Spring MVC Web应用上下文
2016-07-02 17:29
441 查看
Spring MVC是建立在Spring IoC容器的基础上,然而Spring IoC是一个独立的模块,因此并不能直接在Web环境中发挥作用。为了在Web环境中使用Ioc,就需要Spring提供一个适合于Web环境的相关容器(WebApplicationContext),以及基于此容器的IoC启动过程,将IoC导入,这个启动过程应该与Web容器启动过程相集成。下面着重介绍Web应用上下文。
WebApplicationContext 类继承体系 :
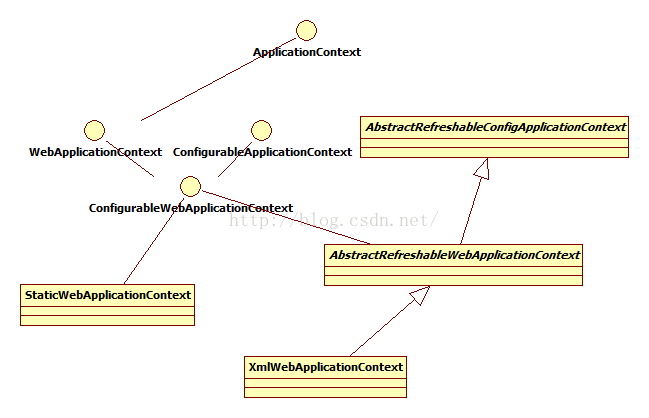
可以看到,Web应用上下文的实现是基于基本Ioc容器ApplicatoionContext相关接口,并在此基础上加入了适用于Web环境的相关功能扩展。
1)WebApplicationContext接口实现
在该接口中,定义了几个常量,比如ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,这个常量用于索引在ServletContext中保存的根Web应用上下文。还有就是ServletContext getServletContext()方法,通过这个方法可以得到当前web容器的Servlet上下文。
2)ConfigurableWebApplicationContext实现
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext继承自WebApplicationContext接口,并且提供了设置ServletContext
以及上下文配置资源路径的相关函数。
3)AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
类
4)Spring MVC使用的WebApplicationContext实现
Spring MVC使用一个默认的WebApplicationContext来作为Ioc容器,这个Ioc容器就是XmlWebApplicationContext。通过类继承体系可以看到其实现继承于AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext抽象类,而AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext又继承自AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext。
XmlWebApplicationContext中基本的上下文功能都通过类继承来获得,需要处理的就是获取Bean定义信息。这里是获取web容器环境指定的资源如/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。在获取到bean定义后,就如同Spring基本Ioc上下文容器ApplicationContext一样通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader来载入bean定义信息,最终完成上下文初始化。
WebApplicationContext 类继承体系 :

可以看到,Web应用上下文的实现是基于基本Ioc容器ApplicatoionContext相关接口,并在此基础上加入了适用于Web环境的相关功能扩展。
1)WebApplicationContext接口实现
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
...
...
ServletContext getServletContext();
}在该接口中,定义了几个常量,比如ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,这个常量用于索引在ServletContext中保存的根Web应用上下文。还有就是ServletContext getServletContext()方法,通过这个方法可以得到当前web容器的Servlet上下文。
2)ConfigurableWebApplicationContext实现
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {
String APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ":";
String SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME = "servletConfig";
//设置与该WebApplicationContext相关的ServletContext
void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext);
//设置与该WebApplicationContext相关的Servlet的servletConfig
void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig);
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
//设置该WebApplicationContext依赖的bean定义资源配置路径
void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);
void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);
String[] getConfigLocations();
}ConfigurableWebApplicationContext继承自WebApplicationContext接口,并且提供了设置ServletContext
以及上下文配置资源路径的相关函数。
3)AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
类
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {
/** Servlet context that this context runs in */
private ServletContext servletContext;
/** Servlet config that this context runs in, if any */
private ServletConfig servletConfig;
/** Namespace of this context, or {@code null} if root */
private String namespace;
/** the ThemeSource for this ApplicationContext */
private ThemeSource themeSource;
public AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext() {
setDisplayName("Root WebApplicationContext");
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.servletContext;
}
@Override
public void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig) {
this.servletConfig = servletConfig;
if (servletConfig != null && this.servletContext == null) {
setServletContext(servletConfig.getServletContext());
}
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return this.servletConfig;
}
@Override
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
if (namespace != null) {
setDisplayName("WebApplicationContext for namespace '" + namespace + "'");
}
}
@Override
public String getNamespace() {
return this.namespace;
}
@Override
public String[] getConfigLocations() {
return super.getConfigLocations();
}
@Override
public String getApplicationName() {
return (this.servletContext != null ? this.servletContext.getContextPath() : "");
}
/**
* Create and return a new {@link StandardServletEnvironment}. Subclasses may override
* in order to configure the environment or specialize the environment type returned.
*/
@Override
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
/**
* Register request/session scopes, a {@link ServletContextAwareProcessor}, etc.
*/
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
/**
* This implementation supports file paths beneath the root of the Serv
4000
letContext.
* @see ServletContextResource
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, path);
}
/**
* This implementation supports pattern matching in unexpanded WARs too.
* @see ServletContextResourcePatternResolver
*/
@Override
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new ServletContextResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
/**
* Initialize the theme capability.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>Replace {@code Servlet}-related property sources.
*/
@Override
protected void initPropertySources() {
ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
}
@Override
public Theme getTheme(String themeName) {
return this.themeSource.getTheme(themeName);
}
}4)Spring MVC使用的WebApplicationContext实现
Spring MVC使用一个默认的WebApplicationContext来作为Ioc容器,这个Ioc容器就是XmlWebApplicationContext。通过类继承体系可以看到其实现继承于AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext抽象类,而AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext又继承自AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext。
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
//设置的默认的BeanDefinition的地方,在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml文件中
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
//默认的bean配置文件目录前缀和文件后缀
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml";
//loadBeanDefinitions函数,在Ioc容器启动时,通过该函数加载、注册BeanDefinition
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//用XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类来对BeanDefinition信息进行解析
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//设置ResourceLoader资源导入器,因ApplicationContext是DefaultResource子类,因此这里传入this,使用该DefaultResourceLoader来定位BeanDefinition资源文件
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//通过定义好的XmlBeanDefinitionReader 来载入BeanDefinition。
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader) {
}
//对多个BeanDefinition定义文件,通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader 逐个载入
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
//获取默认资源位置,默认的位置是/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
@Override
protected String[] getDefaultConfigLocations() {
if (getNamespace() != null) {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX + getNamespace() + DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX};
}
else {
return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION};
}
}
}XmlWebApplicationContext中基本的上下文功能都通过类继承来获得,需要处理的就是获取Bean定义信息。这里是获取web容器环境指定的资源如/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。在获取到bean定义后,就如同Spring基本Ioc上下文容器ApplicationContext一样通过XmlBeanDefinitionReader来载入bean定义信息,最终完成上下文初始化。
相关文章推荐
- 分享微信开发Html5轻游戏中的几个坑
- C# MVC模式下商品抽奖功能实现
- Zend的MVC机制使用分析(二)
- ASP.NET MVC 4 捆绑和缩小实例介绍
- ASP.NET Mvc开发之查询数据
- ASP.NET MVC中将控制器分离到类库的实现
- asp.net实现在非MVC中使用Razor模板引擎的方法
- ASP.NET MVC中的AJAX应用
- 为ASP.NET MVC及WebApi添加路由优先级
- ASP.NET MVC中图表控件的使用方法
- Asp.net mvc实时生成缩率图到硬盘
- 剖析ASP.NET MVC的DependencyResolver组件
- ASP.NET MVC的四种验证编程方式
- ASP.NET MVC @Helper辅助方法和@functons自定义函数的使用方法
- 利用ASP.NET MVC+Bootstrap搭建个人博客之修复UEditor编辑时Bug(四)
- 浅谈JavaScript前端开发的MVC结构与MVVM结构
- 仅30行代码实现Javascript中的MVC
- asp.net MVC利用ActionFilterAttribute过滤关键字的方法
- ASP.NET MVC使用ActionFilterAttribute实现权限限制的方法(附demo源码下载)
- ASP.NET MVC 3仿Server.Transfer效果的实现方法
