哈夫曼树编码及解码,链表实现
2016-07-07 15:10
393 查看
哈夫曼树原理简介:
是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字,有时称之为最佳编码,一般就叫做Huffman编码(有时也称为霍夫曼编码)。
如:字符串 “jdlasjdlajhfhioe”
在此字符串中每个字符的权重为: (出现的次数)
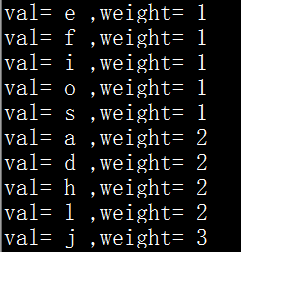
编码方式为:
选取权重最小的俩个字符 进行合并
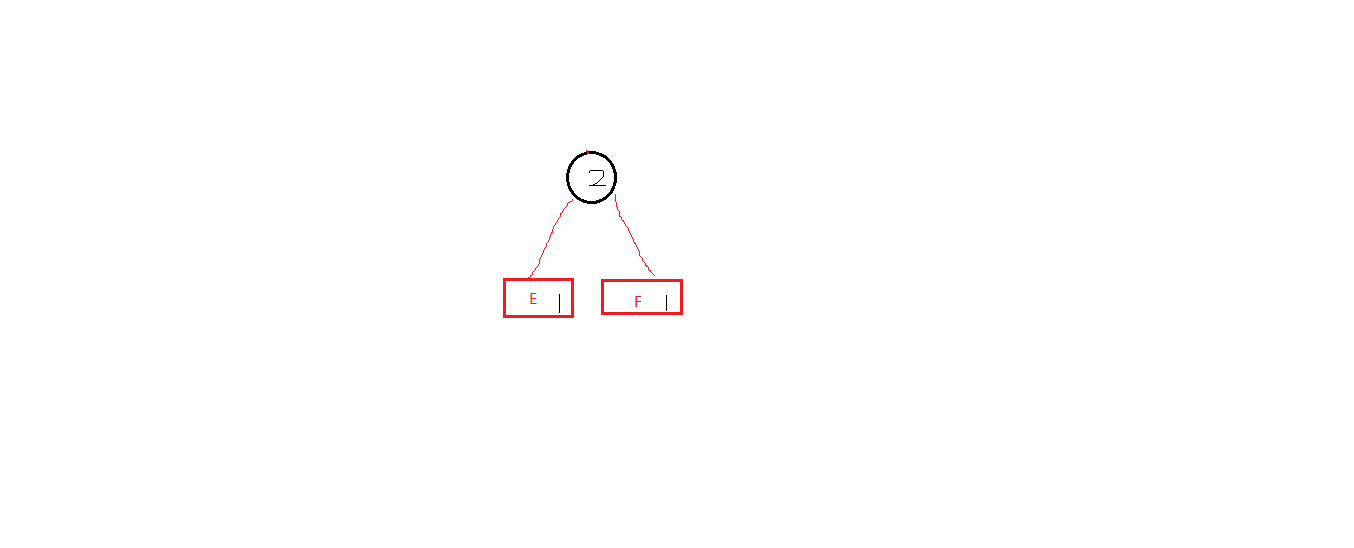
新生成节点的权重为2 将e ,f 节点从原数据中删除,将新节点插入到原数据,并继续选取权重最小的节点进行组合,直到剩一个节点时,此节点便是哈夫曼树的头结点;
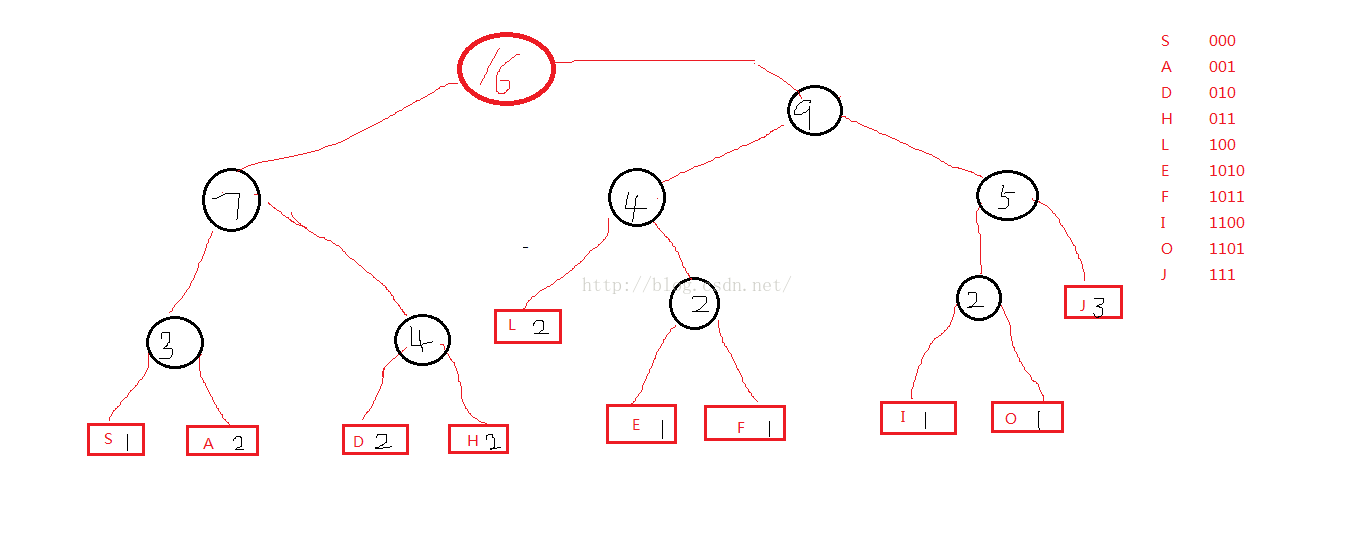
生成的树形左枝编码为 0,右枝编码为 1;得到每个字符的编码;
运行结果1 :只编码 不解码
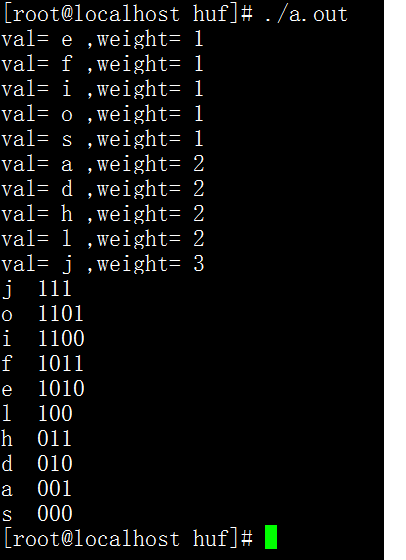
运行结果2 编码后 继续解码
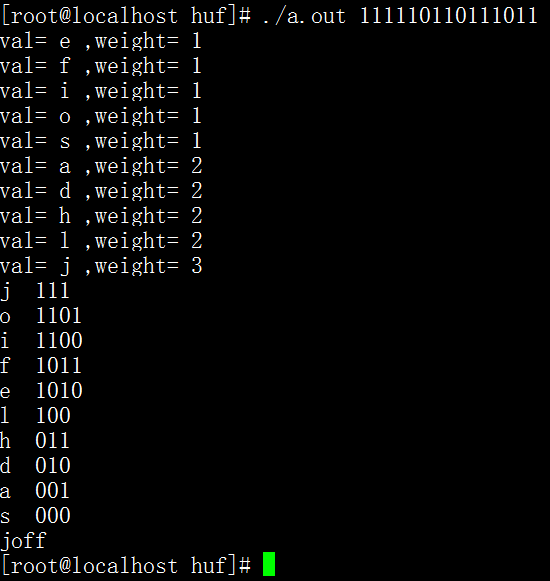
用哪棵树编码 就用哪棵树解码;
是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字,有时称之为最佳编码,一般就叫做Huffman编码(有时也称为霍夫曼编码)。
如:字符串 “jdlasjdlajhfhioe”
在此字符串中每个字符的权重为: (出现的次数)

编码方式为:
选取权重最小的俩个字符 进行合并

新生成节点的权重为2 将e ,f 节点从原数据中删除,将新节点插入到原数据,并继续选取权重最小的节点进行组合,直到剩一个节点时,此节点便是哈夫曼树的头结点;

生成的树形左枝编码为 0,右枝编码为 1;得到每个字符的编码;
<pre name="code" class="cpp">/*
1. 将提供的字符串(自定义字符串)进行排序,获取各个字符的权重;
2. 将字符及对应的权重放入树节点(node)中,用链表将各个节点有序的(按权重升序)链接;
3. 实现链表的增、删功能;
4. 遍历链表,将链表的前两个节点中权重相加,生成新节点,然后将新节点插入到有序链表中;
5. 直到链表中只剩一个节点时,将此节点赋给哈夫曼树头;
6. 利用创建的哈夫曼树得到编码; 用递归得到叶子节点,由叶子节点追溯到根节点,得到编码后反转顺序;
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXL 20 //自定义字符串的最大长度;
typedef struct _node
{
char val;
int weight;
struct _node *p;
struct _node *l;
struct _node *r;
}node; //树节点
typedef struct l_node
{
node *ln;
struct l_node *prev;
struct l_node *next;
}lnode;//链表节点
typedef struct
{
node *head;
}huf_tree;//树头结点
typedef struct
{
lnode *head;
}list;//链表头
char arr[ MAXL ];//有效字符串数组;排重之后的数组,和权重数组一一对应;
int w_a[ MAXL ];//权重数组;
void get_weight(char *ch,int c_long)//从排完序的字符串中得到有效字符和对应的权重;
{
char a_s=ch[0];
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<c_long)
{
if(ch[i]==a_s)
{
w_a[j]++;
i++;
} else{
arr[j]=a_s;
j++;
a_s=ch[i];
}
}
arr[j]=a_s;
}
int quick_part(char *s,int low,int hight)//对字符串进行快排,
{
char f_s=s[low];
int i,j;
i=low; j=hight;
while(i<j){
while(i<j&&s[j]>=f_s) j--;
if(i<j) s[i++]=s[j];
while(i<j && s[i]<=f_s) i++;
if(i<j) s[j]=s[i];
}
s[i]=f_s;
if((i-1)>low)
quick_part(s,low,i-1);
if((i+1)<hight)
quick_part(s,i+1,hight);
}
void r_arr(char *p) //反转字符串
{
int sz=strlen(p);
int i=0;
for(i;i<sz-i;i++)
{
char t;
t=p[i];
p[i]=p[sz-i-1];
p[sz-i-1]=t;
}
}
void print_tree( node *n)//遍历哈夫曼树
{
node *nd=n;
if(nd!=NULL){
print_tree(nd->r);
print_tree(nd->l);
node *sn=nd;
if(nd->val != '\0'){
printf("%c ",nd->val);
char p[10]={};
int i=0;
while(sn->p != NULL)
{
if(sn->p->l==sn){
p[i]='0';
i++;
}
if(sn->p->r==sn){
p[i]='1';
i++;
}
sn=sn->p;
}
r_arr(p);
printf("%s\n",p);
}
}
}
void del_list(list *lst,lnode *p)//删除链表里面的指定节点;
{
lnode *lnd=lst->head->next;
while(lnd!=NULL){
if(lnd == p)
{
if(lnd->next == NULL){
lst->head->next=NULL;
free(p);
}else{
lnd->prev->next=lnd->next;
lnd->next->prev=lnd->prev;
node *s=p->ln;
free (p);
}
break;
}
lnd=lnd->next;
}
}
void add_list(list *lst,node *nd)//向链表中添加节点;
{
lnode *sn=lst->head;
lnode *new_node=(lnode*)malloc(sizeof(lnode));
new_node->prev=NULL;
new_node->next=NULL;
new_node->ln=nd;
if(lst->head->next==NULL)
{
lst->head->next=new_node;
new_node->prev=lst->head;
return ;
}
while(sn->next!=NULL)
{
if(sn->next->ln->weight > nd->weight)
{
new_node->prev = sn->next->prev;
new_node->next = sn->next;
sn->next=new_node;
new_node->next->prev=new_node;
sn=sn->next;
break;
}else {
sn=sn->next;
}
}
if(sn->next==NULL){
sn->next=new_node;
new_node->prev=sn;
}
}
void print_list(list *lst)//打印链表;
{
lnode *lnd=lst->head->next;
while(lnd!=NULL)
{
printf("val= %c ,weight= %d \n",lnd->ln->val,lnd->ln->weight);
lnd=lnd->
b306
;next;
}
}
void add_tree(huf_tree *hr, list *lst)//创建哈夫曼树
{
node *hnd=hr->head;
lnode *lnd=lst->head->next;
//循环:每次将权重最小的两个节点合并成一个新节点,删除权重最小的这两个节点,并将新节点插入链表
while(lnd!=NULL && lnd->next!=NULL)
{
node *n_node=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
n_node->val='\0';
n_node->weight = lnd->ln->weight + lnd->next->ln->weight;
n_node->l=lnd->ln;
n_node->r=lnd->next->ln;
n_node->p=NULL;
lnd->ln->p=n_node;
lnd->next->ln->p=n_node;
del_list(lst,lnd);
del_list(lst,lnd->next);
add_list(lst,n_node);
//printf("=====================\n");
//print_list(lst);
lnd=lst->head->next;
}
if(lst->head->next != NULL)//链表中只剩下一个节点时,将此节点的数据赋给哈夫曼树的头结点;
hr->head=lst->head->next->ln;
}
void de_tree(huf_tree *ht,char *dp)
{
int sz=strlen(dp);
int i=0;
node *hn=ht->head;
for(i=0;i<sz&&hn!=NULL;i++)
{
if(dp[i]=='0')hn=hn->l;
if(dp[i]=='1')hn=hn->r;
if(hn->val!='\0'){
printf("%c",hn->val);
hn=ht->head;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argv,char **argc)
{
huf_tree ht;
list lst;
int i=0;
ht.head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
ht.head->p=NULL;
ht.head->l=NULL;
ht.head->r=NULL;
lst.head=(lnode*)malloc(sizeof(lnode));
lst.head->next=NULL;
lst.head->prev=NULL;
strcpy(arr,"jdlasjdlajhfhioe"); //自定义字符串数组
quick_part(arr,0,15);//快排
get_weight(arr,strlen(arr));//获取各个字符的权重;
for(i=0;w_a[i]!=0;i++)//创建有序链表(以权重排序)
{
node *nd=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
nd->val=arr[i];
nd->weight=w_a[i];
nd->p=NULL;
nd->l=NULL;
nd->r=NULL;
add_list( &lst,nd);
}
print_list(&lst);//打印链表
add_tree(&ht,&lst);//创建哈夫曼树;
print_tree(ht.head);//打印树,包括字符的编码,编码未保存,直接打印出来了;
if(argv==2)
de_tree(&ht,argc[1]);//解码
}运行结果1 :只编码 不解码

运行结果2 编码后 继续解码

用哪棵树编码 就用哪棵树解码;
相关文章推荐
- 如何组织构建多文件 C 语言程序(二)
- 如何写好 C main 函数
- Lua和C语言的交互详解
- 关于C语言中参数的传值问题
- 简要对比C语言中三个用于退出进程的函数
- 深入C++中API的问题详解
- 基于C语言string函数的详解
- C语言中fchdir()函数和rewinddir()函数的使用详解
- C语言内存对齐实例详解
- C语言编程中统计输入的行数以及单词个数的方法
- C语言自动生成enum值和名字映射代码
- C语言练习题:自由落体的小球简单实例
- 使用C语言判断英文字符大小写的方法
- c语言实现的带通配符匹配算法
- C语言实现顺序表基本操作汇总
- C语言中进制知识汇总
- C语言判断一个数是否是2的幂次方或4的幂次方
- C语言中计算正弦的相关函数总结
- 使用C语言详解霍夫曼树数据结构
- C语言实现选择排序、冒泡排序和快速排序的代码示例
