JDBC系列:(3)使用PreparedStatement执行sql语句
2016-05-11 22:10
831 查看
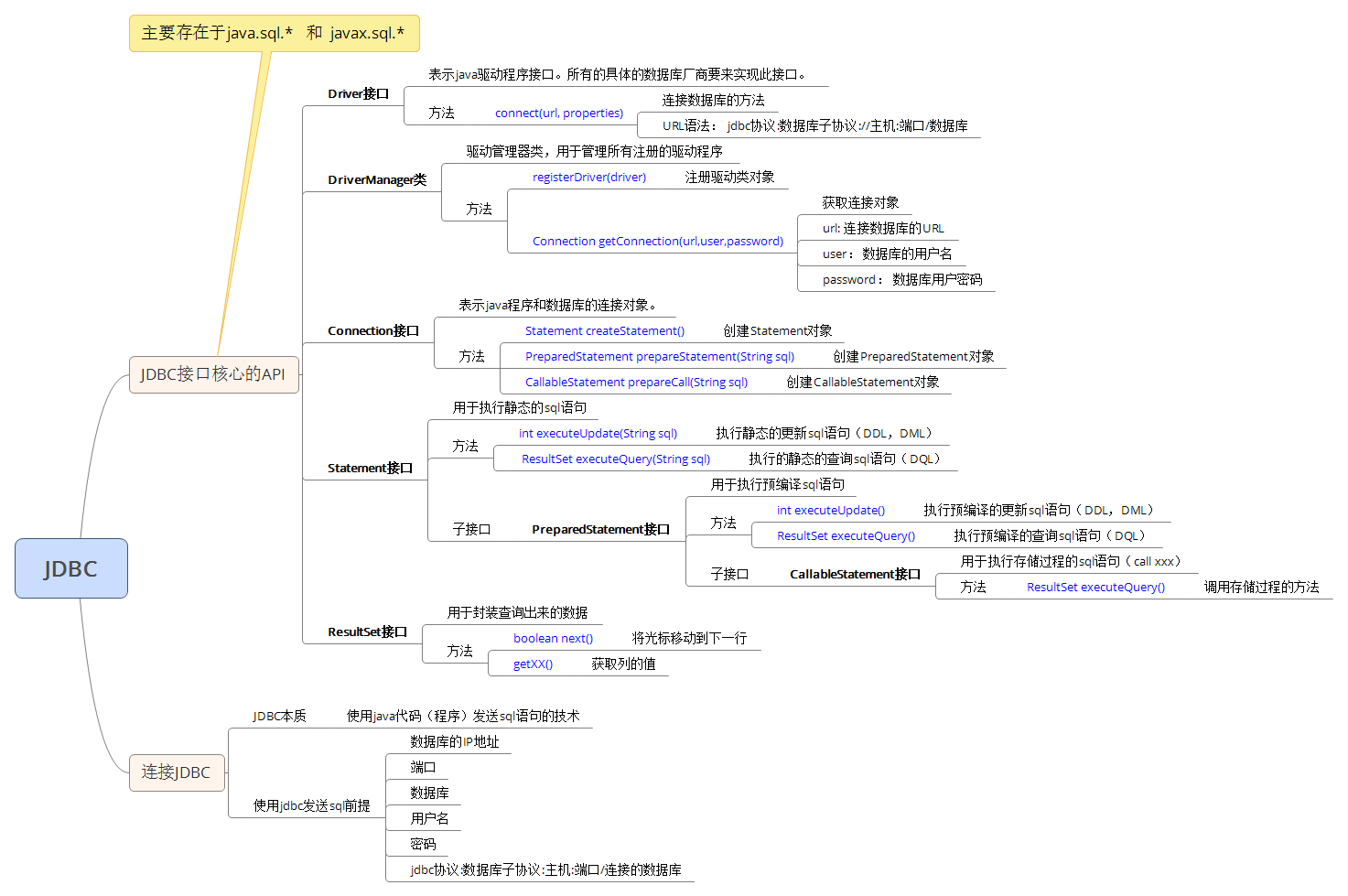
| 接口 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Statement接口 | 用于执行静态的sql语句 |
| PreparedStatement接口 | 用于执行预编译sql语句 |
| CallableStatement接口 | 用于执行存储过程的sql语句(call xxx) |
| 序号 | 不同 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 语法不同 | PreparedStatement可以使用预编译的sql,而Statement只能使用静态的sql |
| 2 | 效率不同 | PreparedStatement可以使用sql缓存区,效率比Statement高 |
| 3 | 安全性不同 | PreparedStatement可以有效防止sql注入,而Statement不能防止sql注入。 |
1、执行Insert语句
package com.rk.db.c_prepared;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import com.rk.db.utils.JDBCUtil;
/**
* 使用PreparedStatement执行Insert语句
* @author RK
*/
public class Demo01
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try
{
//1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
//2.准备预编译的sql
String sql = "INSERT INTO T_Persons(UserName,Pwd) VALUES(?,?)";
//3.执行预编译sql语句(检查语法)
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数值: 参数位置 从1开始
pstmt.setString(1, "地球人");
pstmt.setString(2, "987");
//5.发送参数,执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行!");
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
//关闭资源
JDBCUtil.close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
}2、执行Update语句
package com.rk.db.c_prepared;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import com.rk.db.utils.JDBCUtil;
/**
* 使用PreparedStatement执行Update语句
* @author RK
*/
public class Demo02
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try
{
//1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
//2.准备预编译的sql
String sql = "UPDATE T_Persons SET UserName=?, Pwd=? WHERE Id=?";
//3.执行预编译sql语句(检查语法)
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数值: 参数位置 从1开始
pstmt.setString(1, "火星人");
pstmt.setString(2, "456");
pstmt.setInt(3, 5);
//5.发送参数,执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行!");
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
//关闭资源
JDBCUtil.close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
}3、执行Delete语句
package com.rk.db.c_prepared;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import com.rk.db.utils.JDBCUtil;
/**
* 使用PreparedStatement执行Delete语句
* @author RK
*/
public class Demo03
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try
{
//1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
//2.准备预编译的sql
String sql = "DELETE FROM T_Persons WHERE Id=?";
//3.执行预编译sql语句(检查语法)
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.设置参数值: 参数位置 从1开始
pstmt.setInt(1, 5);
//5.发送参数,执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行!");
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
//关闭资源
JDBCUtil.close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
}4、执行Select语句
package com.rk.db.c_prepared;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import com.rk.db.utils.JDBCUtil;
/**
* 使用PreparedStatement执行Select语句
* @author RK
*/
public class Demo04
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try
{
//1.获取连接
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
//2.准备预编译的sql
String sql = "SELECT * FROM T_Persons";
//3.执行预编译sql语句(检查语法)
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4.执行sql语句,得到返回结果
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//5.输出
while(rs.next())
{
int id = rs.getInt("Id");
String userName = rs.getString("UserName");
String pwd = rs.getString("Pwd");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + userName + "\t" + pwd);
}
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
//关闭资源
JDBCUtil.close(conn, pstmt, rs);
}
}
}5、思维导图
相关文章推荐
- jdbc中的Statement和PreparedStatement接口对象
- JDBC 数据库常用连接 链接字符串
- JDBC连接Access数据库的几种方式介绍
- JDBC程序更新数据库中记录的方法
- JDBC 程序的常见错误及调试方法
- 在Java的JDBC使用中设置事务回滚的保存点的方法
- Java中使用JDBC操作数据库简单实例
- Java加载JDBC驱动程序实例详解
- JSP使用JDBC完成动态验证及采用MVC完成数据查询的方法
- JSP基于JDBC的数据库连接类实例
- JSP中使用JDBC访问SQL Server 2008数据库示例
- jsp+jdbc实现连接数据库的方法
- 解析jdbc处理oracle的clob字段的详解
- JDBC数据库的使用操作总结
- jdbc操作mysql数据库实例
- JSP使用JDBC连接MYSQL数据库的方法
- Java开发Oracle数据库连接JDBC Thin Driver 的三种方法
- java使用jdbc操作数据库示例分享
- JDBC之PreparedStatement类中预编译的综合应用解析
- JDBC常见问答
