第14课:Spark Streaming源码解读之State管理之updateStateByKey和mapWithState解密
2016-05-29 13:57
597 查看
什么是state(状态)管理?我们以wordcount为例。每个batchInterval会计算当前batch的单词计数,那如果需要单词计数一直的累加下去,该如何实现呢?SparkStreaming提供了两种方法:updateStateByKey和mapWithState 。mapWithState 是1.6版本新增功能,目前属于实验阶段。mapWithState具官方说性能较updateStateByKey提升10倍。那么我们来看看他们到底是如何实现的。
代码示例如下:
但是DStream的伴生对象中有一个隐式转换函数
updateStateByKey最终会调用如下同名函数
所以Spark1.6 引入了mapWithState。
代码示例如下:
mapWithState函数中创建了MapWithStateDStreamImpl对象
在InternalMapWithStateDStream中并没有实现getOrCompute方法,是其父类DStream中实现的。
而在getOrCompute方法中最终会调用InternalMapWithStateDStream的compute方法:
在updateRecordWithData方法中
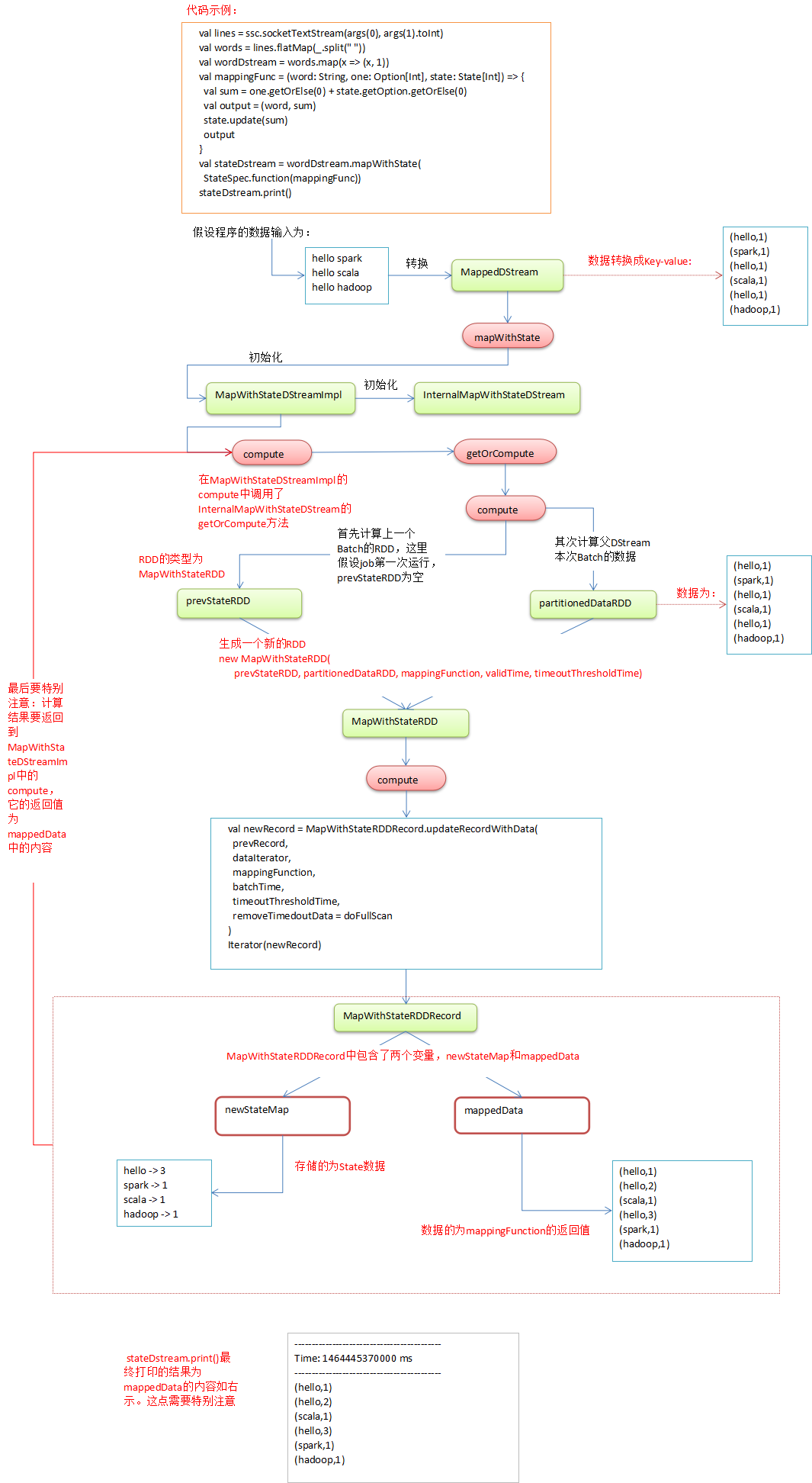
使用如下流程图说明计算过程:
备注:1、DT大数据梦工厂微信公众号DT_Spark
2、IMF晚8点大数据实战YY直播频道号:68917580
3、新浪微博: http://www.weibo.com/ilovepains
代码示例如下:
object UpdateStateByKeyDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("UpdateStateByKeyDemo")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf,Seconds(20))
//要使用updateStateByKey方法,必须设置Checkpoint。
ssc.checkpoint("/checkpoint/")
val socketLines = ssc.socketTextStream("spark-master",9999)
socketLines.flatMap(_.split(",")).map(word=>(word,1))
.updateStateByKey(
(currValues:Seq[Int],preValue:Option[Int]) =>{
val currValue = currValues.sum
Some(currValue + preValue.getOrElse(0))
}).print()
// socketLines.flatMap(_.split(",")).map(word=>(word,1)).reduceByKey()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
ssc.stop()
}
}我们知道map返回的是MappedDStream,而MappedDStream并没有updateStateByKey方法,并且它的父类DStream中也没有该方法。但是DStream的伴生对象中有一个隐式转换函数
implicit def toPairDStreamFunctions[K, V](stream: DStream[(K, V)])
(implicit kt: ClassTag[K], vt: ClassTag[V], ord: Ordering[K] = null):
PairDStreamFunctions[K, V] = {
new PairDStreamFunctions[K, V](stream)
}在PairDStreamFunction中有updateStateByKey的定义:def updateStateByKey[S: ClassTag](
updateFunc: (Seq[V], Option[S]) => Option[S]
): DStream[(K, S)] = ssc.withScope {
updateStateByKey(updateFunc, defaultPartitioner())
}它接收一个函数作为参数,Seq[V]表示当前batch对应的key的value,而Option[S]表示key的以前的累计值(以示例为准),返回值是新的状态值。updateStateByKey最终会调用如下同名函数
def updateStateByKey[S: ClassTag](
updateFunc: (Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => Iterator[(K, S)],
partitioner: Partitioner,
rememberPartitioner: Boolean
): DStream[(K, S)] = ssc.withScope {
new StateDStream(self, ssc.sc.clean(updateFunc), partitioner, rememberPartitioner, None)
}在这里面new出了一个StateDStream对象。在其compute方法中,会先获取上一个batch计算出的RDD(包含了至程序开始到上一个batch单词的累计计数),然后在获取本次batch中StateDStream的父类计算出的RDD(本次batch的单词计数)分别是prevStateRDD和parentRDD,然后在调用private [this] def computeUsingPreviousRDD (
parentRDD : RDD[(K, V)], prevStateRDD : RDD[(K, S)]) = {
// Define the function for the mapPartition operation on cogrouped RDD;
// first map the cogrouped tuple to tuples of required type,
// and then apply the update function
val updateFuncLocal = updateFunc
val finalFunc = (iterator: Iterator[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[S]))]) => {
val i = iterator.map(t => {
val itr = t._2._2.iterator
val headOption = if (itr.hasNext) Some(itr.next()) else None
(t._1, t._2._1.toSeq, headOption)
})
updateFuncLocal(i)
}
val cogroupedRDD = parentRDD.cogroup(prevStateRDD, partitioner)
val stateRDD = cogroupedRDD.mapPartitions(finalFunc, preservePartitioning)
Some(stateRDD)
}两个RDD进行cogroup然后应用updateStateByKey传入的函数。cogroup的性能是比较低下的。所以Spark1.6 引入了mapWithState。
代码示例如下:
object mapWithStateTest {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("StatefulNetworkWordCount").setMaster("local[2]")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(5))
ssc.checkpoint(".")
// Initial state RDD for mapWithState operation
val initialRDD = ssc.sparkContext.parallelize(List(("hello", 1), ("world", 1)))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("spark-master", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordDstream = words.map(x => (x, 1))
val mappingFunc = (word: String, one: Option[Int], state: State[Int]) => {
val sum = one.getOrElse(0) + state.getOption.getOrElse(0)
val output = (word, sum)
state.update(sum)
output
}
val stateDstream = wordDstream.mapWithState(
StateSpec.function(mappingFunc)
)
stateDstream.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}mapWithState接收的参数是一个StateSpec对象。在StateSpec中封装了状态管理的函数mapWithState函数中创建了MapWithStateDStreamImpl对象
def mapWithState[StateType: ClassTag, MappedType: ClassTag](
spec: StateSpec[K, V, StateType, MappedType]
): MapWithStateDStream[K, V, StateType, MappedType] = {
new MapWithStateDStreamImpl[K, V, StateType, MappedType](
self,
spec.asInstanceOf[StateSpecImpl[K, V, StateType, MappedType]]
)
}而在MapWithStateDStreamImpl中有创建了一个InternalMapWithStateDStream。并且MapWithStateDStreamImpl的compute方法调用了InternalMapWithStateDStream的getOrCompute方法private val internalStream =
new InternalMapWithStateDStream[KeyType, ValueType, StateType, MappedType](dataStream, spec)
override def slideDuration: Duration = internalStream.slideDuration
override def dependencies: List[DStream[_]] = List(internalStream)
override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[MappedType]] = {
internalStream.getOrCompute(validTime).map { _.flatMap[MappedType] { _.mappedData } }
}我们先看InternalMapWithStateDStream的getOrCompute方法:在InternalMapWithStateDStream中并没有实现getOrCompute方法,是其父类DStream中实现的。
而在getOrCompute方法中最终会调用InternalMapWithStateDStream的compute方法:
/** Method that generates a RDD for the given time */
override def compute(validTime: Time): Option[RDD[MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E]]] = {
// Get the previous state or create a new empty state RDD
val prevStateRDD = getOrCompute(validTime - slideDuration) match {
case Some(rdd) =>
if (rdd.partitioner != Some(partitioner)) {
// If the RDD is not partitioned the right way, let us repartition it using the
// partition index as the key. This is to ensure that state RDD is always partitioned
// before creating another state RDD using it
MapWithStateRDD.createFromRDD[K, V, S, E](
rdd.flatMap { _.stateMap.getAll() }, partitioner, validTime)
} else {
rdd
}
case None =>
MapWithStateRDD.createFromPairRDD[K, V, S, E](
spec.getInitialStateRDD().getOrElse(new EmptyRDD[(K, S)](ssc.sparkContext)),
partitioner,
validTime
)
}
// Compute the new state RDD with previous state RDD and partitioned data RDD
// Even if there is no data RDD, use an empty one to create a new state RDD
val dataRDD = parent.getOrCompute(validTime).getOrElse {
context.sparkContext.emptyRDD[(K, V)]
}
val partitionedDataRDD = dataRDD.partitionBy(partitioner)
val timeoutThresholdTime = spec.getTimeoutInterval().map { interval =>
(validTime - interval).milliseconds
}
Some(new MapWithStateRDD(
prevStateRDD, partitionedDataRDD, mappingFunction, validTime, timeoutThresholdTime))
}
}在这里根据先前的状态prevStateRDD,和MappedDStream中计算的当前batch对应的RDD生成了一个MapWithStateRDD,compute方法如下:override def compute(
partition: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E]] = {
val stateRDDPartition = partition.asInstanceOf[MapWithStateRDDPartition]
val prevStateRDDIterator = prevStateRDD.iterator(
stateRDDPartition.previousSessionRDDPartition, context)
val dataIterator = partitionedDataRDD.iterator(
stateRDDPartition.partitionedDataRDDPartition, context)
val prevRecord = if (prevStateRDDIterator.hasNext) Some(prevStateRDDIterator.next()) else None
val newRecord = MapWithStateRDDRecord.updateRecordWithData(
prevRecord,
dataIterator,
mappingFunction,
batchTime,
timeoutThresholdTime,
removeTimedoutData = doFullScan // remove timedout data only when full scan is enabled
)
Iterator(newRecord)
}MapWithStateRDD 的一个分区,对应一个MapWithStateRDDRecord对象,在MapWithStateRDDRecord中维护了两个数据结构var stateMap: StateMap[K, S], var mappedData: Seq[E])分别用来存储状态和mappingFunction的返回值。
在updateRecordWithData方法中
def updateRecordWithData[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, S: ClassTag, E: ClassTag](
prevRecord: Option[MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E]],
dataIterator: Iterator[(K, V)],
mappingFunction: (Time, K, Option[V], State[S]) => Option[E],
batchTime: Time,
timeoutThresholdTime: Option[Long],
removeTimedoutData: Boolean
): MapWithStateRDDRecord[K, S, E] = {
// Create a new state map by cloning the previous one (if it exists) or by creating an empty one
val newStateMap = prevRecord.map { _.stateMap.copy() }. getOrElse { new EmptyStateMap[K, S]() }
val mappedData = new ArrayBuffer[E]
val wrappedState = new StateImpl[S]()
// Call the mapping function on each record in the data iterator, and accordingly
// update the states touched, and collect the data returned by the mapping function
dataIterator.foreach { case (key, value) =>
wrappedState.wrap(newStateMap.get(key))
val returned = mappingFunction(batchTime, key, Some(value), wrappedState)
if (wrappedState.isRemoved) {
newStateMap.remove(key)
} else if (wrappedState.isUpdated
|| (wrappedState.exists && timeoutThresholdTime.isDefined)) {
newStateMap.put(key, wrappedState.get(), batchTime.milliseconds)
}
mappedData ++= returned
}
// Get the timed out state records, call the mapping function on each and collect the
// data returned
if (removeTimedoutData && timeoutThresholdTime.isDefined) {
newStateMap.getByTime(timeoutThresholdTime.get).foreach { case (key, state, _) =>
wrappedState.wrapTimingOutState(state)
val returned = mappingFunction(batchTime, key, None, wrappedState)
mappedData ++= returned
newStateMap.remove(key)
}
}
MapWithStateRDDRecord(newStateMap, mappedData)
}
}维护状态值,并且返回MapWithStateRDDRecord.使用如下流程图说明计算过程:

备注:1、DT大数据梦工厂微信公众号DT_Spark
2、IMF晚8点大数据实战YY直播频道号:68917580
3、新浪微博: http://www.weibo.com/ilovepains
相关文章推荐
- android Google Map获取地理位置信息的方法
- Spark RDD API详解(一) Map和Reduce
- Python中map()函数浅析
- Android使用Google Map浅谈
- Java Runtime Environment 5.0 Update 12 下载
- sql update 触发器 可获得被update的行的信息
- Mysql 原生语句中save or update 的写法汇总
- oracle中UPDATE nowait 的使用方法介绍
- sqlserver中delete、update中使用表别名和oracle的区别
- SQL Server UPDATE语句的用法详解
- SQL Server中的XML数据进行insert、update、delete
- SQL Server中的XML数据进行insert、update、delete操作实现代码
- MySQL中UPDATE语句使用的实例教程
- MySQL中UPDATE与DELETE语句的使用教程
- Erlang中的映射组Map详细介绍
- 使用 TOP 子句限制UPDATE 语句更新的数据
- sql server的 update from 语句的深究
- c++中map的基本用法和嵌套用法实例分析
- SQL Update多表联合更新的方法
- update 子查询使用介绍
