JavaSE 基础 第11节 深入理解字符串
2016-06-29 12:21
309 查看
2016-06-29
1 字符串处理
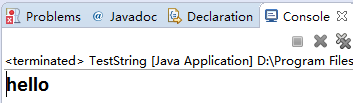
求子串。 helloworld
String str="helloworld";
//5<= n <9
//str=str.substring(5,10);
str=str.substring(0,5);
测试字符串是否相等。equals
Object equals:比较内存地址
String equals:比较内容
API 1.6
1,寄存器
2,栈
3,堆 * new
4,静态存储区
5,常量存储区 * final static String常量池
6,其他存储位置
字符串编辑
字符串的内容不会变,改变的是引用
String a="hello";
a=a+"world";
System.out.println(a);
2 字符串其他常用操作
【参考资料】
[1] Java轻松入门经典教程【完整版】
1 字符串处理
求子串。 helloworld
String str="helloworld";
//5<= n <9
//str=str.substring(5,10);
str=str.substring(0,5);
package com.java1995;
/**
* 求子串
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args){
String str="helloworld";
// 5<= n < 9
//str=str.substring(5,10);
str=str.substring(0,5);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
测试字符串是否相等。equals
Object equals:比较内存地址
String equals:比较内容
API 1.6
1,寄存器
2,栈
3,堆 * new
4,静态存储区
5,常量存储区 * final static String常量池
6,其他存储位置
package com.java1995;
/**
* 判断字符串是否相等
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestString2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s1="hello";//声明一个String类型的变量
String s2="hello";//声明另一个内容相同的String类型变量
String s3="hello"+"world";
//比较内容
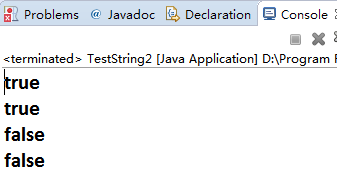
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//比较内存地址 true
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
//比较内容
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
//比较内存地址
System.out.println(s1 == s3);
// 运行结果 true true false false
}
}
package com.java1995;
/**
* String常量池、堆内存
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestString3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//维护在常量池里面
String a="hello";
String b="hello";
//new出来的所有对象都是在堆内存
//只要是new出来的,都是新对象
String c= new String("hello");
String d= new String("hello");
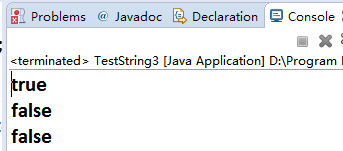
System.out.println(a==b);//true
System.out.println(a==c);//false
System.out.println(c==d);//false
}
}
字符串编辑
字符串的内容不会变,改变的是引用
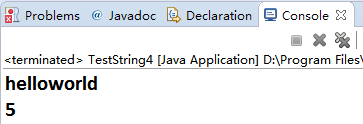
String a="hello";
a=a+"world";
System.out.println(a);
package com.java1995;
/**
* 字符串编辑
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class TestString4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
String a="hello";
a=a+"world";
int count=a.indexOf("world");
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
2 字符串其他常用操作
【参考资料】
[1] Java轻松入门经典教程【完整版】
相关文章推荐
- 85-002-5 Struts环境的搭建
- 85-002-3 spring与hibernate的整合(采用AOP来管理事务实现声明式事务)
- java本地化 国际化
- 算法_栈与队列的Java链表实现
- Java 关于finally、static
- Spring+SpringMVC 文件批量同步上传
- spring 3 bean配置--注入属性配置细节(1)
- java中的四舍五入的问题
- 待补充:java.math.BigDecimal.toPlainString() 详解
- 算法-百鸡问题 Java
- Java基础题
- Spring 注解配置(2)——@Autowired
- spring mvc 单元测试示例
- Java中单例模式的七种写法
- Servlet的运行过程
- JAVA读写文件方法总结
- 浅谈java中异步多线程超时导致的服务异常
- java之synchronized
- eclipse中导入外部jar包
- Java基础知识强化106:Java中 int 的各进制之间的转换
