽然直观,但是实施困难且缺陷多
2、事前分析估算:
依据统计的方法对算法效率进行估算,影响算法效率的主要因素,算法采用的策略和方法,问题的输入规模,编译器所产生的代码,计算机执行速度。
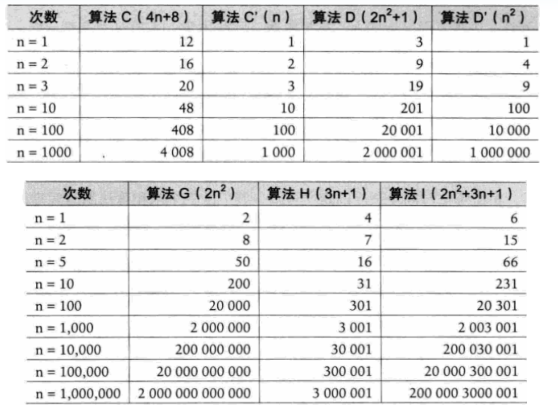
时间复杂度案例
注意1:判断一个算法的效率时,往往只需要关注操作数量的最高次项,其它次要项和常数项可以忽略。
注意2:在没有特殊说明时,我们所分析的算法的时间复杂度都是指最坏时间复杂度
大O表示法:
算法效率严重依赖于操作(Operation)数量
在判断时首先关注操作数量的最高次项
操作数量的估算可以作为时间复杂度的估算
O(5) = O(1)
O(2n + 1) = O(2n) = O(n)
O(n2+ n + 1) = O(n2)
O(3n3+1) = O(3n3) = O(n3)
常见时间复杂度
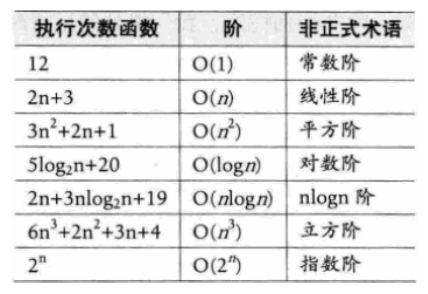
关系
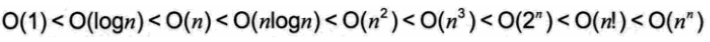
空间复杂度
算法的空间复杂度通过计算算法的存储空间实现
S(n) = O(f(n))
其中,n为问题规模,f(n))为在问题规模为nn时所占用存储空间的函数
大O表示法同样适用于算法的空间复杂度
当算法执行时所需要的空间是常数时,空间复杂度为O(1)
空间与时间的策略
多数情况下,算法执行时所用的时间更令人关注
如果有必要,可以通过增加空间复杂度来降低时间复杂度
同理,也可以通过增加时间复杂度来降低空间复杂度
练习1:分析sum1 sum2 sum3函数的空间复杂度
O(4n+12) O(8)=O(1) O(4)=O(1)
总结:实现算法时,需要分析具体问题,对执行时间和空间的要求。
时间换空间案例
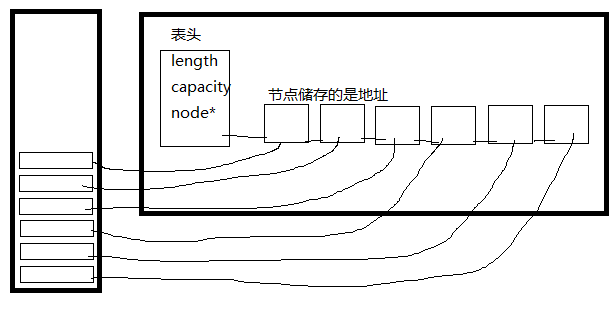
线性表
线性表中的数据元素之间是有顺序的
线性表中的数据元素个数是有限的
线性表中的数据元素的类型必须相同
1,线性表初步认识:
VS环境
【项目创建】
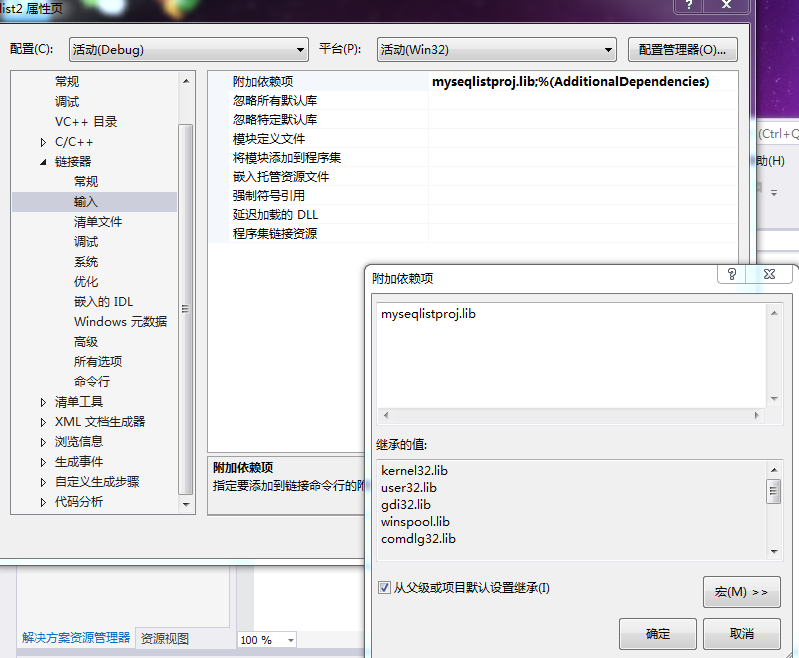
【连接器 添加.lib】
封装好的代码:3个文件
myseqlistproj.dll 放在可执行程序的同级目录
myseqlistproj.lib 放在主函数文件的同级目录,在连接器-输入里面添加myseqlistproj.lib
seqlist.h 放在主函数文件的同级目录
已上传至网盘:下载链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pJKK4w7 密码:a0re
代码:
主函数:
线性表顺序结构案例,C代码
三个文件:VS环境编译:
主函数main.c
文件2:
文件3:seqlist.c
线性表,单文件版,可以在Linux GCC 下编译运行:
无需为线性表中的逻辑关系增加额外的空间可以快速的获取表中合法位置的元素缺点:
插入和删除操作需要移动大量元素当线性表长度变化较大时难以确定存储空间的容量
企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现
3个文件:
linklist.h
linklist.c
main.c
文件1 main.c
文件2:linklist.h
linklist.c
企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现 单文件版
企业级线性表链式存储案例,我的练习
无需一次性定制链表的容量插入和删除操作无需移动数据元素缺点:
数据元素必须保存后继元素的位置信息获取指定数据的元素操作需要顺序访问之前的元素
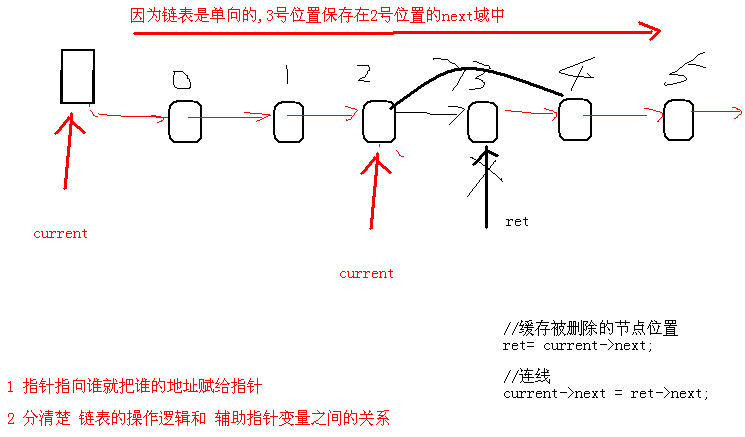
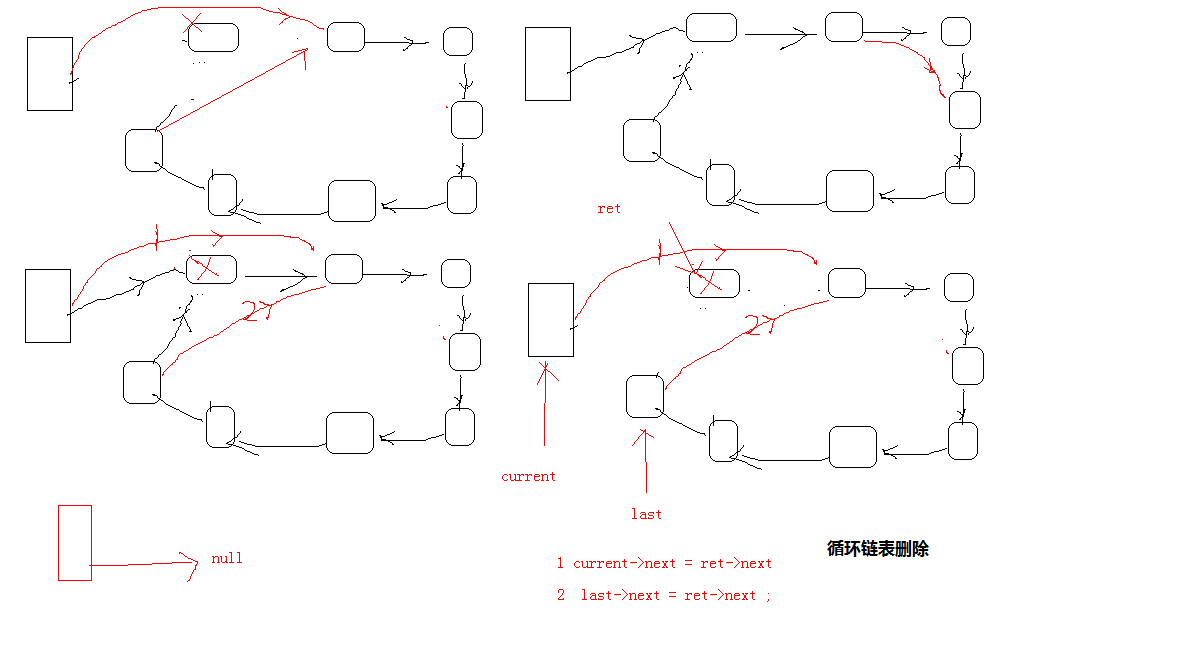
循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:
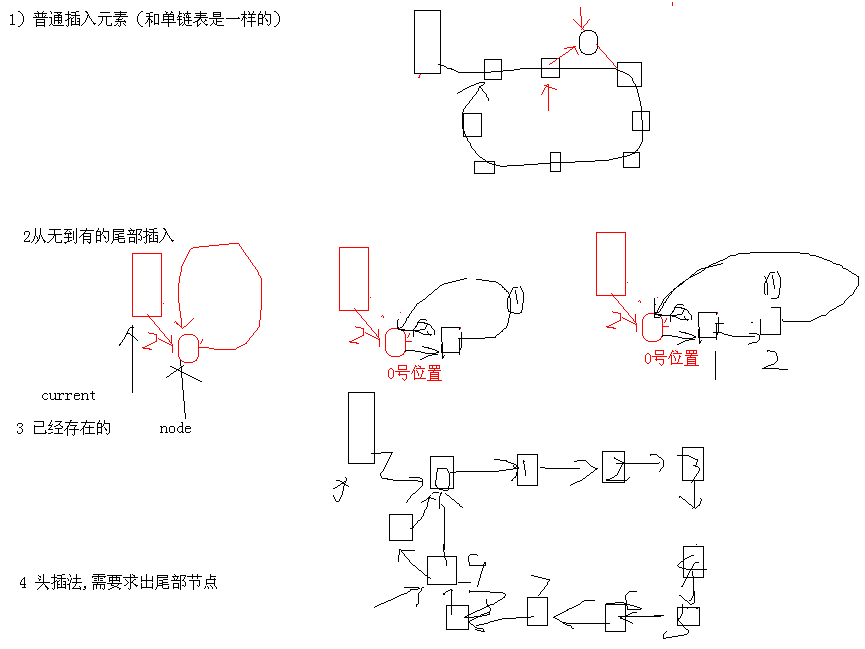
02_循环链表头插法操作逻辑和辅助指针变量之间的关系场景
3个文件:
CircleList.h
CircleList.c
main.c
main.c
CircleList.h
CircleList.c
循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:单文件
循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:我的练习
《大纲》 数据结构: 起源: 基本概念 数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系 逻辑结构 物理结构 数据的运算 算法概念: 概念 算法和数据结构区别 算法特性 算法效率的度量 大O表示法 时间复杂度案例 空间复杂度 时间换空间案例 1)线性表: 线性表初步认识: 线性表顺序结构案例 线性表顺序结构案例,单文件版 线性表的优缺点 企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现 企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现 单文件版 企业级线性表链式存储案例,我的练习 线性表链式存储优点缺点 单向循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例 循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:单文件版 循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:我的练习
数据结构
起源:
计算机从解决数值计算问题到解决生活中的问题
现实生活中的问题涉及不同个体间的复杂联系
需要在计算机程序中描述生活中个体间的联系
数据结构主要研究非数值计算程序问题中的操作对象以及它们之间的关系
不是研究复杂的算法
基本概念
数据 – 程序的操作对象,用于描述客观事物
数据的特点:
可以输入到计算机
可以被计算机程序处理
数据是一个抽象的概念,将其进行分类后得到程序设计语言中的类型。如:int,float,char等等
数据元素:组成数据的基本单位
数据项:一个数据元素由若干数据项组成
数据对象 – 性质相同的数据元素的集合
兑现代码:
//声明一个结构体类型
struct _MyTeacher //一种数据类型
{
char name[32];
char tile[32];
int age;
char addr[128];
};
int main21()
{
struct _MyTeacher t1; //数据元素
struct _MyTeacher tArray[30]; //数据对象
memset(&t1, 0, sizeof(t1));
strcpy(t1.name, "name"); //数据项
strcpy(t1.addr, "addr"); //数据项
strcpy(t1.tile, "addr"); //数据项
t1.age = 1;
}数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系
数据元素之间不是独立的,存在特定的关系,这些关系即结构
数据结构指数据对象中数据元素之间的关系
如:数组中各个元素之间存在固定的线性关系
编写一个“好”的程序之前,必须分析待处理问题中各个对象的特性,以及对象之间的关系。
基本概念总结:

逻辑结构
指数据元素之间的逻辑关系。即从逻辑关系上描述数据,它与数据的存储无关,是独立于计算机的。逻辑结构可细分为4类:

物理结构

数据的运算

算法概念概念:
算法是特定问题求解步骤的描述
在计算机中表现为指令的有限序列
算法是独立存在的一种解决问题的方法和思想。
对于算法而言,语言并不重要,重要的是思想。
算法和数据结构区别:
数据结构只是静态的描述了数据元素之间的关系
高效的程序需要在数据结构的基础上设计和选择算法
程序=数据结构+算法
总结:
算法是为了解决实际问题而设计的
数据结构是算法需要处理的问题载体
数据结构与算法相辅相成
算法特性:
算法特性
输入
算法具有0个或多个输入
输出
算法至少有1个或多个输出
有穷性
算法在有限的步骤之后会自动结束而不会无限循环
确定性
算法中的每一步都有确定的含义,不会出现二义性
可行性
算法的每一步都是可行的
算法效率的度量
1、事后统计法
比较不同算法对同一组输入数据的运行处理时间缺陷 ,为了获得不同算法的运行时间必须编写相应程序,运行时间严重依赖硬件以及运行时的环境因素,算法的测试数据的选取相当困难。
事后统计法虽然直观,但是实施困难且缺陷多
2、事前分析估算:
依据统计的方法对算法效率进行估算,影响算法效率的主要因素,算法采用的策略和方法,问题的输入规模,编译器所产生的代码,计算机执行速度。
时间复杂度案例
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c++$ cat main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//算法最终要编译成具体的计算机指令
//每一个指令,在具体的计算机 cpu上运行的时间是固定的
//通过具体的n的步骤就可以推导出算法的复杂度
long sum1(int n) //需要2n+3个步骤 --> 大O表示法:算法复杂度O(n)
{
long ret = 0; //需要1个步骤
int* array = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); //需要1个步骤
int i = 0; //需要1个步骤
for(i=0; i<n; i++) //需要n个步骤
{
array[i] = i + 1;
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++) //需要n个步骤
{
ret += array[i];
}
free(array); //需要1个步骤
return ret;
}
long sum2(int n) //需要n+2个步骤 --> 大O表示法:算法复杂度O(n)
{
long ret = 0; //需要1个步骤
int i = 0; //需要1个步骤
for(i=1; i<=n; i++) //需要n个步骤
{
ret += i;
}
return ret;
}
long sum3(int n) //需要2个步骤 --> 大O表示法:算法复杂度O(1)
{
long ret = 0; //需要1个步骤
if( n > 0 ) //需要1个步骤
{
ret = (1 + n) * n / 2;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
printf("%ld\n", sum1(100));
printf("%ld\n", sum2(100));
printf("%ld\n", sum3(100));
return 0;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c++$ gcc -g -o run main.c && ./run
5050
5050
5050
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c++$
注意1:判断一个算法的效率时,往往只需要关注操作数量的最高次项,其它次要项和常数项可以忽略。
注意2:在没有特殊说明时,我们所分析的算法的时间复杂度都是指最坏时间复杂度
大O表示法:
算法效率严重依赖于操作(Operation)数量
在判断时首先关注操作数量的最高次项
操作数量的估算可以作为时间复杂度的估算
O(5) = O(1)
O(2n + 1) = O(2n) = O(n)
O(n2+ n + 1) = O(n2)
O(3n3+1) = O(3n3) = O(n3)
常见时间复杂度

关系
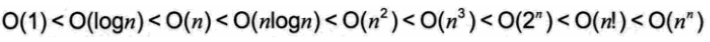
空间复杂度
算法的空间复杂度通过计算算法的存储空间实现
S(n) = O(f(n))
其中,n为问题规模,f(n))为在问题规模为nn时所占用存储空间的函数
大O表示法同样适用于算法的空间复杂度
当算法执行时所需要的空间是常数时,空间复杂度为O(1)
空间与时间的策略
多数情况下,算法执行时所用的时间更令人关注
如果有必要,可以通过增加空间复杂度来降低时间复杂度
同理,也可以通过增加时间复杂度来降低空间复杂度
练习1:分析sum1 sum2 sum3函数的空间复杂度
O(4n+12) O(8)=O(1) O(4)=O(1)
总结:实现算法时,需要分析具体问题,对执行时间和空间的要求。
时间换空间案例
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ cat Data_Structures_and_Algorithm.c
/*
问题:
在一个由自然数1-1000中某些数字所组成的数组中,每个数字可能出现零次或者多次。
设计一个算法,找出出现次数最多的数字。
方法1: 排序,然后找出出现次数最多的数字
方法2:空间换时间
*/
//方法2:空间换时间
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void search(int a[], int len)
{
int sp[1000] = {0}; //它用来存储每个数字的次数
int i = 0;
int max = 0;
for(i=0; i<len; i++) //统计每个数字出现的次数
{
int index = a[i] - 1;
sp[index]++;
}
for(i=0; i<1000; i++) //把次数最多的揪出来
{
if( max < sp[i] )
{
max = sp[i];
}
}
for(i=0; i<1000; i++) //看看是哪个的次数和它一样
{
if( max == sp[i] )
{
printf("出现次数最多的元素是:%d\n", i+1);//找到了
}
}
}
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 1, 6, 1, 6, 1, 6, 2, 3};
search(array, sizeof(array)/sizeof(*array));
return 0;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ gcc -g -o run Data_Structures_and_Algorithm.c && ./run
出现次数最多的元素是:1
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$
另外一种方法:
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ cat Data_Structures_and_Algorithm.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<ctime>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
time_t t;
srand((unsigned int)time(&t));
int a[100] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
a[i] = rand() % 100;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)//打印
{
cout << a[i] << "\t";
}
map<int, int> M;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
pair<map<int, int>::iterator, bool> pairIt = M.insert(pair<int, int>(a[i], 1));
if (pairIt.second != true)
{
M[a[i]]++;
}
}
int max = 0;//存储频率
int n = 0;//下标
int data=0;//a[i]
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
if (M[a[i]]>max)
{
n = i;
data = a[i];
max = M[a[i]];
}
}
cout << "\n出现最多的是:a[" << n << "]=" << data << " 出现次数:" << max << endl;
return 0;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ g++ -g -o run Data_Structures_and_Algorithm.cpp && ./run
4 27 2 81 42 65 85 41 61 75 31 86 84 49 13 61 8 30 22 67 61 51 14 3 49 63 64 61 57 58 82 61 85 36 94 79 1 79 20 14 6 51 1 91 53 66 4 13 96 78 32 57 81 46 12 31 61 77 92 19 87 26 32 24 62 27 16 58 75 30 17 78 83 60 31 50 64 96 98 94 28 8 76 26 20 7 88 97 51 59 36 77 91 60 91 18 63 7 77
出现最多的是:a[8]=61 出现次数:6
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$线性表
线性表定义
线性表(List)是零个或多个数据元素的集合线性表中的数据元素之间是有顺序的
线性表中的数据元素个数是有限的
线性表中的数据元素的类型必须相同
1,线性表初步认识:
VS环境
【项目创建】

【连接器 添加.lib】

封装好的代码:3个文件
myseqlistproj.dll 放在可执行程序的同级目录
myseqlistproj.lib 放在主函数文件的同级目录,在连接器-输入里面添加myseqlistproj.lib
seqlist.h 放在主函数文件的同级目录
已上传至网盘:下载链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pJKK4w7 密码:a0re
代码:
主函数:
//线性表顺序存储模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include "seqlist.h"//把seqlist.dll放在exe同级目录
typedef struct Teacher
{
int age;
//char name[64];
}Teacher;
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
Teacher t1; t1.age = 31;
Teacher t2; t2.age = 32;
Teacher t3; t3.age = 33;
Teacher t4; t4.age = 34;
Teacher t5; t5.age = 35;
SeqList* list = NULL;
list = SeqList_Create(10);
if (list == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in SeqList_Create\n");
return -1;
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t1,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t2,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t3,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t4,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t5,0);//0头插法
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i<SeqList_Length(list);i++)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i)\n");
}
printf("age = %d \n",tmp->age);
}
while(SeqList_Length(list) > 0)
{
SeqList_Delete(list,0);//删除头部元素
}
//printf("Hello World\n");
getchar();
return 0;
}
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli\Desktop\list2\Debug>list2.exe
age = 35
age = 34
age = 33
age = 32
age = 31
C:\Users\chunli\Desktop\list2\Debug>线性表顺序结构案例,C代码
三个文件:VS环境编译:
主函数main.c
//线性表顺序存储模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "seqlist.h" //线性表,只接受指针
typedef struct Teacher
{
int age;
char name[64];
}Teacher;
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
Teacher t1; t1.age = 31; strcpy(t1.name,"老王");
Teacher t2; t2.age = 32; strcpy(t2.name,"利纳斯");
Teacher t3; t3.age = 33; strcpy(t3.name,"比尔·盖茨");
Teacher t4; t4.age = 34; strcpy(t4.name,"斯瓦辛格");
Teacher t5; t5.age = 35; strcpy(t5.name,"汤姆孙");
SeqList* list = NULL;
list = SeqList_Create(10);
if (list == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in SeqList_Create\n");
return -1;
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t1,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t2,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t3,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t4,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(SeqListNode*) &t5,0);//0头插法
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i<SeqList_Length(list);i++)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i)\n");
}
printf("age = %d \t name = %s \n",tmp->age,tmp->name);
}
while(SeqList_Length(list) > 0)
{
SeqList_Delete(list,0);//删除头部元素
}
//printf("Hello World\n");
getchar();
return ret;
}文件2:
seqlist.h #ifndef __MY_SEQLIST_H__ #define __MY_SEQLIST_H__ typedef void SeqList; typedef void SeqListNode; SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity); void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list); void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos); SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos); SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos); #endif //__MY_SEQLIST_H__
文件3:seqlist.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "seqlist.h"
//申明一个结构体类型,用来存储线性表自己的信息
typedef struct _tag_SeqList
{
int length; //线性表的实际利用长度
int capacity; //线性表一共有多长
unsigned int *node;
}TSeqList;
//创建线性表
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity)//相当于分配数组的大小
{
TSeqList * tmp = NULL;
//创建线性表的头,放在堆内存中
tmp = (TSeqList*)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in (TSeqList*)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList)) \n");
return NULL;
}
//做个细心的人
memset(tmp,0,sizeof(TSeqList));
//根据capacity的大小,创建线性表的长度
tmp->node = (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int *) * capacity );
if(tmp->node == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int *) * capacity ) \n");
return NULL;
}
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->capacity = capacity;
return tmp;
}
//销毁链表
void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list)
{
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return;
}
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
if(tlist ->node != NULL)
{
free(tlist->node);//释放存储内存区
}
free(tlist); //释放线性表头
return ;
}
//清空链表的长度
void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list)
{
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return;
}
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
tlist->length = 0;
return ;
}
//返回线性表的长度
int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list)
{
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
return tlist->length;
}
//返回线性表的容量
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list)
{
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
return tlist->capacity;
}
//节点的插入
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || node == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL || node == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
//判断容量是不是 满了
if(tlist->length >= tlist->capacity)
{
printf("插入失败,线性表已经装满了\n");
}
//容错修正 20个容量,已经用到6,要求在10插入
if(pos >= tlist->length )
{
pos = tlist->length;
}
for(int i = tlist->length;i > pos;i--)
{
tlist->node[i] = tlist->node[i-1];
}
tlist->length ++;
tlist->node[pos] = (unsigned int*)node;
return 0;
}
SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return NULL;
}
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
return tlist->node[pos];
}
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return NULL;
}
TSeqList *tlist = NULL;
tlist = (TSeqList *)list;
for(int i = pos+1;i<tlist->length;i++)
{
tlist->node[i-1] = tlist->node[i];
}
tlist->length --;
return NULL;
}
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli\Desktop\list2\Debug>list2.exe
age = 35 name = 汤姆孙
age = 34 name = 斯瓦辛格
age = 33 name = 比尔·盖茨
age = 32 name = 利纳斯
age = 31 name = 老王线性表,单文件版,可以在Linux GCC 下编译运行:

chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ cat main.c
/*
1)程序功能:演示线性表的顺序存储功能,在底层可以像数组一样操作
2)兼容GCC 与 VS编译环境
3)兼容32 64位操作系统
4)线性表的顺序存储只是储存指针,可以兼容任意数据类型,包括自定义的结构体数据类型
*/
//线性表顺序存储模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//申明一个结构体类型,用来存储线性表自己的信息
struct seq_list_head
{
int length; //线性表的实际利用长度
int capacity; //线性表一共有多长
size_t *node; //存储节点
};
//创建线性表
void* SeqList_Create(int capacity)//最大能装多少个元素
{
struct seq_list_head * tmp = NULL;
//创建线性表的头,放在堆内存中
tmp = (struct seq_list_head*)malloc(sizeof(struct seq_list_head));
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in (struct seq_list_head*)malloc(sizeof(struct seq_list_head)) \n");
return NULL;
}
//做个细心的人
memset(tmp,0,sizeof(struct seq_list_head));
//根据capacity的大小,创建线性表的长度
tmp->node = (size_t *)malloc(sizeof(size_t *) * capacity );
if(tmp->node == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int *) * capacity ) \n");
return NULL;
}
tmp->length = 0;
tmp->capacity = capacity;
return tmp;
}
//销毁链表
void SeqList_Destroy(void* list)
{
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return;
}
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
if(tlist ->node != NULL)
{
free(tlist->node);//释放存储内存区
}
free(tlist); //释放线性表头
return ;
}
//清空链表的长度
void SeqList_Clear(void* list)
{
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return;
}
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
tlist->length = 0;
return ;
}
//返回线性表的长度
int SeqList_Length(void* list)
{
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
return tlist->length;
}
//返回线性表的容量
int SeqList_Capacity(void* list)
{
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
return tlist->capacity;
}
//节点的插入
int SeqList_Insert(void* list, void* node, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || node == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL || node == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
struct seq_list_head *tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
//判断容量是不是 满了
if(tlist->length >= tlist->capacity)
{
printf("插入失败,线性表已经装满了\n");
}
//容错修正 20个容量,已经用到6,要求在10插入
if(pos >= tlist->length )
{
pos = tlist->length;
}
for(int i = tlist->length;i > pos;i--)
{
tlist->node[i] = tlist->node[i-1];
}
tlist->length ++;
tlist->node[pos] = (size_t)node;
return 0;
}
size_t SeqList_Get(void* list, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
exit(-1);
}
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
return tlist->node[pos];
}
void* SeqList_Delete(void* list, int pos)
{
if(list == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL \n");
return NULL;
}
struct seq_list_head *tlist = NULL;
tlist = (struct seq_list_head *)list;
for(int i = pos+1;i<tlist->length;i++)
{
tlist->node[i-1] = tlist->node[i];
}
tlist->length --;
return NULL;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main()
{
typedef struct Teacher
{
int age;
char name[64];
}Teacher;
int ret = 0;
Teacher t1; t1.age = 31; strcpy(t1.name,"老王");
Teacher t2; t2.age = 32; strcpy(t2.name,"利纳斯");
Teacher t3; t3.age = 33; strcpy(t3.name,"比尔盖茨");
Teacher t4; t4.age = 34; strcpy(t4.name,"斯瓦辛格");
Teacher t5; t5.age = 35; strcpy(t5.name,"汤姆孙");
void* list = SeqList_Create(10);
if (list == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in SeqList_Create\n");
return -1;
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(void*) &t1,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(void*) &t2,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(void*) &t3,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(void*) &t4,0);//0头插法
ret = SeqList_Insert(list,(void*) &t5,0);//0头插法
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i<SeqList_Length(list);i++)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(list,i)\n");
}
printf("age = %d \t name = %s \n",tmp->age,tmp->name);
}
while(SeqList_Length(list) > 0)
{
SeqList_Delete(list,0);//删除头部元素
}
return ret;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ gcc -Wall -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
age = 35 name = 汤姆孙
age = 34 name = 斯瓦辛格
age = 33 name = 比尔盖茨
age = 32 name = 利纳斯
age = 31 name = 老王
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$优点和缺点
优点:无需为线性表中的逻辑关系增加额外的空间可以快速的获取表中合法位置的元素缺点:
插入和删除操作需要移动大量元素当线性表长度变化较大时难以确定存储空间的容量
企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现


3个文件:
linklist.h
linklist.c
main.c
文件1 main.c
//线性表顺序存储模型
//链表 与 数据 分离
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "linklist.h"
typedef struct Teacher
{
LinkListNode node;//让万事万物来包含链表
int age;
char name[60];
}Teacher;
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
int len = 0;
LinkList *list = NULL;
Teacher t1; t1.age = 31;
Teacher t2; t2.age = 32;
Teacher t3; t3.age = 33;
Teacher t4; t4.age = 34;
Teacher t5; t5.age = 35;
list = LinkList_Create();
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("创建链表头失败\n");
}
len = LinkList_Length(list);
ret = LinkList_Insert(list,(LinkListNode*)(&t1),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list,(LinkListNode*)(&t2),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list,(LinkListNode*)(&t3),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list,(LinkListNode*)(&t4),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list,(LinkListNode*)(&t5),0); //头插
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i<LinkList_Length(list);i++)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher*)LinkList_Get(list,i);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return -1;
}
printf("age = %d \n",tmp->age);
}
printf("\n");
//删除链表
while(LinkList_Length(list) > 0)
{
Teacher *tmp = LinkList_Delete(list,0); //始终从0除开始删除
printf("%d \n",tmp->age);
}
//销毁链表
LinkList_Destroy(list);
getchar();
return ret;
}文件2:linklist.h
#ifndef _MYLINKLIST_H_
#define _MYLINKLIST_H_
typedef void LinkList;
/*
typedef struct _tag_LinkListNode LinkListNode;
struct _tag_LinkListNode
{
LinkListNode* next;
};
*/
typedef struct _tag_LinkListNode
{
struct _tag_LinkListNode* next;
}LinkListNode;
LinkList* LinkList_Create();
void LinkList_Destroy(LinkList* list);
void LinkList_Clear(LinkList* list);
int LinkList_Length(LinkList* list);
int LinkList_Insert(LinkList* list, LinkListNode* node, int pos);
LinkListNode* LinkList_Get(LinkList* list, int pos);
LinkListNode* LinkList_Delete(LinkList* list, int pos);
#endiflinklist.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "linklist.h"
//typedef struct _tag_LinkListNode LinkListNode;
typedef struct _tag_LinkLis
{
LinkListNode *header;
int length;
}TLinkList;
LinkList* LinkList_Create()
{
TLinkList *ret = NULL;
ret = (TLinkList*)malloc(sizeof(TLinkList));
if(ret == NULL)
{
printf("创建首节点失败\n");
}
memset(ret,0,sizeof(TLinkList));
ret->header = NULL;
ret->length = 0;
return ret;
}
void LinkList_Destroy(LinkList* list)
{
if(list != NULL)
{
free(list);
list = NULL;
}
return ;
}
//恢复链表到初始状态
void LinkList_Clear(LinkList* list)
{
if(list != NULL)
{
return ;
}
TLinkList *tList = NULL;
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
tList->length = 0;
tList->header->next = NULL;
return 0;
}
int LinkList_Length(LinkList* list)
{
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("LinkList_Length NULL \n");
return -1;
}
TLinkList *tList = NULL;
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
return tList->length;
}
int LinkList_Insert(LinkList* list, LinkListNode* node, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
TLinkList *tList = NULL;
LinkListNode *current = NULL;
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
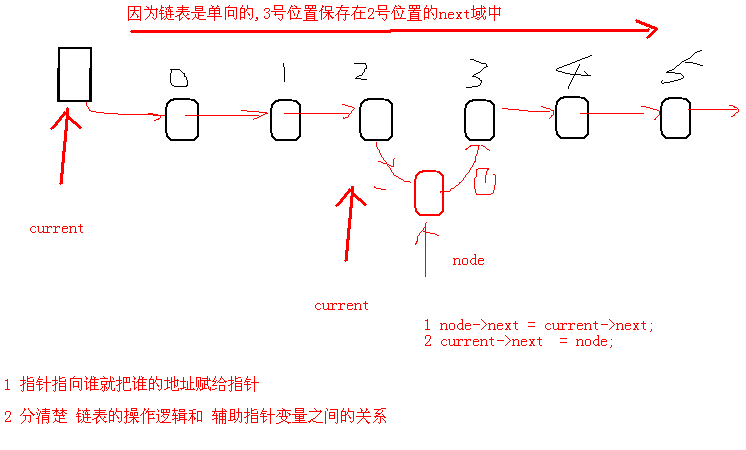
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
current = &tList->header;
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//让node节点链接后续链表
node->next = current->next ;
//让前边的链表。链接node
current->next = node;
tList->length ++;
return 0;
/*
int ret = 0;
LinkListNode *tList = NULL;
if(list == NULL || node == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("list == NULL || node == NULL || pos <0\n");
return -1;
}
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
LinkListNode *current = NULL;
current = &(tList->header);
return 0;
*/
}
LinkListNode* LinkList_Get(LinkList* list, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
TLinkList *tList = NULL;
LinkListNode *current = NULL;
LinkListNode *ret = NULL;
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
current = &tList->header;
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
return ret;
}
LinkListNode* LinkList_Delete(LinkList* list, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
TLinkList *tList = NULL;
LinkListNode *current = NULL;
LinkListNode *ret = NULL;
tList = (TLinkList *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
current = &tList->header;
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
//删除算法
current->next =ret->next;
tList->length--;
return ret;
}
VS2013环境编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli\Desktop\list2\Debug>list2.exe
age = 35
age = 34
age = 33
age = 32
age = 31
35
34
33
32
31
C:\Users\chunli\Desktop\list2\Debug>企业级线性表链式存储案例:C语言实现 单文件版
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct link_list_node
{
struct link_list_node* next;
};
struct link_list_head
{
struct link_list_node *header;
int length;
};
void* LinkList_Create()
{
struct link_list_head *head = (struct link_list_head*)malloc(sizeof(struct link_list_head));
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("创建首节点失败\n");
}
memset(head,0,sizeof(struct link_list_head));
head->header = NULL;
head->length = 0;
//printf("LinkList_Create %p \n",head->header);
return head;
}
void LinkList_Destroy(void* list)
{
if(list != NULL)
{
free(list);
list = NULL;
}
return ;
}
//恢复链表到初始状态
void LinkList_Clear(void* list)
{
if(list != NULL)
{
return ;
}
struct link_list_head *tList = NULL;
tList = (struct link_list_head *)list;
tList->length = 0;
tList->header->next = NULL;
return ;
}
int LinkList_Length(void* list)
{
if(list == NULL)
{
printf("LinkList_Length NULL \n");
return -1;
}
struct link_list_head *tList = NULL;
tList = (struct link_list_head *)list;
return tList->length;
}
int LinkList_Insert(void* list, struct link_list_node* node, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
struct link_list_head *tList = (struct link_list_head *)list;
struct link_list_node *current = (struct link_list_node*)(&tList->header); //注意理解&tList->header的作用
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++) //pos等于0,直接跳过去
{
current = current->next;
}
node->next = current->next; //让node节点链接后续链表
current->next = node; //让前边的链表。链接node
tList->length ++;
return 0;
}
struct link_list_node* LinkList_Get(void* list, int pos)
{
int i = 0;
struct link_list_head *tList = NULL;
struct link_list_node* current = NULL;
struct link_list_node* ret = NULL;
tList = (struct link_list_head *)list;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
current = (struct link_list_node*)&tList->header;
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
return ret;
}
struct link_list_node* LinkList_Delete(void* list, int pos) //删除指定位置的元素,会返回这个元素节点的地址
{
int i = 0;
struct link_list_head *tList = (struct link_list_head *)list;
struct link_list_node *current = (struct link_list_node*)&tList->header;
struct link_list_node *ret = NULL;
if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length)
{
return NULL;
}
//准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点
for (i=0; i<pos &&(current->next!=NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
//删除算法
current->next =ret->next;
tList->length--;
return ret;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main()
{
typedef struct Teacher
{
struct link_list_node node;//让万事万物来包含链表
int age;
char name[60];
}Teacher;
int ret = 0;
int len = 0;
Teacher t1; t1.age = 31;
Teacher t2; t2.age = 32;
Teacher t3; t3.age = 33;
Teacher t4; t4.age = 34;
Teacher t5; t5.age = 35;
void *list_head = LinkList_Create();
if(list_head == NULL)
{
printf("创建链表头失败\n");
}
//printf("LinkList_Create %p \n",((struct link_list_head*)list_head)->header);
ret = LinkList_Insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t1),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t2),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t3),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t4),0); //头插
ret = LinkList_Insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t5),0); //头插
len = LinkList_Length(list_head);
printf("链表的长度是: %d\n",len);
//遍历
for(int i = 0;i<LinkList_Length(list_head);i++)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher*)LinkList_Get(list_head,i);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return -1;
}
printf("age = %d \n",tmp->age);
}
printf("\n");
//删除链表
while(LinkList_Length(list_head) > 0)
{
Teacher *tmp = (Teacher*)LinkList_Delete(list_head,0); //始终从0除开始删除
printf("正在删除节点 %d \n",tmp->age);
}
//销毁链表
LinkList_Destroy(list_head);
return ret;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ gcc -Wall -std=c99 main.c && ./a.out
链表的长度是: 5
age = 35
age = 34
age = 33
age = 32
age = 31
正在删除节点 35
正在删除节点 34
正在删除节点 33
正在删除节点 32
正在删除节点 31
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$企业级线性表链式存储案例,我的练习
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com/tmp$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//链表节点,仅储存下一个节点的地址
struct link_list_node
{
struct link_list_node *next;
};
//链表的头结点专用
struct link_list_head
{
struct link_list_node *head;
int length;
};
//返回链表的头节点
void *link_list_create()
{
struct link_list_head *list_head = (struct link_list_head*)malloc(sizeof(struct link_list_head));
if(list_head == NULL)
{
printf("创建首节点失败\n");
}
memset(list_head,0,sizeof(struct link_list_head));
list_head->head = NULL;
list_head->length = 0;
return list_head;
}
//链表的插入操作
int link_list_insert(void *list_head,struct link_list_node* node,int pos)
{
if(list_head == NULL || node == NULL || pos < 0 )
{
printf("link_list_insert() 函数参数传递错误\n");
return -1;
}
struct link_list_head *tmp_head = (struct link_list_head *)list_head;
struct link_list_node *node_curr = (struct link_list_node *)&(tmp_head->head);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<pos && node_curr->next != NULL ;i++) //如果不存在有效节点,直接跳过
{
node_curr = node_curr->next;
}
node->next = node_curr->next;
node_curr->next = node;
tmp_head->length++;
//printf("length = %d\n",tmp_head->length);
return 0;
}
//返回链表的长度
int link_list_length(struct link_list_head * list_head)
{
if(list_head == NULL)
{
printf("link_list_length()函数参数传递错误");
}
return list_head->length;
}
//返回一个链表节点的地址
void *link_list_get(struct link_list_head *list_head,int pos)
{
if(list_head == NULL || list_head->head == NULL || pos <0)
{
printf("link_list_get()函数参数传递错误\n");
return NULL;
}
struct link_list_head *tmp_head = list_head;
struct link_list_node *tmp_node = (struct link_list_node*)list_head->head;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<pos && list_head->head != NULL ;i++)
{
tmp_node = tmp_node -> next;
}
return tmp_node;
}
//删除链表的一个节点
int link_list_delete(struct link_list_head *list_head,int pos)
{
if(list_head == NULL || list_head->head == NULL || pos < 0)
{
printf("link_list_delete()参数传递错误\n");
}
struct link_list_node *tmp_node = (struct link_list_node*)(&list_head->head);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<pos;i++)
{
tmp_node = tmp_node -> next;
}
tmp_node->next = tmp_node->next->next;
list_head->length--;
return 0;
}
//恢复链表到初始状态
int link_list_clear(struct link_list_head *list_head)
{
if(list_head == NULL)
{
printf("link_list_clear()函数参数传递错误\n");
return -1;
}
list_head->length = 0;
list_head->head = NULL;
return 0;
}
//销毁链表
int link_list_destroy(struct link_list_head *list_head)
{
if(list_head == NULL)
{
printf("link_list_destroy()函数参数传递错误\n");
return -1;
}
free(list_head);
return 0;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main()
{
struct Teacher
{
struct link_list_node *node;
int age;
};
struct Teacher t1; t1.age = 11;
struct Teacher t2; t2.age = 21;
struct Teacher t3; t3.age = 31;
struct Teacher t4; t4.age = 41;
struct Teacher t5; t5.age = 51;
struct Teacher t6; t6.age = 61;
//创建链表头
void *list_head = link_list_create();
//把节点的地址压入链表
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t1),0);
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t2),0);
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t3),0);
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t4),0);
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t5),0);
link_list_insert(list_head,(struct link_list_node*)(&t6),0);
//获取链表的长度
int len = link_list_length(list_head);
printf("链表的长度为%d \n",len);
//遍历链表
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<link_list_length(list_head);i++)
{
struct Teacher *tmp = (struct Teacher*)link_list_get(list_head,i);
printf("正在遍历 age = %d\n",tmp->age);
}
//链表节点删除
printf("链表删除操作\n");
while(((struct link_list_head *)list_head)->length > 0)
{
link_list_delete(list_head,0);
}
link_list_destroy(list_head);
for(i = 0;i<link_list_length(list_head);i++)
{
struct Teacher *tmp = (struct Teacher*)link_list_get(list_head,i);
printf("正在遍历 age = %d\n",tmp->age);
}
return 0;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com/tmp$ gcc main.c && ./a.out
链表的长度为6
正在遍历 age = 61
正在遍历 age = 51
正在遍历 age = 41
正在遍历 age = 31
正在遍历 age = 21
正在遍历 age = 11
链表删除操作
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com/tmp$线性表的链式存储优点和缺点
优点:无需一次性定制链表的容量插入和删除操作无需移动数据元素缺点:
数据元素必须保存后继元素的位置信息获取指定数据的元素操作需要顺序访问之前的元素
循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:

02_循环链表头插法操作逻辑和辅助指针变量之间的关系场景

3个文件:
CircleList.h
CircleList.c
main.c
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "CircleList.h"
struct Value
{
CircleListNode header;
int v;
};
void main()
{
int i = 0;
CircleList* list = CircleList_Create();
struct Value v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8;
v1.v = 1; v2.v = 2; v3.v = 3; v4.v = 4;
v5.v = 5; v6.v = 6; v7.v = 7; v8.v = 8;
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v1, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v2, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v3, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v4, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v5, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v6, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v7, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v8, CircleList_Length(list));
for(i=0; i<CircleList_Length(list); i++)
{
//获取游标所指元素,然后游标下移
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Next(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
printf("\n");
//重置游标
CircleList_Reset(list);
while( CircleList_Length(list) > 0 )
{
struct Value* pv = NULL;
for(i=1; i<3; i++)
{
CircleList_Next(list);
}
pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Current(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
CircleList_DeleteNode(list, (CircleListNode*)pv);
}
CircleList_Destroy(list);
system("pause");
return ;
}CircleList.h
#ifndef _CIRCLELIST_H_
#define _CIRCLELIST_H_
typedef void CircleList;
typedef struct _tag_CircleListNode
{
struct _tag_CircleListNode * next;
}CircleListNode;
CircleList* CircleList_Create();
void List_Destroy(CircleList* list);
void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list);
int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list);
int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node, int pos);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list, int pos);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list, int pos);
//add
CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Reset(CircleList* list);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list);
#endifCircleList.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "CircleList.h"
typedef struct _tag_CircleList
{
CircleListNode header;
CircleListNode* slider;//游标
int length;
} TCircleList;
//创建头,用于存储信息。
CircleList* CircleList_Create() // O(1)
{
TCircleList* ret = (TCircleList*)malloc(sizeof(TCircleList));
if (ret == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
ret->length = 0;
ret->header.next = NULL;
ret->slider = NULL;//建立游标
return ret;
}
//销毁链表
void CircleList_Destroy(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
if (list == NULL)
{
return ;
}
free(list);
}
//链表清理
void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
if (sList == NULL)
{
return ;
}
sList->length = 0;
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
//链表的长度
int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
int ret = -1;
if (list == NULL)
{
return ret;
}
ret = sList->length;
return ret;
}
//节点插入
int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node, int pos) // O(n)
{
int ret = 0, i=0;
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
if (list == NULL || node== NULL || pos<0)
{
return -1;
}
//if( ret )
{
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
for(i=0; (i<pos) && (current->next != NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//current->next 0号节点的地址
node->next = current->next; //1
current->next = node; //2
//若第一次插入节点
if( sList->length == 0 )
{
sList->slider = node;
}
sList->length++;
//若头插法
if( current == (CircleListNode*)sList )
{
//获取最后一个元素
CircleListNode* last = CircleList_Get(sList, sList->length - 1);
last->next = current->next; //3
}
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if (list==NULL || pos<0)
{
return NULL;
}
//if( (sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0) && (sList->length > 0) )
{
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
for(i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if( (sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0) && (sList->length > 0) )
{
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
CircleListNode* last = NULL;
for(i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//若删除第一个元素
if( current == (CircleListNode*)sList )
{
last = (CircleListNode*)CircleList_Get(sList, sList->length - 1);
}
//求要删除的元素
ret = current->next;
current->next = ret->next;
sList->length--;
//判断链表是否为空
if( last != NULL )
{
sList->header.next = ret->next;
last->next = ret->next;
}
//若删除的元素为游标所指的元素
if( sList->slider == ret )
{
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
//若删除元素后,链表长度为0
if( sList->length == 0 )
{
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if( sList != NULL )
{
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
//查找node在循环链表中的位置i
for(i=0; i<sList->length; i++)
{
if( current->next == node )
{
ret = current->next;
break;
}
current = current->next;
}
//如果ret找到,根据i去删除
if( ret != NULL )
{
CircleList_Delete(sList, i);
}
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Reset(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if( sList != NULL )
{
sList->slider = sList->header.next;
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if( sList != NULL )
{
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if( (sList != NULL) && (sList->slider != NULL) )
{
ret = sList->slider;
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
VS环境编译运行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3
6
1
5
2
8
4
7
请按任意键继续. . .循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:单文件
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ cat main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct cricle_list_node
{
struct cricle_list_node * next;
};
struct cricle_list_head
{
struct cricle_list_node header;
struct cricle_list_node *slider;//游标
int length;
};
//创建头,用于存储信息。
void* void_Create() // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* ret = (struct cricle_list_head*)malloc(sizeof(struct cricle_list_head));
if (ret == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
ret->length = 0;
ret->header.next = NULL;
ret->slider = NULL;//建立游标
return ret;
}
//销毁链表
void void_Destroy(void* list) // O(1)
{
if (list == NULL)
{
return ;
}
free(list);
}
//链表清理
void void_Clear(void* list) // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
if (sList == NULL)
{
return ;
}
sList->length = 0;
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
//链表的长度
int void_Length(void* list) // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
int ret = -1;
if (list == NULL)
{
return ret;
}
ret = sList->length;
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_Get(void* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if (list==NULL || pos<0)
{
return NULL;
}
//if( (sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0) && (sList->length > 0) )
{
struct cricle_list_node* current = (struct cricle_list_node*)sList;
for(i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
}
return ret;
}
//节点插入
int cricle_list_insert(void* list, struct cricle_list_node* node, int pos) // O(n)
{
int ret = 0, i=0;
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
if (list == NULL || node== NULL || pos<0)
{
return -1;
}
//if( ret )
{
struct cricle_list_node* current = (struct cricle_list_node*)sList;
for(i=0; (i<pos) && (current->next != NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//current->next 0号节点的地址
node->next = current->next; //1
current->next = node; //2
//若第一次插入节点
if( sList->length == 0 )
{
sList->slider = node;
}
sList->length++;
//若头插法
if( current == (struct cricle_list_node*)sList )
{
//获取最后一个元素
struct cricle_list_node* last = void_Get(sList, sList->length - 1);
last->next = current->next; //3
}
}
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_Delete(void* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if( (sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0) && (sList->length > 0) )
{
struct cricle_list_node* current = (struct cricle_list_node*)sList;
struct cricle_list_node* last = NULL;
for(i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//若删除第一个元素
if( current == (struct cricle_list_node*)sList )
{
last = (struct cricle_list_node*)void_Get(sList, sList->length - 1);
}
//求要删除的元素
ret = current->next;
current->next = ret->next;
sList->length--;
//判断链表是否为空
if( last != NULL )
{
sList->header.next = ret->next;
last->next = ret->next;
}
//若删除的元素为游标所指的元素
if( sList->slider == ret )
{
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
//若删除元素后,链表长度为0
if( sList->length == 0 )
{
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
}
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_DeleteNode(void* list, struct cricle_list_node* node) // O(n)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if( sList != NULL )
{
struct cricle_list_node* current = (struct cricle_list_node*)sList;
//查找node在循环链表中的位置i
for(i=0; i<sList->length; i++)
{
if( current->next == node )
{
ret = current->next;
break;
}
current = current->next;
}
//如果ret找到,根据i去删除
if( ret != NULL )
{
void_Delete(sList, i);
}
}
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_Reset(void* list) // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
if( sList != NULL )
{
sList->slider = sList->header.next;
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_Current(void* list) // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
if( sList != NULL )
{
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
struct cricle_list_node* void_Next(void* list) // O(1)
{
struct cricle_list_head* sList = (struct cricle_list_head*)list;
struct cricle_list_node* ret = NULL;
if( (sList != NULL) && (sList->slider != NULL) )
{
ret = sList->slider;
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main()
{
struct Teacher
{
struct cricle_list_node header;
int id;
};
int i = 0;
void* list = void_Create();
struct Teacher v1; v1.id = 1; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v1, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v2; v2.id = 2; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v2, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v3; v3.id = 3; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v3, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v4; v4.id = 4; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v4, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v5; v5.id = 5; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v5, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v6; v6.id = 6; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v6, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v7; v7.id = 7; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v7, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v8; v8.id = 8; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v8, void_Length(list));
struct Teacher v9; v9.id = 9; cricle_list_insert(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)&v9, void_Length(list));
for(i=0; i<void_Length(list); i++)
{
//获取游标所指元素,然后游标下移
struct Teacher* pv = (struct Teacher*)void_Next(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->id);
}
printf("\n");
//重置游标
void_Reset(list);
while( void_Length(list) > 0 )
{
struct Teacher* pv = NULL;
for(i=1; i<3; i++)
{
void_Next(list);
}
pv = (struct Teacher*)void_Current(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->id);
void_DeleteNode(list, (struct cricle_list_node*)pv);
}
void_Destroy(list);
return 0;
}
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$ gcc main.c && ./a.out
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
3
6
9
4
8
5
2
7
1
chunli@http://990487026.blog.51cto.com~/c$循环链表 解决约瑟夫问题案例:我的练习
相关文章推荐
- [C/C++]反转链表
- C#实现基于链表的内存记事本实例
- C#中循环语句:while、for、foreach的使用
- Lua中数字for循环实例
- C#用链式方法表达循环嵌套
- Sql存储过程游标循环的用法及sql如何使用cursor写一个简单的循环
- Shell中的for和while循环详细总结
- C#模拟链表数据结构的实例解析
- C语言循环结构与时间函数用法实例教程
- C语言实现带头结点的链表的创建、查找、插入、删除操作
- C++利用静态成员或类模板构建链表的方法讲解
- C++实现简单的学生管理系统
- php循环table实现一行两列显示的方法
- ThinkPHP采用<volist>实现三级循环代码实例
- ASP 循环导入导出数据处理 不使用缓存
- 详解JavaScript中循环控制语句的用法
- asp中for循环的使用方法
- JavaScript中利用各种循环进行遍历的方式总结
- Javascript循环绑定事件的示例代码
- 详解C语言 三大循环 四大跳转 和判断语句
