Spring MVC hello world example
2016-06-13 08:45
761 查看
很不错的一篇文章,还有sample source。
http://www.mkyong.com/spring-mvc/spring-mvc-hello-world-example/
By mkyong | July
29, 2010 | Updated : June 16, 2015 | Viewed : 600,102 times
Note
This tutorial is based on Spring 2.5.6, quite outdated. Try considering the new tutorials :
Gradle + Spring 4 MVC Hello World
Maven + Spring 3 MVC Hello World
In this tutorial, we will show you a Spring MVC hello world web application.
Technologies used :
Spring 2.5.6
JDK 1.6
Eclipse 3.6
Maven 3
In Spring MVC web application, it consists of 3 standard MVC (Model, Views, Controller) components :
Models – Domain objects that are processed by the service layer (business logic) or persistent layer (database operation).
Views – Display data, normally it’s a JSP page written with the Java Standard Tag Library (JSTL).
Controllers – URL mapping and interact with service layer for business processing and return a Model.
The following figures demonstrates how the Spring MVC web application handles a web request.
Figure 1.1 – Image is copied from Spring
MVC reference with slightly modified.
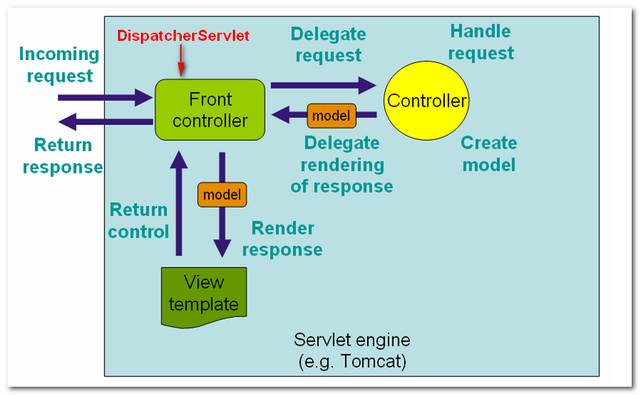
Figure 1.2 – Image is copied from this book : Spring
Recipes
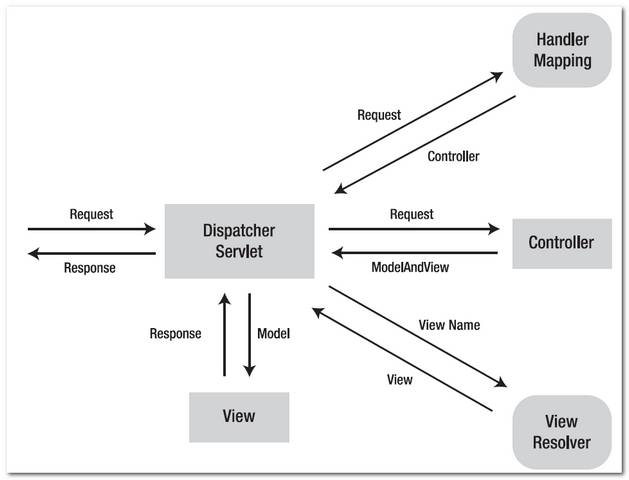
Note
In Spring MVC , the core dispatcher component is the
front-controller (design pattern). Every web request has to go through this
and the

Declares the
will help you manage the transitive dependencies automatically (download other dependencies that are required by
like
If you are using the JSP page with JSTL technology, include the
also.
pom.xml
Markup
Spring comes with many Controllers, normally, you just need to extend the
and override the
HelloWorldController.java
Java
4.1 ModelAndView(“HelloWorldPage”) – To identify which view should return back to the user, in this example
be returned.
4.2 model.addObject(“msg”, “hello world”) – Add a “hello world” string into a model named “msg”, later you can use EL
display the “hello world” string.
In this case, “view” is a JSP page, you can display the value “hello world” that is stored in the model “msg” via expression language (EL) ${msg}.
HelloWorldPage.jsp
Markup
Note
If the ${msg} is displayed as it is, not the value inside the “msg” model, it may caused by the old JSP 1.2 descriptor, which make the expression languages disabled by default, see the solution here.
6.1 Declared the Spring Controller and viewResolver.
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
Markup
1. Controller – Declared a bean name
map it to
is requested, the
2. viewResolver – Define how Spring will look for the view template. In this case, the controller
return a view named
mechanism : prefix + view name + suffix, which is
Note
Actually, you don’t need to define the
by default, if no handler mapping can be found, the DispatcherServlet will create a
See this article – BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping example for
detail.
6.2 In
to act as the front-controller to handle all the entire web request which end with
web.xml
Markup
Note
The
By default, it will look for Spring XML configuration file by joining the servlet name
In this example, Spring will look for this file –
7.1 To run this project with Maven :
Bash
7.2 To run this project in Eclipse IDE, create Eclipse project settings with the following Maven command :
Bash
Imports the project manually and start with the server plugin.
URL : http://localhost:8080/spring2/welcome.htm
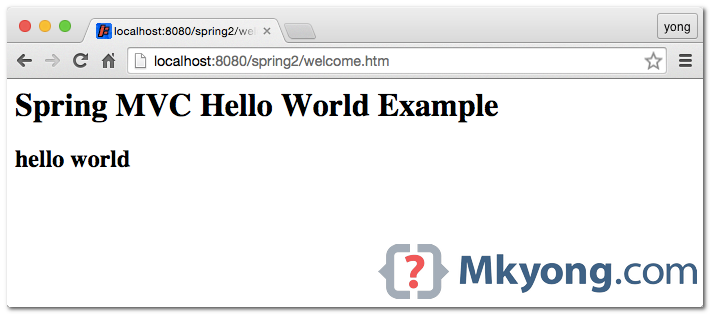
How it works? http://localhost:8080/spring2/welcome.htm is requested.
URL is end with “.htm” extension, so it will redirect to “DispatcherServlet” and send requests to the default BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping return HelloWorldController to the DispatcherServlet.
DispatcherServlet forward request to the HelloWorldController.
HelloWorldController process it and return a ModelAndView object, with view name “HelloWorldPage”.
DispatcherServlet received the ModelAndView and call the viewResolver to process it.
viewResolver return the
DispatcherServlet return the “HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to the user.
Download it – spring2-mvc-xml-hello-world.zip (14 KB)
Spring MVC documentation
http://www.mkyong.com/spring-mvc/spring-mvc-hello-world-example/
Spring MVC hello world example
By mkyong | July29, 2010 | Updated : June 16, 2015 | Viewed : 600,102 times
Note
This tutorial is based on Spring 2.5.6, quite outdated. Try considering the new tutorials :
Gradle + Spring 4 MVC Hello World
Maven + Spring 3 MVC Hello World
In this tutorial, we will show you a Spring MVC hello world web application.
Technologies used :
Spring 2.5.6
JDK 1.6
Eclipse 3.6
Maven 3
1. MVC Basic
In Spring MVC web application, it consists of 3 standard MVC (Model, Views, Controller) components :Models – Domain objects that are processed by the service layer (business logic) or persistent layer (database operation).
Views – Display data, normally it’s a JSP page written with the Java Standard Tag Library (JSTL).
Controllers – URL mapping and interact with service layer for business processing and return a Model.
The following figures demonstrates how the Spring MVC web application handles a web request.
Figure 1.1 – Image is copied from Spring
MVC reference with slightly modified.

Figure 1.2 – Image is copied from this book : Spring
Recipes

Note
In Spring MVC , the core dispatcher component is the
DispatcherServlet, which act as the
front-controller (design pattern). Every web request has to go through this
DispatcherServlet,
and the
DispatcherServletwill dispatch the web request to suitable handlers.
2. Directory Structure
A standard Maven project directory structure.
3. Maven
Declares the spring-webmvcdependency, Maven
will help you manage the transitive dependencies automatically (download other dependencies that are required by
spring-webmvc,
like
spring-contextor
spring-beans).
If you are using the JSP page with JSTL technology, include the
jstldependency
also.
pom.xml
Markup
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.mkyong.common</groupId> <artifactId>spring2-mvc-xml-hello-world</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>Spring 2 MVC</name> <properties> <jdk.version>1.6</jdk.version> <spring.version>2.5.6</spring.version> <jstl.version>1.2</jstl.version> <servletapi.version>2.5</servletapi.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- Spring MVC framework --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- JSTL --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>${jstl.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- for compile only, your container should have this --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>${servletapi.version}</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3</version> <configuration> <source>${jdk.version}</source> <target>${jdk.version}</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- embedded jetty, good for testing --> <plugin> <groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId> <artifactId>jetty-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>9.2.11.v20150529</version> <configuration> <scanIntervalSeconds>10</scanIntervalSeconds> <webApp> <contextPath>/spring2</contextPath> </webApp> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- configure Eclipse workspace --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.9</version> <configuration> <downloadSources>true</downloadSources> <downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs> <wtpversion>2.0</wtpversion> <wtpContextName>spring2</wtpContextName> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
4. Spring Controller
Spring comes with many Controllers, normally, you just need to extend the AbstractController,
and override the
handleRequestInternal()method.
HelloWorldController.java
Java
package com.mkyong.common.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.AbstractController;
public class HelloWorldController extends AbstractController{
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("HelloWorldPage");
model.addObject("msg", "hello world");
return model;
}
}4.1 ModelAndView(“HelloWorldPage”) – To identify which view should return back to the user, in this example
HelloWorldPage.jspwill
be returned.
4.2 model.addObject(“msg”, “hello world”) – Add a “hello world” string into a model named “msg”, later you can use EL
${msg} todisplay the “hello world” string.
5. View (JSP page)
In this case, “view” is a JSP page, you can display the value “hello world” that is stored in the model “msg” via expression language (EL) ${msg}.HelloWorldPage.jsp
Markup
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Spring MVC Hello World Example</h1>
<h2>${msg}</h2>
</body>
</html>Note
If the ${msg} is displayed as it is, not the value inside the “msg” model, it may caused by the old JSP 1.2 descriptor, which make the expression languages disabled by default, see the solution here.
6. Spring XML Configuration
6.1 Declared the Spring Controller and viewResolver.mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
Markup
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean name="/welcome.htm" class="com.mkyong.common.controller.HelloWorldController" /> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" > <property name="prefix"> <value>/WEB-INF/pages/</value> </property> <property name="suffix"> <value>.jsp</value> </property> </bean> </beans>
1. Controller – Declared a bean name
/welcome.htmand
map it to
HelloWorldController. It means, if an URL with
/welcome.htmpattern
is requested, the
HelloWorldControllercontroller will handle the request.
2. viewResolver – Define how Spring will look for the view template. In this case, the controller
HelloWorldControllerwill
return a view named
HelloWorldPage, the viewResolver will find the file with following
mechanism : prefix + view name + suffix, which is
/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jsp.
Note
Actually, you don’t need to define the
BeanNameUrlHandlerMappingin the
web.xml,
by default, if no handler mapping can be found, the DispatcherServlet will create a
BeanNameUrlHandlerMappingautomatically.
See this article – BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping example for
detail.
6.2 In
web.xml, declared a
DispatcherServletservlet
to act as the front-controller to handle all the entire web request which end with
htmextension.
web.xml
Markup
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <display-name>Spring Web MVC Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Note
The
mvc-dispatcheris used to define which file to load the Spring XML configurations.
By default, it will look for Spring XML configuration file by joining the servlet name
mvc-dispatcherwith
-servlet.xml.
In this example, Spring will look for this file –
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml.
7. Demo
7.1 To run this project with Maven :Bash
$ mvn jetty:run
7.2 To run this project in Eclipse IDE, create Eclipse project settings with the following Maven command :
Bash
$ mvn eclipse:eclipse
Imports the project manually and start with the server plugin.
URL : http://localhost:8080/spring2/welcome.htm

How it works? http://localhost:8080/spring2/welcome.htm is requested.
URL is end with “.htm” extension, so it will redirect to “DispatcherServlet” and send requests to the default BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping return HelloWorldController to the DispatcherServlet.
DispatcherServlet forward request to the HelloWorldController.
HelloWorldController process it and return a ModelAndView object, with view name “HelloWorldPage”.
DispatcherServlet received the ModelAndView and call the viewResolver to process it.
viewResolver return the
/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jspback to the DispatcherServlet.
DispatcherServlet return the “HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to the user.
Download Source Code
Download it – spring2-mvc-xml-hello-world.zip (14 KB)
References
Spring MVC documentation
相关文章推荐
- 开源 java CMS - FreeCMS2.4 栏目管理
- Eclipse插件开发 实现 复制 粘贴 剪切功能
- JAVA.SWT/JFace: JFace篇之MVC的表格、树和列表
- JDK的get请求方式
- JAVA.SWT/JFace: SWT中的事件模型/SWT常见的事件/SWT类所代表的事件常量/按键与其对应的常量表、KeyEvent事件比较、VerifyEvent事件比较
- GEF 和 eclipse 视图对象
- eclipse 查询结果 在新窗口中打开
- java中堆和栈的区别,递归和迭代的区别
- JAVA中calendar,date,string 的相互转换和详细用法
- struts2 action以及页面跳转
- 当我们说线程安全时,到底在说什么——Java进阶系列(二)
- Dubbo分布式服务+Springmvc容器+Maven项目整合,分布式,kakfka消息中间件整合
- 当我们说线程安全时,到底在说什么——Java进阶系列(二)
- org.xml.sax.SAXParseException: Failed to read schema document错误的完美解决方法 以及 Spring如何加载XSD文件
- 16_AOP入门准备_Jdk动态代理模式
- org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationException: Data truncation: Data too long for column '
- java实现裴波那契堆
- 浅谈附属类,内部类,匿名内部类,静态内部类
- RxJava操作符(03-变换操作)
- RxJava操作符(03-变换操作)
