数据结构之队列
2016-05-01 08:56
351 查看
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaituorensheng/archive/2013/02/28/2937865.html
队列特性:先进先出(FIFO)——先进队列的元素先出队列。来源于我们生活中的队列(先排队的先办完事)。

队列有下面几个操作:
InitQueue() ——初始化队列
EnQueue() ——进队列
DeQueue() ——出队列
IsQueueEmpty()——判断队列是否为空
IsQueueFull() ——判断队列是否已满
队列可以由数组和链表两种形式实现队列操作(c语言),下面仅以数组为例:
数组实现:
队列数据结构
InitQueue() ——初始化队列
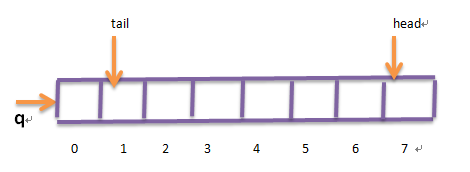
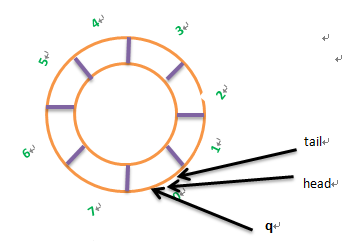
这样有个缺陷,空间利用率不高。采用循环队列:
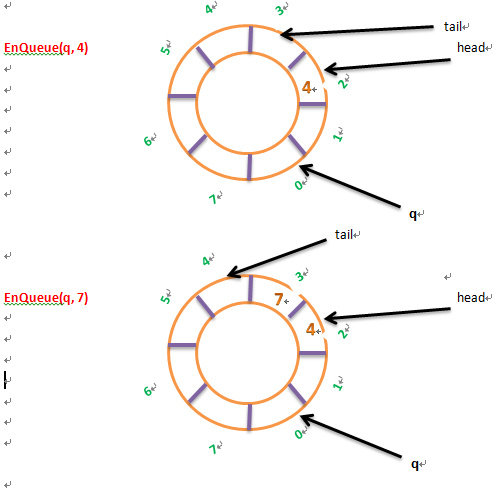
EnQueue() ——进队列
DeQueue() ——出队列
IsQueueEmpty()——判断队列是否为空
IsQueueFull()——判断队列是否已满
更多数据结构相关学习网址:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html
队列特性:先进先出(FIFO)——先进队列的元素先出队列。来源于我们生活中的队列(先排队的先办完事)。

队列有下面几个操作:
InitQueue() ——初始化队列
EnQueue() ——进队列
DeQueue() ——出队列
IsQueueEmpty()——判断队列是否为空
IsQueueFull() ——判断队列是否已满
队列可以由数组和链表两种形式实现队列操作(c语言),下面仅以数组为例:
数组实现:
队列数据结构
typedef struct queue
{
int queuesize; //数组的大小
int head, tail; //队列的头和尾下标
int *q; //数组头指针
}Queue;InitQueue() ——初始化队列
void InitQueue(Queue *q)
{
q->queuesize = 8;
q->q = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * q->queuesize); //分配内存
q->tail = 0;
q->head = 0;
}
这样有个缺陷,空间利用率不高。采用循环队列:

EnQueue() ——进队列
void EnQueue(Queue *q, int key)
{
int tail = (q->tail+1) % q->queuesize; //取余保证,当quil=queuesize-1时,再转回0
if (tail == q->head) //此时队列没有空间
{
printf("the queue has been filled full!");
}
else
{
q->q[q->tail] = key;
q->tail = tail;
}
}
DeQueue() ——出队列
int DeQueue(Queue *q)
{
int tmp;
if(q->tail == q->head) //判断队列不为空
{
printf("the queue is NULL\n");
}
else
{
tmp = q->q[q->head];
q->head = (q->head+1) % q->queuesize;
}
return tmp;
}IsQueueEmpty()——判断队列是否为空
int IsQueueEmpty(Queue *q)
{
if(q->head == q->tail)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}IsQueueFull()——判断队列是否已满
int IsQueueFull(Queue *q)
{
if((q->tail+1)% q->queuesize == q->head)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}更多数据结构相关学习网址:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html
相关文章推荐
- Java千百问_06数据结构(003)_什么是基本类型包装器
- 回溯法 -数据结构与算法
- 回溯法 -数据结构与算法
- 二叉树遍历 - 数据结构
- 二叉树遍历 - 数据结构
- 数据结构- 串的模式匹配算法:BF和 KMP算法
- 数据结构-栈和队列
- 数据结构- 串的模式匹配算法:BF和 KMP算法
- 数据结构-栈和队列
- 数据结构-线性表
- 数据结构-线性表
- 算法基础 - 线段树
- 数据结构算法——单链表的应用
- 2016 UESTC Training for Data Structures B - 卿学姐与基本法 自己构建了一个和堆有点像的数据结构
- redis数据结构--下
- 广义表的建立与求深度
- 数据结构之队列和栈学习笔记
- [数据结构]Priority_queue(优先级队列)
- [数据结构]Radix_sort(MSD)
- 数据结构与逻辑代码(一)
