线性表--单链表(C++)
2016-06-06 10:28
375 查看
单链表演示图:
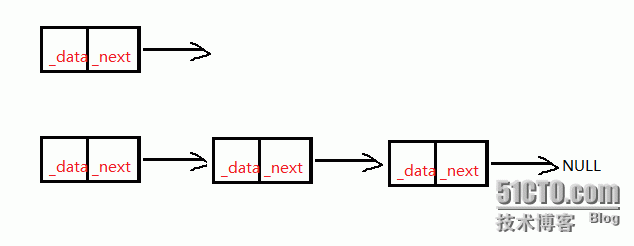
单链表结构体:
多一个Tail指针的好处就是很方便可以找到链表尾部,方便在尾部插入一个元素什么的。
下面我们用类来实现单链表:class SList
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const SList& s); //输出运算符重载(友元)
public:
SList() //构造函数
:_head(NULL)
,_tail(NULL)
{}
SList(const SList& s) //拷贝构造
:_head(NULL)
, _tail(NULL)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
PushBack(cur->_data );
cur = cur->_next;
}
_tail = cur;
}
~SList() //析构函数
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
Node *cur = _head;
if (cur != NULL)
{
Node *del = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete del;
}
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
SList& operator=(SList s) //赋值运算符重载
{
swap(_head, s._head);
swap(_tail, s._tail);
return *this;
}
单链表最基本的四个函数:void SList::PushBack(const DataType& d) //尾插
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d); //构建一个新的节点
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
_tail->_next = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
}
void SList::PushFront(const DataType& d) //头插
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d);
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->_next = _head;
_head = newNode;
}
}
void SList::PopBack() //尾删
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
else if (_head == _tail)
{
delete _tail;
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
else
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur->_next != _tail)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
delete _tail;
_tail = cur;
_tail->_next = NULL;
}
}
void SList::PopFront() //头删
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
else if (_head == _tail)
{
delete _tail;
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
else
{
Node *del = _head;
_head = _head->_next;
delete del;
}
}
给一个数据,若找到该节点则返回该节点,没找到则返回NULL
Node* SList::Find(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}给定一个节点,在该节点后插入一个新的节点
void SList::Insert(Node* pos, const DataType& d)
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d);
if (pos == _tail) //若给定的节点是尾节点,此处可以直接调用尾插
{
_tail->_next = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->_next = pos->_next;
pos->_next = newNode;
}
}链表的逆序:此处用三个指针来实现
void SList::Reverse()
{
Node *p1 = NULL;
Node *p2 = _head;
Node *newhead = NULL;
while (p2)
{
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2->_next;
p1->_next = newhead;
newhead = p1;
}
_head = newhead;
}链表的排序:采用冒泡排序void SList::Sort()
{
Node *cur = _head;
Node *end = NULL;
while (cur != end)
{
while (cur->_next != end)
{
if (cur->_data > cur->_next->_data)
{
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
end = cur;
cur = _head;
}
}删除某个节点(给定一个数据,删除数据与之相等的第一个节点)void SList::Remove(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
{
Node *del = cur->_next;
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
cur->_next = cur->_next->_next;
delete del;
return;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
}删除某些节点(给定一个数据,删除数据与之相等的每一个节点)void SList::RemoveAll(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
{
Node *del = cur->_next;
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
cur->_next = cur->_next->_next;
delete del;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return;
}删除非尾节点void SList::EarseNotTail(Node *pos)
{
Node *del = pos;
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur->_next!=pos) //找到该节点的前一个节点
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
cur->_next = pos->_next; //让它的_next指向要删除节点的_next
delete del;
}找到中间节点Node* SList::FindMinNode() //快慢指针问题
{ //两个指针都指向头结点
Node *cur = _head; //快的一次走两步,慢的一次走一步
Node *fast = cur; //当快指针走到尾的时候,慢指针指向中间节点
Node *slow = cur;
while (fast)
{
fast = fast->_next->_next;
slow = slow->_next;
}
return slow;
}删除倒数第K个节点
void SList::DelKNode(int k)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int i = k - 1;
while (i) //先让cur指向正数第K个节点
{
cur = cur->_next;
i = i - 1;;
}
Node *p1 = _head;
Node *tmp = NULL;
while (cur->_next ) //让一个指向头结点的指针和cur一起走
{
tmp = p1;
p1 = p1->_next;
cur = cur->_next; //当cur指向尾节点时,那个指针指向倒第K个节点
}
Node *del = p1;
tmp->_next = p1->_next ;
delete p1;
}检测是否带环
//检测是否带环
int SList::CheckCycle(const SList& s) //快慢指针问题
{
Node *fast = _head;
Node *slow = _head;
while (slow)
{
if (slow == fast)
{
return 1;
}
fast = fast->_next->_next;
slow = slow->_next;
}
return 0;
}获取环的入口点
Node* SList::GetCycleEoryNode()
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur == _tail)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}判断是否相交
int SList::CheckCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur = l1._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l2._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
else
{
Node *cur = l2._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l1._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return 0;
}合并两个链表
int SList::CheckCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur = l1._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l2._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
else
{
Node *cur = l2._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l1._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return 0;
}
求两个链表的交点
Node* SList::GetLinkCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
while (cur2)
{
if (cur2->_next == cur1->_next )
return cur1;
else
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
}
}
else
{
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
while (cur1)
{
if (cur2->_next == cur1->_next)
return cur1;
else
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}求链表长度
int SList::LengthOfList(const SList& s)
{
int length = 0;
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
length++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return length;
}
以后会有改进版奉上,希望大家多多支持


单链表结构体:
struct Node
{
Node(const DataType& d)//节点的构造函数
:_data(d)
,_next(NULL)
{}
DataType _data; //数据
struct Node *_next; //指向下一个节点的指针
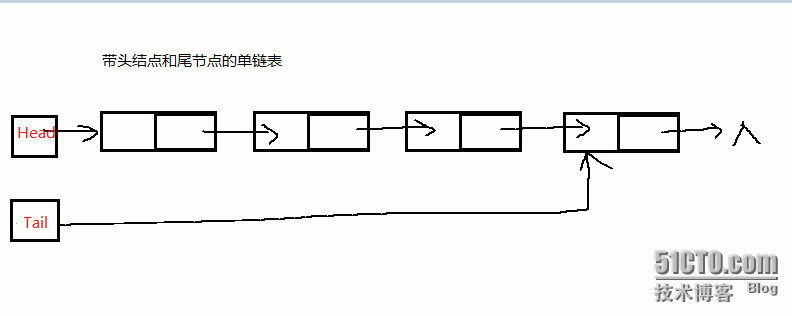
};带头结点和尾节点的单链表:
多一个Tail指针的好处就是很方便可以找到链表尾部,方便在尾部插入一个元素什么的。
下面我们用类来实现单链表:class SList
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const SList& s); //输出运算符重载(友元)
public:
SList() //构造函数
:_head(NULL)
,_tail(NULL)
{}
SList(const SList& s) //拷贝构造
:_head(NULL)
, _tail(NULL)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
PushBack(cur->_data );
cur = cur->_next;
}
_tail = cur;
}
~SList() //析构函数
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
Node *cur = _head;
if (cur != NULL)
{
Node *del = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete del;
}
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
SList& operator=(SList s) //赋值运算符重载
{
swap(_head, s._head);
swap(_tail, s._tail);
return *this;
}
单链表最基本的四个函数:void SList::PushBack(const DataType& d) //尾插
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d); //构建一个新的节点
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
_tail->_next = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
}
void SList::PushFront(const DataType& d) //头插
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d);
if (_head == NULL)
{
_head = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->_next = _head;
_head = newNode;
}
}
void SList::PopBack() //尾删
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
else if (_head == _tail)
{
delete _tail;
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
else
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur->_next != _tail)
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
delete _tail;
_tail = cur;
_tail->_next = NULL;
}
}
void SList::PopFront() //头删
{
if (_head == NULL)
return;
else if (_head == _tail)
{
delete _tail;
_tail = NULL;
_head = NULL;
}
else
{
Node *del = _head;
_head = _head->_next;
delete del;
}
}
给一个数据,若找到该节点则返回该节点,没找到则返回NULL
Node* SList::Find(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}给定一个节点,在该节点后插入一个新的节点
void SList::Insert(Node* pos, const DataType& d)
{
Node *newNode = new Node(d);
if (pos == _tail) //若给定的节点是尾节点,此处可以直接调用尾插
{
_tail->_next = newNode;
_tail = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->_next = pos->_next;
pos->_next = newNode;
}
}链表的逆序:此处用三个指针来实现
void SList::Reverse()
{
Node *p1 = NULL;
Node *p2 = _head;
Node *newhead = NULL;
while (p2)
{
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2->_next;
p1->_next = newhead;
newhead = p1;
}
_head = newhead;
}链表的排序:采用冒泡排序void SList::Sort()
{
Node *cur = _head;
Node *end = NULL;
while (cur != end)
{
while (cur->_next != end)
{
if (cur->_data > cur->_next->_data)
{
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
end = cur;
cur = _head;
}
}删除某个节点(给定一个数据,删除数据与之相等的第一个节点)void SList::Remove(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
{
Node *del = cur->_next;
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
cur->_next = cur->_next->_next;
delete del;
return;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
}删除某些节点(给定一个数据,删除数据与之相等的每一个节点)void SList::RemoveAll(const DataType& d)
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->_data == d)
{
Node *del = cur->_next;
DataType tmp = cur->_data;
cur->_data = cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data = tmp;
cur->_next = cur->_next->_next;
delete del;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return;
}删除非尾节点void SList::EarseNotTail(Node *pos)
{
Node *del = pos;
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur->_next!=pos) //找到该节点的前一个节点
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
cur->_next = pos->_next; //让它的_next指向要删除节点的_next
delete del;
}找到中间节点Node* SList::FindMinNode() //快慢指针问题
{ //两个指针都指向头结点
Node *cur = _head; //快的一次走两步,慢的一次走一步
Node *fast = cur; //当快指针走到尾的时候,慢指针指向中间节点
Node *slow = cur;
while (fast)
{
fast = fast->_next->_next;
slow = slow->_next;
}
return slow;
}删除倒数第K个节点
void SList::DelKNode(int k)
{
Node *cur = _head;
int i = k - 1;
while (i) //先让cur指向正数第K个节点
{
cur = cur->_next;
i = i - 1;;
}
Node *p1 = _head;
Node *tmp = NULL;
while (cur->_next ) //让一个指向头结点的指针和cur一起走
{
tmp = p1;
p1 = p1->_next;
cur = cur->_next; //当cur指向尾节点时,那个指针指向倒第K个节点
}
Node *del = p1;
tmp->_next = p1->_next ;
delete p1;
}检测是否带环
//检测是否带环
int SList::CheckCycle(const SList& s) //快慢指针问题
{
Node *fast = _head;
Node *slow = _head;
while (slow)
{
if (slow == fast)
{
return 1;
}
fast = fast->_next->_next;
slow = slow->_next;
}
return 0;
}获取环的入口点
Node* SList::GetCycleEoryNode()
{
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur == _tail)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}判断是否相交
int SList::CheckCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur = l1._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l2._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
else
{
Node *cur = l2._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l1._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return 0;
}合并两个链表
int SList::CheckCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur = l1._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l2._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
else
{
Node *cur = l2._head;
while (cur)
{
if (l1._tail == cur)
return 1;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return 0;
}
求两个链表的交点
Node* SList::GetLinkCross(SList& l1, SList& l2)
{
int count1 = l1.LengthOfList(l1);
int count2 = l2.LengthOfList(l2);
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
if (count1 > count2)
{
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
while (cur2)
{
if (cur2->_next == cur1->_next )
return cur1;
else
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
}
}
else
{
Node *cur1 = l1._head;
Node *cur2 = l2._head;
while (cur1)
{
if (cur2->_next == cur1->_next)
return cur1;
else
{
cur1 = cur1->_next;
cur2 = cur2->_next;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}求链表长度
int SList::LengthOfList(const SList& s)
{
int length = 0;
Node *cur = _head;
while (cur)
{
length++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return length;
}
以后会有改进版奉上,希望大家多多支持

相关文章推荐
- c++常用字符串操作函数
- 【JNI】Java与C++中文字串的传递
- C++程序设计语言练习6.10 字符串函数的写法
- 如何检查C++中的内存泄漏 vs自带
- C/C++ 内存泄漏检测工具 Visual Leak Detector
- C++作业7
- C语言 声明的一般 解读 方法
- 第七次作业
- 默认浏览器打开指定网址
- C++作业7
- C++实验7
- 数论 - 用扩展欧几里得解模线性方程ax≡b (mod n) + 生理周期
- 成为C++高手之头文件与条件编译
- c++第七次作业
- C++第7次作业
- c++第七次作业
- C++第7次实验-项目一:素数与回文
- C++第7次作业
- C++作业7
- 字典树实现词频统计及频率字典序双重融合排序算法
