20145219 《Java程序设计》第03周学习总结
2016-03-19 22:11
405 查看
20145219 《Java程序设计》第03周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
基本类型和类类型基本类型:第三章中讲述的那几种,
short、
long、
int、
byte、
double、
char、
boolean等这些。
类类型:指
class类型,把一些基本的类型和方法整合到一起,体现出了类的封装特性,便于实现模块化。
对象和类:使用Java撰写程序几乎都在使用对象,要产生对象必须先定义类,类是对象的设计图,对象是类的实例。
定义类
程序示例
class Clothes
{
String color;
char size;
}
public class Field
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes sun = new Clothes();
Clothes spring = new Clothes();
sun.color = "red";
sun.size = 'S';
spring.color = "green";
spring.size = 'M';
System.out.printf("sun(%s,%c)%n",sun.color,sun.size);
System.out.printf("spring(%s,%c)%n",spring.color,spring.size);
}
}
使用
class关键字定义类,在
Field.java中定义了两个类,一个是非公开的
Clothes类,另一个是公开(public)的
Field类(文档中的主文档名必须与公开类名称一致)。
Clothes类中定义了
color和
size两个变量,叫作定义两个值域成员或定义两个数据对象成员。
Clothes sun = new Clothes()为将sun名称参考至新建对象,其中
Clothes sun叫作声明参考名称、参考变量或直接叫参考,
=是指定,
new关键字是建立对象实例。
有几个类就会产生几个
.class文档。
函数
函数又称方法,是定义在类中的具有特定功能的一段独立的小程序。
格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 函数名(参数类型 形式参数1,参数类型 形式参数2,...)
{
执行语句;
return 返回值;
}返回值类型函数运行后结果的数据类型,
return结束函数,
返回值返回给调用处,
形式参数变量,存储调用函数时传递给函数的实际参数,
实际参数传递给形式参数的具体数值。
不用返回值的函数可以用void声明。
程序示例
class Clothes2
{
String color;
char size;
Clothes2(String color, char size)
{
this.color=color;
this.size=size;
}
}
public class Field2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes2 sun = new Clothes2("red",'S');
Clothes2 spring = new Clothes2("green",'M');
System.out.printf("sun(%s,%c)%n",sun.color,sun.size);
System.out.printf("spring(%s,%c)%n",spring.color,spring.size);
}
}
this是将这个参数的值指定给这个参数。
注意:函数中可以调用函数,但是不能在函数的内部再定义新函数。
标准类
标准API可以省去撰写程序时重新打造基础的需求,包名为java开头的类表示标准API提供的类。
java.util.Scanner取得用户输入
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Guess
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
int number = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
int guess;
do
{
System.out.printf("猜数字(0~9):");
guess = scanner.nextInt();
}
while(guess != number);
System.out.println("猜中了...XD");
}
}
import java.util.Scanner告诉程序你想偷懒,这样不用每次使用
Scanner都输入前面的
java.util.。
nextInt()方法会看看标准输入中有没有下一个字符串,有的话会尝试将之剖析为int型。
next()是直接取得上一个字符串,
nextLine()是取得用户输入的整行文字。
java.math.BigDecimalJava遵守IEEE754浮点数运算,用分数与指数来表示小数,会产生浮点数误差,而
java.math.BigDecimal可以解决这一点。
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class DecimalDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BigDecimal operand1 = new BigDecimal ("1.0");
BigDecimal operand2 = new BigDecimal ("0.8");
BigDecimal result = operand1.subtract(operand2);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
BigDecimal提供
plus()、
substract()、
multiply()、
divide()等方法,可以进行加减乘除等运算。还有
equals()可以比较两个BigDecimal实质上是否相等。
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class DecimalDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BigDecimal o1 = new BigDecimal ("0.1");
BigDecimal o2 = new BigDecimal ("0.1");
BigDecimal o3 = new BigDecimal ("0.1");
BigDecimal result = new BigDecimal("0.3");
if(o1.add(o2).add(o3).equals(result))
{
System.out.println("等于0.3");
}
else
{
System.out.println("不等于0.3");
}
}
}
打包:使用Long、Integer、Double、Float、Boolean、Byte等类来打包基本类型,将基本类型当作对象操作。J2SE5.0后可以自动装箱、拆箱。
程序示例
public class IntegerDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int data1 = 10;
int data2 = 20;
Integer w1 = new Integer(data1);
Integer w2 = new Integer(data2);
System.out.println(data1/3);
System.out.println(w1.doubleValue()/3);
System.out.println(w1.compareTo(w2));
}
}
数组
是同一类型数据的集合,是一个容器。它会自动从0开始编号。
格式:
元素类型[] 数组名=new 元素类型[元素个数或数组长度];
元素类型[] 数组名=new 元素类型[]{元素,元素,...};
元素类型[] 数组名={元素,元素,...};数组一被定义即有默认初始值。
程序示例
public class Score
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores={88,81,74,68,78,76,77,85,95,93};
for(int i=0;i<scores.length;i++)
{
System.out.printf("学生分数:%d %n",scores[i]);
}
}
}
增强式for循环
for(int score:scores)
{
System.out.printf("学生分数:%d %n",scores);
}
二维数组
public class XY
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] cords={
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
for(int[] row : cords)
{
for(int value : row)
{
System.out.printf("%2d",value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
使用
java.util.Arrays的
fill()方法改变数组的默认初始值
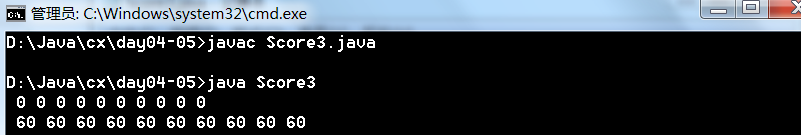
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Score3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[10];
for(int score : scores)
{
System.out.printf("%2d",score);
}
System.out.println();
Arrays.fill(scores,60);
for(int score : scores)
{
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
}
}
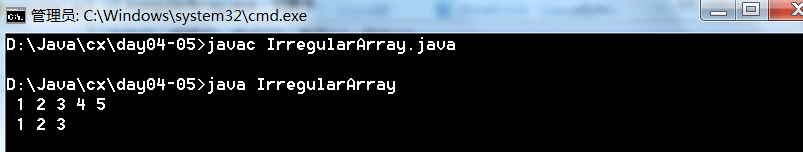
二维数组也可以是不规则的数组
public class IrregularArray
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] arr=new int[2][];
arr[0]=new int[] {1,2,3,4,5};
arr[1]=new int[] {1,2,3};
for(int[] row:arr)
{
for(int value:row)
{
System.out.printf("%2d",value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
数组复制
-浅层复制:仅将每个索引处所参考的对象给复制的参考,并没有复制出对象。
System.arraycopy()和
Arrays.copyof()都是执行的浅层复制。
Arrays.copyof()的第二个参数是新建立的数组长度。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyArray
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores1 = {88,81,74,68,78,76,77,85,95,93};
int[] scores2 = Arrays.copyOf(scores1,scores1.length);
for(int score : scores2)
{
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
System.out.println();
scores2[0] = 99;
for(int score : scores1)
{
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
}
}
System.arraycopy()中的五个参数分别是来源数组、来源起始索引、目的数组、目的起始索引、复制长度。
-深层复制:连同对象一同复制,必须自行操作。
class Clothes2
{
String color;
char size;
Clothes2(String color, char size)
{
this.color=color;
this.size=size;
}
}
public class DeepCopy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes2[] c1 = {new Clothes2("red",'S'),new Clothes2("green",'M')};
Clothes2[] c2 = new Clothes2[c1.length];
for(int i = 0; i < c1.length; i++)
{
Clothes2 c = new Clothes2(c1[i].color, c1[i].size);
c2[i] = c;
}
c1[0].color = "yellow";
System.out.println(c2[0].color);
}
}
字符串
字符串的本质是打包字符数组的对象,是
java.lang.String类的实例。
length()是取得字符串长度,
charAt()是取得字符串中某个字符,
toUpperCase()是将原本小写的字符串内容转为大写的字符串内容。
用户输入程序,求总和
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Sum
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long sum = 0;
long number = 0;
do
{
System.out.print("input numbers:");
number = Long.parseLong(scanner.nextLine());
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0);
System.out.println("sum:"+sum);
}
}
用 "" 写下的字符串称为字符串常量,使用 + 连接字符串会产生新的String实例。
封装
不用重复撰写对象初始化流程。构造函数就是在实现对象初始化流程的封装。
用
private定义私有数据类型。
类语法
public为公开类,在构造函数上声明public表示其他包中的类可以直接调用这个构造函数,在方法上声明public表示其他包的方法可以直接调用这个方法。
只有编译程序自动加入的构造函数,才成为默认构造函数。如果自行撰写无参数、没有内容的构造函数就不是默认构造函数了。
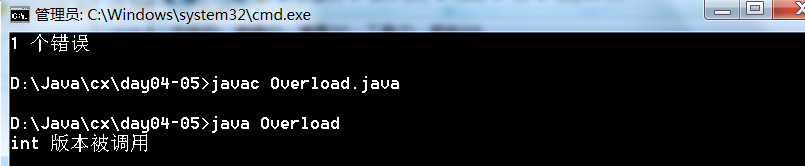
重载
在同一个类中,允许存在一个以上的同名函数,只要他们的参数个数或者参数类型不同即可。
程序示例
class Some
{
void someMethod(int i)
{
System.out.println("int 版本被调用");
}
void someMethod(Integer integer)
{
System.out.println("Integer 版本被调用");
}
}
public class Overload
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Some s = new Some();
s.someMethod(1);
}
}
this
除了被声明为static的地方外,this关键字可以出现在类中任何地方,在构造函数与对象数据成员同名时,可用this加以区别。
程序示例
class Other{
{
System.out.println("对象初始区块");
}
Other() {
System.out.println("Other() 构造函数");
}
Other(int o) {
this();
System.out.println("Other(int o) 构造函数");
}
}
public class Object {
public static void main(String[] args){
new Other(1);
}
}
static类成员
被声明为static的成员,不会让个别对象拥有,而是属于类,将类名称作为名称空间。
程序示例
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.System.in;
import static java.lang.System.out;
public class ImportStatic
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(in);
out.print("请输入姓名:");
out.printf("%s 你好!%n",scanner.nextLine());
}
}
其它
不定长度自变量:使用不定长度自变量时,方法上声明的不定长度参数必须是参数列最后一个。
内部类:在类中再定义类。
传值调用
public class Call
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Customer c1=new Customer("Justin");
some(c1);
System.out.println(c1.name);
Customer c2=new Customer("Justin");
other(c2);
System.out.println(c2.name);
}
static void some(Customer c)
{
c.name="Jhon";
}
static void other(Customer c)
{
c=new Customer("Bill");
}
}
class Customer
{
String name;
Customer(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
}
完成第一次代码托管

教材学习中的问题和解决过程
问题:书上p148的传值调用程序,我还是不太懂为什c2的名字没有改变?解决方法:待解决......
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
问题:在编译书上p96的Score程序时,我错将System.out.printf("学生分数:%d %n",scores[i])打成System.out.println("学生分数:%d %n",scores[i]),结果弹出来很多错误。在上一章中书上说System.out.printf是按格式输出,而
System.out.println是输出后换行,如果仅仅只是换行的差别的话那为什么用后面一种不行呢?我也有试着将输出中的
%n删去 ,但依旧是错的。

解决方法:还没解决......
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
这一周的任务明显比上一周多,上一周的知识和C语言很像,有了大一的基础能够比较快的理解和掌握,但是这一周概念性的东西很多,知识的盲点也就体现出来了,需要静下心来反复读才能明白。这一周最大的收获就是学会了代码托管,而且帮助宿舍的同学完成了第一次代码托管,很有成就感。学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 150/150 | 2/2 | 15/15 | 学会搭建Java环境,学会写Hello World小程序 |
| 第二周 | 500/500 | 3/3 | 35/35 | 掌握IDE的使用方法,学会Java的基本语法规则 |
| 第三周 | 900/900 | 4/4 | 70/70 | 学会代码托管,学习了类类型、面向对象、函数等知识 |
参考资料
Java学习笔记(第8版)《Java学习笔记(第8版)》学习指导
...
相关文章推荐
- Java实现Mongo嵌套查询
- Java面向对象05-抽象方法,抽象类和接口
- java图像压缩
- NIIT实训 java笔记--3.11
- Struts和Hibernate整合中分页实现解析
- EL表达式使用了java保留关键字
- Java Map
- 网页页面自动刷新的3中实现方式
- Java单例你所不知道的事,与Volatile关键字有染
- 创建第一个Spring MVC程序helloworld
- eclipse不能新建server
- 教你如何使用Java泛型
- Java - 常量 - 变量
- Spring相关jar说明
- path、classpath、JAVA_HOME的作用
- Java大牛养成记(3)——SSH框架
- 【转】Java经典问题:传值与传引用?
- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError错误
- NIIT 实训java笔记--3.10
- Java开发编程基础-1
