java线程(5)——线程池(上)
2016-04-15 16:17
573 查看
引入:
在之前的例子中,我们需要使用线程时就直接去创建一个线程,这样既不浪费资源又十分方便。但如果我们需要创建多个并发的线程,而且短时间执行就结束了,如果还用之前的方式,就会大大降低效率和性能了。
因此就引入了线程池。
在java线程池中,涉及到的有Executors、Executor、ExecutorService等,Executor接口表示线程池,ExecutorService负责管理线程池,Executors负责创建生成ExecutorService的实例,提供了线程池的简单实现。他们相互之间的关系如下:
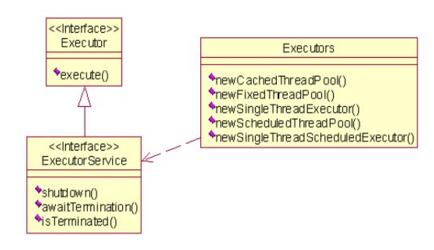
1、Executor
在上面的例子中,我们就调用了execute()方法。execute()方法用来执行Runnable类型的任务,它的子接口是ExecutorService。
ExecutorService负责管理线程池,提供了包括关闭、提交等一系列的操作。
2、Executors
Executors类负责生成各种类型的线程池的实例,但主要有三种:固定线程池、可变和单任务线程池。其他详细的方法可参见下面:
我们先通过简单的例子看一下这三种线程池的不同。
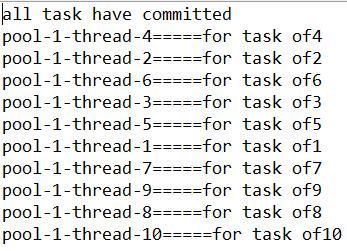
1)固定线程池
执行结果:

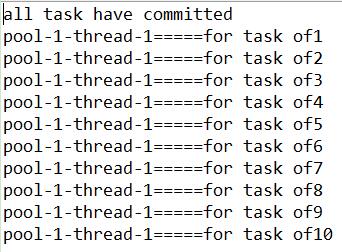
2)缓存(不固定)线程池
修改一行代码,创建缓存可变长的线程池。执行结果为
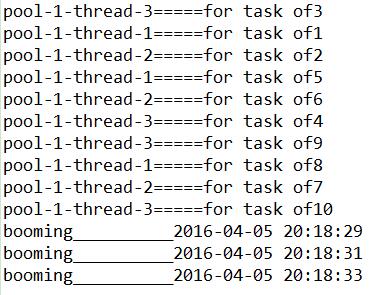
3)单任务线程池
在该线程池中只有一个线程执行。虽然看起来跟单线程没什么区别,但他的优点是,有替补线程可以随时补上。如果该单线程出现问题,立马就会有一个线程继续执行,安全性大大提高。执行结果如下:
4)延迟连接池
其中scheduleAtFixedRate方法参数:
时间单位为秒,初始延迟为3秒,每隔2秒执行一次。执行结果为:
使用:
1)直接使用Executors
上面的例子都是直接通过调用Executors中的静态方法实现创建线程池的,很容易理解。
再看一下具体是如何创建线程池的,以其中一种为例:
在ThreadPoolExecutor中,需要传入参数Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),他是默认的线程工厂。
DefaultThreadFactory依旧在Executors类中。
在创建线程池之后,返回的threadpool只有部分参数信息,包括最大线程数、线程名称等,此时只有main主线程。
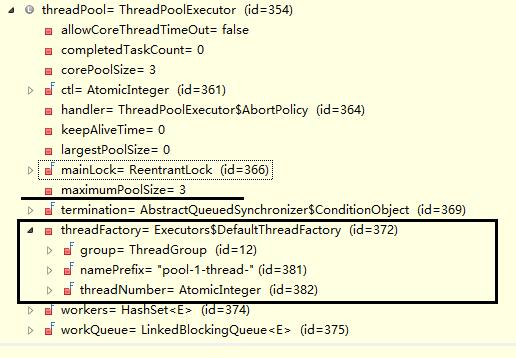
当执行threadPool.execute()时,会调用上述的默认线程工厂中的newThread方法,创建线程。
2)直接使用ThreadPoolExecutor类创建
这种方式并不推荐使用,因为对于开发者来说比较困难,也不好管理和维护。但这种方式可以做到对线程池更细致更自由化的控制。
这块内容是线程创建的核心,我们下篇继续介绍。
在之前的例子中,我们需要使用线程时就直接去创建一个线程,这样既不浪费资源又十分方便。但如果我们需要创建多个并发的线程,而且短时间执行就结束了,如果还用之前的方式,就会大大降低效率和性能了。
因此就引入了线程池。
在java线程池中,涉及到的有Executors、Executor、ExecutorService等,Executor接口表示线程池,ExecutorService负责管理线程池,Executors负责创建生成ExecutorService的实例,提供了线程池的简单实现。他们相互之间的关系如下:

1、Executor
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}在上面的例子中,我们就调用了execute()方法。execute()方法用来执行Runnable类型的任务,它的子接口是ExecutorService。
ExecutorService负责管理线程池,提供了包括关闭、提交等一系列的操作。
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
void shutdown();
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
boolean isShutdown();
boolean isTerminated();
//提交
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
......
}2、Executors
Executors类负责生成各种类型的线程池的实例,但主要有三种:固定线程池、可变和单任务线程池。其他详细的方法可参见下面:
public class Executors {
//1、固定大小线程池
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
//2、可变尺寸线程池
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
//3、单任务线程池
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
//4、延迟连接池
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
//5、单任务延迟连接池
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
}我们先通过简单的例子看一下这三种线程池的不同。
1)固定线程池
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 固定线程池:创建一个线程池,有三个线程
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
final int task = i;
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "=====" + "for task of" + task);
}
});
}
System.out.println("all task have committed");
}执行结果:

2)缓存(不固定)线程池
ExecutorService threadPool=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
修改一行代码,创建缓存可变长的线程池。执行结果为

3)单任务线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
在该线程池中只有一个线程执行。虽然看起来跟单线程没什么区别,但他的优点是,有替补线程可以随时补上。如果该单线程出现问题,立马就会有一个线程继续执行,安全性大大提高。执行结果如下:

4)延迟连接池
// 启动定时器
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3).scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("booming__________"
+ getTime());
}
}, 3, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);其中scheduleAtFixedRate方法参数:
ScheduledFuture<?> java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
时间单位为秒,初始延迟为3秒,每隔2秒执行一次。执行结果为:

使用:
1)直接使用Executors
上面的例子都是直接通过调用Executors中的静态方法实现创建线程池的,很容易理解。
再看一下具体是如何创建线程池的,以其中一种为例:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}在ThreadPoolExecutor中,需要传入参数Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),他是默认的线程工厂。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}DefaultThreadFactory依旧在Executors类中。
/**
* The default thread factory默认线程工厂
*/
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
//线程组
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
//构造方法
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
//拼接线程名称:如"pool-1-thread-1"
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
//重写newThread方法
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
//如果是守护进程,置为false
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
//设置默认优先级
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}在创建线程池之后,返回的threadpool只有部分参数信息,包括最大线程数、线程名称等,此时只有main主线程。

当执行threadPool.execute()时,会调用上述的默认线程工厂中的newThread方法,创建线程。
2)直接使用ThreadPoolExecutor类创建
这种方式并不推荐使用,因为对于开发者来说比较困难,也不好管理和维护。但这种方式可以做到对线程池更细致更自由化的控制。
这块内容是线程创建的核心,我们下篇继续介绍。
相关文章推荐
- C#线程间不能调用剪切板的解决方法
- C#多线程学习之(四)使用线程池进行多线程的自动管理
- C#线程同步的三类情景分析
- C#获取进程或线程相关信息的方法
- C#停止线程的方法
- C#子线程更新UI控件的方法实例总结
- C#线程队列用法实例分析
- C++使用CriticalSection实现线程同步实例
- c++线程池实现方法
- 基于C++实现的线程休眠代码
- C语言实现支持动态拓展和销毁的线程池
- c++实现简单的线程池
- VB读取线程、句柄及写入内存的API代码实例
- C#网络编程基础之进程和线程详解
- C#通过Semaphore类控制线程队列的方法
- C#多线程处理多个队列数据的方法
- C#实现线程安全的简易日志记录方法
- C#中线程同步对象的方法分析
- ASP.NET线程相关配置
- 浅析linux环境下一个进程最多能有多少个线程
