【数据结构】处理哈希冲突的开链法(哈希桶)算法实现
2016-05-08 11:53
691 查看
实现哈希表时,我们常见的方法是线性探测、二次探测,这两个算法也很简单。若有兴趣,可以查看我的博客 http://10740184.blog.51cto.com/10730184/1771160。但是,这两个算法有一个共同点就是:空间利用率低。为什么这么说呢?线性探测、二次探测的高效性很大程度上要取决于它的载荷因子,载荷因子即:存放关键字个数/空间大小。
通过查阅资料,我发现,使用素数做除数可以减少哈希冲突(具体原因不详,大师专研的,发现很好用,就在这里分享给大家)。见下:
----素数表
// 使用素数表对齐做哈希表的容量,降低哈希冲突
const int _PrimeSize = 28;
static const unsigned long _PrimeList [_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
开链法(哈希桶)结构:
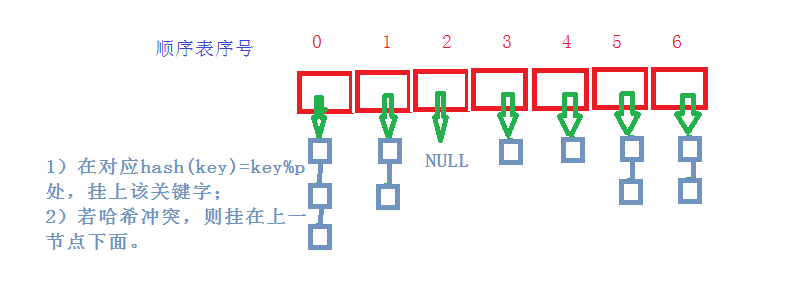
而哈希桶实现时,我们可以将载荷因子设成1.
代码如下:
通过查阅资料,我发现,使用素数做除数可以减少哈希冲突(具体原因不详,大师专研的,发现很好用,就在这里分享给大家)。见下:
----素数表
// 使用素数表对齐做哈希表的容量,降低哈希冲突
const int _PrimeSize = 28;
static const unsigned long _PrimeList [_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
开链法(哈希桶)结构:

而哈希桶实现时,我们可以将载荷因子设成1.
代码如下:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
template<class K,class V>
struct HashTableNode
{
K _key;
V _value;
HashTableNode* _next;
HashTableNode(const K& key,const V& value)
:_key(key)
, _value(value)
, _next(NULL)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class HashTable
{
public:
typedef HashTableNode<K,V> Node;
HashTable()
:_table(NULL)
, _size()
{}
size_t _HashFunc(const K& key)
{
//_table.size()表示哈希桶的空间大小
return key % _table.size();
}
//拷贝构造
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
//将哈希表ht拷贝给this
this->_table.resize(ht._table.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->_key, cur->_value);
tmp->_next = _table[i];
_table[i] = tmp;
this->_size++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
HashTable<K, V> operator=(const HashTable<K, V>& ht)
{
if (&ht != this)
{
//删除哈希表this
for (int i = 0; i < this->_table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* del = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
/*delete del;
del = NULL;*/
Remove(del->_key);
}
}
//将哈希表ht拷贝给this
this->_table.resize(ht._table.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->_key, cur->_value);
tmp->_next = _table[i];
_table[i] = tmp;
this->_size++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
return *this;
}
//赋值运算符重载的现代写法
HashTable<K, V> operator=(HashTable<K, V> ht)
{
if (&ht != this)
{
swap(_table, ht._table);
swap(_size, ht._size);
}
return *this;
}
~HashTable()
{
//删除哈希表ht
if (this->_table.size() !=0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this->_table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* del = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete del;
del = NULL;
}
}
}
}
//获取新的哈希表容量大小
size_t _GetnewSize()
{
static const int _PrimeSize = 28;
static const unsigned long _PrimeList[_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
for (int i = 0; i < _PrimeSize; i++)
{
if (_PrimeList[i]> _table.size())
{
return _PrimeList[i];
}
}
return _PrimeList[_PrimeSize - 1];
}
//给哈希桶扩容
void _ExpandCapacity()
{
//开辟新的更大容量的哈希表
size_t newSize = _GetnewSize();
vector<Node*> newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize);
//将每处顺序表上的单链表元素摘下来插入到新的顺序表上
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
int index = _HashFunc(tmp->_key);
//头插法插插节点
tmp->_next = newTable[index];
newTable[index] = tmp;
}
_table[i] = NULL;
}
_table.swap(newTable);
}
//插入关键字
bool Insert(const K& key,const V& value)
{
//检查载荷因子,考虑是否扩容
//哈希桶的载荷因子设置为1
if (_size == _table.size())
{
_ExpandCapacity();
}
//往顺序表的index处插入节点
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
Node* begin = _table[index];
while (begin)
{
//设计成不可出现重复元素
if (begin->_key == key)
{
return false;
}
begin = begin->_next;
}
//考虑到同一条单链表上,无所谓元素存放顺序,且较尾插简单。--》头插
Node* tmp = new Node(key, value);
tmp->_next =_table[index];
_table[index] = tmp;
_size++;
return true;
}
//查找关键字
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
int index = _HashFunc(key);
Node* cur = _table[index];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
//删除关键字
bool Remove(const K& key)
{
int index = _HashFunc(key);
Node* cur = _table[index];
Node* prev = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
break;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
if (cur)
{
if (cur == _table[index])
{
_table[index] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
}
delete cur;
cur = NULL;
--_size;
return true;
}
return false;
}
//打印哈希桶
void PrintHashTable()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
cout << i<<":" ;
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->_key << "->";
cur = cur->_next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _size;//数据个数
};
void TestHashTableBucket()
{
typedef HashTableNode<int, char> Node;
HashTable<int, char> ht;
ht.Insert(1, 'a');
ht.Insert(2, 'b');
ht.Insert(3, 'c');
ht.Insert(4, 'd');
ht.Insert(5, 'd');
ht.Insert(54, 'x');
ht.Insert(55, 'y');
ht.Insert(56, 'z');
ht.PrintHashTable();
/*Node* ret = ht.Find(5);
cout << ret->_value << endl;
ht.Remove(1);
ht.Remove(6);
ht.PrintHashTable();*/
/*HashTable<int, char> ht1(ht);
ht1.PrintHashTable();*/
HashTable<int, char> ht2;
ht2.Insert(54, 'x');
ht2.Insert(55, 'y');
ht2.Insert(56, 'z');
ht2.Insert(1, 'a');
ht2.Insert(2, 'b');
ht2.Insert(3, 'c');
ht2.Insert(4, 'd');
ht2.Insert(5, 'd');
ht2.PrintHashTable();
ht = ht2;
ht.PrintHashTable();
}
int main()
{
TestHashTableBucket();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 如何解决双网卡冲突
- C#数据结构之顺序表(SeqList)实例详解
- Lua教程(七):数据结构详解
- 解析从源码分析常见的基于Array的数据结构动态扩容机制的详解
- C#数据结构之队列(Quene)实例详解
- C#数据结构揭秘一
- C#数据结构之单链表(LinkList)实例详解
- 两个打印机服务spoolsv.exe存在冲突的解决方法
- 数据结构之Treap详解
- 用C语言举例讲解数据结构中的算法复杂度结与顺序表
- C#数据结构之堆栈(Stack)实例详解
- C#数据结构之双向链表(DbLinkList)实例详解
- JavaScript数据结构和算法之图和图算法
- setAttribute 与 class冲突解决
- 实例讲解避免javascript冲突的方法
- jQuery与其它库冲突的解决方法
- jQuery prototype冲突的2种解决方法(附demo示例下载)
- 解决jquery版本冲突的有效方法
- 快速解决jquery.touchSwipe左右滑动和垂直滚动条冲突
- 快速解决jQuery与其他库冲突的方法介绍
