python实现简单神经网络算法
2016-06-20 16:06
916 查看
python实现简单神经网络算法
python实现二层神经网络
包括输入层和输出层
import numpy as np
#sigmoid function
def nonlin(x, deriv = False):
if(deriv == True):
return x*(1-x)
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
#input dataset
x = np.array([[0,0,1],
[0,1,1],
[1,0,1],
[1,1,1]])
#output dataset
y = np.array([[0,0,1,1]]).T
np.random.seed(1)
#init weight value
syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,1))-1
for iter in xrange(100000):
l0 = x #the first layer,and the input layer
l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the output layer
l1_error = y-l1
l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,True)
syn0 += np.dot(l0.T, l1_delta)
print "outout after Training:"
print l1
这里,
l0:输入层
l1:输出层
syn0:初始权值
l1_error:误差
l1_delta:误差校正系数
func nonlin:sigmoid函数
这里迭代次数为100时,预测结果为

迭代次数为1000时,预测结果为:
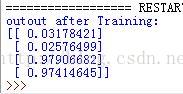
迭代次数为10000,预测结果为:
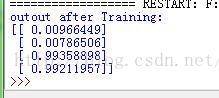
迭代次数为100000,预测结果为:
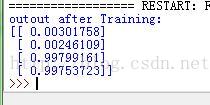
可见迭代次数越多,预测结果越接近理想值,当时耗时也越长。
python实现三层神经网络
包括输入层、隐含层和输出层
import numpy as np
def nonlin(x, deriv = False):
if(deriv == True):
return x*(1-x)
else:
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
#input dataset
X = np.array([[0,0,1],
[0,1,1],
[1,0,1],
[1,1,1]])
#output dataset
y = np.array([[0,1,1,0]]).T
syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,4)) - 1 #the first-hidden layer weight value
syn1 = 2*np.random.random((4,1)) - 1 #the hidden-output layer weight value
for j in range(60000):
l0 = X #the first layer,and the input layer
l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the hidden layer
l2 = nonlin(np.dot(l1,syn1)) #the third layer,and the output layer
l2_error = y-l2 #the hidden-output layer error
if(j%10000) == 0:
print "Error:"+str(np.mean(l2_error))
l2_delta = l2_error*nonlin(l2,deriv = True)
l1_error = l2_delta.dot(syn1.T) #the first-hidden layer error
l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,deriv = True)
syn1 += l1.T.dot(l2_delta)
syn0 += l0.T.dot(l1_delta)
print "outout after Training:"
print l2
python实现二层神经网络
包括输入层和输出层
import numpy as np
#sigmoid function
def nonlin(x, deriv = False):
if(deriv == True):
return x*(1-x)
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
#input dataset
x = np.array([[0,0,1],
[0,1,1],
[1,0,1],
[1,1,1]])
#output dataset
y = np.array([[0,0,1,1]]).T
np.random.seed(1)
#init weight value
syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,1))-1
for iter in xrange(100000):
l0 = x #the first layer,and the input layer
l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the output layer
l1_error = y-l1
l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,True)
syn0 += np.dot(l0.T, l1_delta)
print "outout after Training:"
print l1
这里,
l0:输入层
l1:输出层
syn0:初始权值
l1_error:误差
l1_delta:误差校正系数
func nonlin:sigmoid函数
这里迭代次数为100时,预测结果为

迭代次数为1000时,预测结果为:

迭代次数为10000,预测结果为:

迭代次数为100000,预测结果为:

可见迭代次数越多,预测结果越接近理想值,当时耗时也越长。
python实现三层神经网络
包括输入层、隐含层和输出层
import numpy as np
def nonlin(x, deriv = False):
if(deriv == True):
return x*(1-x)
else:
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
#input dataset
X = np.array([[0,0,1],
[0,1,1],
[1,0,1],
[1,1,1]])
#output dataset
y = np.array([[0,1,1,0]]).T
syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,4)) - 1 #the first-hidden layer weight value
syn1 = 2*np.random.random((4,1)) - 1 #the hidden-output layer weight value
for j in range(60000):
l0 = X #the first layer,and the input layer
l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the hidden layer
l2 = nonlin(np.dot(l1,syn1)) #the third layer,and the output layer
l2_error = y-l2 #the hidden-output layer error
if(j%10000) == 0:
print "Error:"+str(np.mean(l2_error))
l2_delta = l2_error*nonlin(l2,deriv = True)
l1_error = l2_delta.dot(syn1.T) #the first-hidden layer error
l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,deriv = True)
syn1 += l1.T.dot(l2_delta)
syn0 += l0.T.dot(l1_delta)
print "outout after Training:"
print l2
相关文章推荐
- Python动态类型的学习---引用的理解
- Python3写爬虫(四)多线程实现数据爬取
- 垃圾邮件过滤器 python简单实现
- 下载并遍历 names.txt 文件,输出长度最长的回文人名。
- install and upgrade scrapy
- Scrapy的架构介绍
- Centos6 编译安装Python
- 使用Python生成Excel格式的图片
- 让Python文件也可以当bat文件运行
- [Python]推算数独
- Python中zip()函数用法举例
- Python中map()函数浅析
- Python将excel导入到mysql中
- Python在CAM软件Genesis2000中的应用
- 使用Shiboken为C++和Qt库创建Python绑定
- FREEBASIC 编译可被python调用的dll函数示例
- Python 七步捉虫法
