【数据结构】邻接表表示法的图的深度广度优先遍历递归和非递归遍历
2016-02-02 18:41
801 查看
图有多种表示方法,在 《无向邻接矩阵表示法的图的遍历》这篇文章中,讲了邻接矩阵表示法的遍历,这篇文章中将讨论邻接表表示法的图的遍历。邻接矩阵表示法在稀疏图(边少的图中)中比邻接矩阵表示法节省内存空间。不管以何种方式来表示,他们的遍历顺序是没有改变的。继续贴上图,方便我们理解。
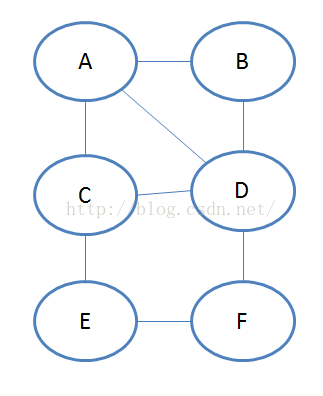
上面的图可以用下面的邻接表表示。
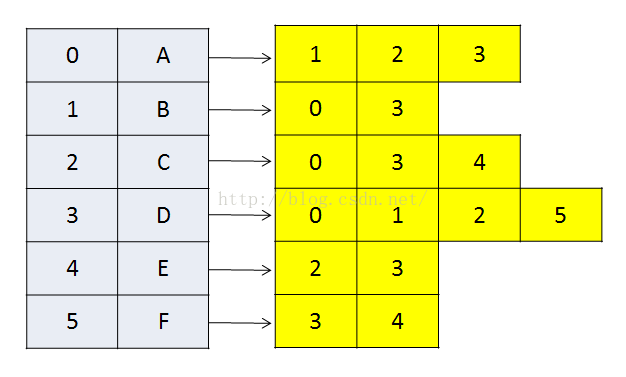
左边的灰色区域表示各个顶点,我们可以用数组来表示,右边的黄色区域代表着各个顶点与其他顶点的关系。
邻接表表示法深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历代码如下:

上面的图可以用下面的邻接表表示。

左边的灰色区域表示各个顶点,我们可以用数组来表示,右边的黄色区域代表着各个顶点与其他顶点的关系。
邻接表表示法深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历代码如下:
package 邻接表图的遍历;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
/**
* @author zyw
*无向邻接表表示法的图的遍历
*/
private static class Vertex{
String data;//顶点的数据
int idx;//顶点的索引
int[] vertexs;//存储与该顶点所连的顶点
}//图的顶点的定义,赋值就不要修改他的字段的值
private static Vertex[] list=new Vertex[6];
/**
* 无向邻接表表示法图的深度优先遍历
* @param vertex 开始遍历的顶点
*/
private static void DFS(Vertex vertex) {
Stack<Vertex> stack=new Stack<Vertex>();//深度优先遍历用栈存储
Vertex tempVertex,firstVertex = null;
boolean[] isVisit=new boolean[6];//用于标记每个顶点是否被访问过
Arrays.fill(isVisit,false);
stack.push(vertex);
boolean isFirst=false;
while(!stack.empty())
{
tempVertex=stack.pop();
//如果没有被访问过才访问
if(!isVisit[tempVertex.idx]){
isVisit[tempVertex.idx]=true;
System.out.print(tempVertex.data+" ");
}
isFirst=true;
for(int i=0;i<tempVertex.vertexs.length;i++)
{
if(!isVisit[list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs[i]])
{
if(isFirst)
{
//记录第一个节点
firstVertex=list[list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs[i]];
isFirst=false;
}else{
//表中非第一个节点入栈
//请注意这个长长的数据访问
stack.push(list[list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs[i]]);
}
}
}
//第一个节点最后入栈
if(!isVisit[firstVertex.idx])
{
stack.push(firstVertex);
}
}
}
/**
* 无向邻接表表示法图的广度优先遍历
* @param vertex 开始遍历的顶点
*/
private static void BFS(Vertex vertex) {
Queue<Vertex> queue=new LinkedList<Vertex>();//广度优先遍历用队列存储
boolean[] isVisit=new boolean[6];//用于标记每个顶点是否被访问过
Arrays.fill(isVisit,false);
Vertex tempVertex;
queue.offer(vertex);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
tempVertex=queue.poll();
if(!isVisit[tempVertex.idx])
{
isVisit[tempVertex.idx]=true;
System.out.print(tempVertex.data+" ");
}
for (int i = 0; i < list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs.length; i++) {
if(!isVisit[list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs[i]]){
//请注意这个长长的数据访问
queue.offer(list[list[tempVertex.idx].vertexs[i]]);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 主函数
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
create();
System.out.println("无向邻接表表示的图的深度优先遍历");
DFS(list[0]);
System.out.println("\n无向邻接表表示的图的广度优先遍历");
BFS(list[0]);
}
/**
* 构造无向邻接表表示法图
*/
private static void create() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
list[i]=new Vertex();
list[i].idx=i;
}
list[0].vertexs=new int[]{1,2,3};
list[0].data="A";
list[1].vertexs=new int[]{0,3};
list[1].data="B";
list[2].vertexs=new int[]{0,3,4};
list[2].data="C";
list[3].vertexs=new int[]{0,1,2,5};
list[3].data="D";
list[4].vertexs=new int[]{2,3};
list[4].data="E";
list[5].vertexs=new int[]{3,4};
list[5].data="F";
}
}
相关文章推荐
- 【数据结构】邻接矩阵表示法的图的深度广度优先遍历递归和非递归遍历
- nginx学习六 高级数据结构之双向链表ngx_queue_t
- 数据结构之链表队列基本操作
- [数据结构与算法分析] 链表的游标实现
- [数据结构与算法分析] 单链表基本操作的实现
- [数据结构与算法分析] 求连续子数组的最大和问题
- 数据结构:JavaScript实现散列
- 数据结构之链式栈的构建
- [数据结构与算法分析] 链表的游标实现
- 学习笔记------数据结构(C语言版)栈应用 行编辑程序
- 数据结构图文解析之:栈的简介及C++模板实现
- linux内核数据结构之kfifo
- 2015年大二上-数据结构-图-2-(1)-Prim算法
- 小蚂蚁学习数据结构(28)——题目——顺序栈的遍历输出
- SICP 习题 (2.7) 解题总结 : 定义区间数据结构
- 数据结构与算法——二叉搜索树的操作集(C语言)
- 数据结构——树
- 【数据结构学习笔记】——根据中缀表达式构建二叉树并输出
- [数据结构与算法分析] 单链表基本操作的实现
- 数据结构《17》---- 自己主动补齐之《二》----Ternary Search Tree
