SpringData学习笔记
2016-02-02 11:32
441 查看
使用Spring Data JPA开发步骤
1. 导入相关jar包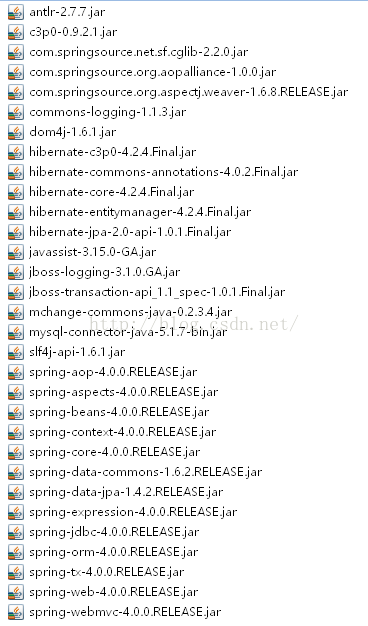
2. 配置applicationContext.xml配置文件
1) 配置数据源

2) 配置JPA的EntityManagerFactory

3) 配置事务管理器

4) 配置支持注解的事务

5) 配置SpringData
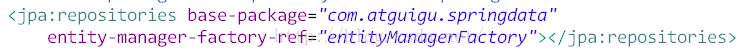
3. 编写实体类对象
4. 编写抽象接口:继承Repository接口,或继承Repository系列接口。在这个接口中定义抽象方法。
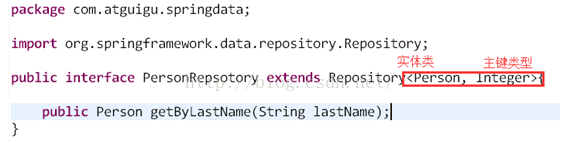
声明一个方法。
5. 使用:直接调用接口方法即可查询数据库获得结果。
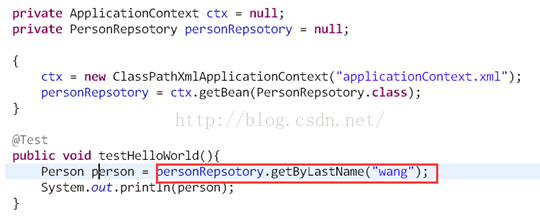
Repository接口
1. Repository是一个标识接口,即是一个空接口不提供任何方法,开发者需要在自己敬意的接口中声明需要的方法。2. 继承Repository的接口,则该接口会被IOC容器识别为一个Repository Bean纳入到IOC容器中,进而可以在改接口中定义满足一定规范的方法。
3. 与继承 Repository 等价的一种方式,就是在持久层接口上使用 @RepositoryDefinition 注解,并为其指定 domainClass 和 idClass 属性。如下两种方式是完全等价的
Repository子接口
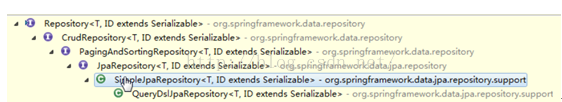
1. Repository: 仅仅是一个标识,表明任何继承它的均为仓库接口类。2. CrudRepository: 继承 Repository,实现了一组 CRUD 相关的方法。
3. PagingAndSortingRepository: 继承 CrudRepository,实现了一组分页排序相关的方法。
4. JpaRepository: 继承PagingAndSortingRepository,实现一组 JPA 规范相关的方法。
5. 自定义的 XxxxRepository 需要继承 JpaRepository,这样的 XxxxRepository 接口就具备了通用的数据访问控制层的能力。
6. JpaSpecificationExecutor: 不属于Repository体系,实现一组 JPA
Criteria查询相关的方法
Repository中方法定义规范
1. 查询方法以find|read|get开头。2. 涉及条件时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接。其中条件属性首字母大写。
例如:定义一个 Entity 实体类
class User{
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
}
使用And条件连接时,应这样写:
findByLastNameAndFirstName(String lastName,StringfirstName);
1) 条件的属性名称、个数要与参数的位置、个数一一对应。
2) 支持的关键字
| 关键字 | 方法名 | 条件 |
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | …where x.lastname=? and x.firstname=? |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname=? and x.firstname=? |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | …where x.startDate between ? and ? |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | …where x.age < ? |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | …where x.age > ? |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | …where x.startDate > ? |
| Before | findByStartDateBafore | …where x.startDate < ? |
| IsNull | findByAgelsNull | …where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(is)NotNull | …where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | …where x.firstname like ? |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameStartingWith | …where x.firstname not like ? |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | …where x.firstname like ? |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | …where x.firstname like ? |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | …wherex.firstname like ? |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | …where .age=? orser by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | …where x.lastname<>? |
| In(NotIn) | findByAge(Not)In | …where x.age (not) in ? |
| True | findByActive True() | …where x.active = true |
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse | …where x.active = false |
3. 支持属性的级联查询。
4. 若当前类有符合条件的属性,则优先使用,而不使用级联属性。若需要使用级联属性时,则属性之间使用“_”进行连接。
使用@Query注解定义Repository中方法
1. 使用@Query自定义查询:将查询直接在相应的接口方法中声明。@Query("Select c form Customer c where c.cunstomerId=?1")
Customer testGetCustomerId(Integer id);
2. 参数传递:索引参数和命名参数
1) 索引参数如下所示,索引值从1开始,查询中”?X”个数需要与方法定义的参数个数相一致,并且顺序也要一致。
@Query("Select p from Person p where p.lastName=?1 And p.email=?2")
List<Person> testQueryAnnotationParams(String lastName,String email);
2) 命名参数(推荐使用这种方式):可以定义好参数名,赋值时采用@Param("参数名"),而不用管顺序。
@Query("Select p from Person p where p.firstName=:firstname or p.lastName=:lastName")
List<Person> testQueryAnnotationParams(@Param("lastname") String lastName,@Param("firstname")String firstname);
3) LIKE关键字:
a) 后面的参数需要前面或者后面加 %
b) 这样在传递参数值的时候就可以不加 %
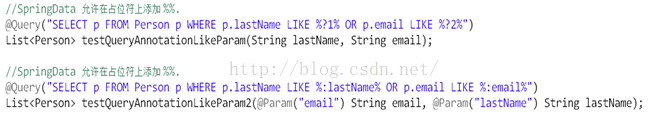
3. 使用@Query进行本地SQL查询

@Modifying注解和事务
1. 执行更新操作用:@Query 与 @Modifying 这两个 annotation一起声明。@Modifying
@Query("UPDATE Customer c SET c.customerName=?1")
int updateCustomerName(String cn);
1) 方法的返回值应该是 int,表示更新语句所影响的行数
2) 在调用的地方必须加事务,没有事务不能正常执行
Repository子接口
CurdRepository接口
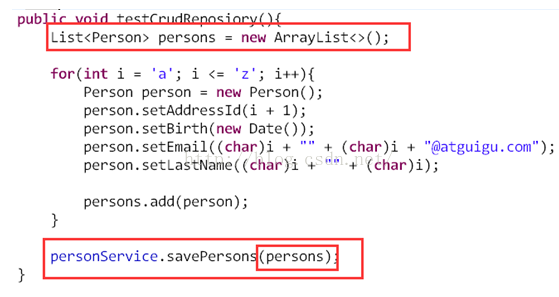
1. 作用:CurdRepository接口提供了最基本的对实体类的增删改查操作。1) T save(T entity);//保存单个实体
2) Iterable<T>save(Iterable<? extends T> entities);//保存集合
3) T findOne(ID id);//根据id查找实体
4) boolean exists(ID id);//根据id判断实体是否存在
5) Iterable<T> findAll();//查询所有实体,不用或慎用!
6) long count();//查询实体数量
7) void delete(ID id);//根据Id删除实体
8) void delete(T entity);//删除一个实体
9) void delete(Iterable<?extends T> entities);//删除一个实体的集合
10) void deleteAll();//删除所有实体,不用或慎用!
2. 实现
1) 接口继承CurdRepository。
2) 使用CurdRepository接口方法
PageingAndSortingRepository接口
1. 作用:该接口提供了分页与排序功能1) Iterable<T> findAll(Sortsort); //排序
2) Page<T> findAll(Pageablepageable); //分页查询(含排序功能)
2. Pageable接口
1) Pageable接口通常使用其PageRequest实现类。在该类中封装了需要分页的信息。初始化参数如下:
a) page:要查询的页号。
b) size:每一页的大小。
c) sort:排序规则。
2) Sort:排序的相关规则的信息封装在Sort类中。参数类型Order。
3. 实例
1) 继承PageingAndSortingRepository接口。
2)

JpaRepository接口
1. 作用:1) List<T> findAll(); //查找所有实体
2) List<T> findAll(Sortsort); //排序、查找所有实体
3) List<T>save(Iterable<? extends T> entities);//保存集合
4) void flush();//执行缓存与数据库同步
5) T saveAndFlush(T entity);//强制执行持久化
6) voiddeleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);//删除一个实体集合
JpaSpecificationExecutor接口
1. 特点:不属于Repository体系,实现一组 JPA Criteria 查询相关的方法 。
2. 作用:实现带条件的分页。
3. 分页的使用:findAll(Specification<T>,Pageable),参数说明:
1) Specification:封装了查询的查询条件。
2) Pageable:封装了请求分页的信息:如pageNo,pageSize,Sort
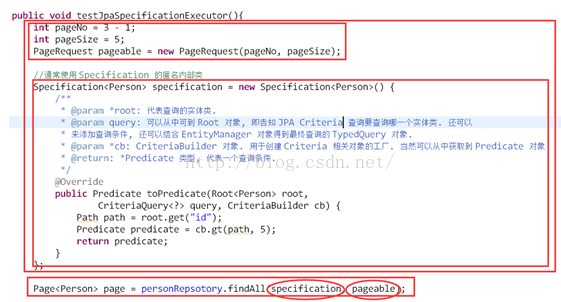
4. Specification:封装 JPA Criteria 查询条件。通常使用匿名内部类的方式来创建该接口的对象
1) 使用Specification<Person>()匿名内部类。
2) 内部方法:toPredicate(Root<Person> root, CriteriaQuery<?>query, CriteriaBuilder cb)
a) root:代表要查询的实体类。
b) query: 可以从中得到 Root 对象, 即告知 JPACriteria 查询要查询哪一个实体类。还可以来添加查询条件, 还可以结合 EntityManager 对象得到最终查询的 TypedQuery 对象。
c) cb: CriteriaBuilder 对象. 用于创建 Criteria相关对象的工厂. 当然可以从中获取到 Predicate 对象。
d) 返回值Predicate 类型, 代表一个查询条件。
5. 实例:
相关文章推荐
- 一个jar包里的网站
- 一个jar包里的网站之文件上传
- 一个jar包里的网站之返回对媒体类型
- Spring整合Quartz(JobDetailBean方式)
- Spring整合Quartz(JobDetailBean方式)
- 模拟Spring的简单实现
- spring+html5实现安全传输随机数字密码键盘
- Spring中属性注入详解
- SpringMVC框架下JQuery传递并解析Json格式的数据是如何实现的
- struts2 spring整合fieldError问题
- spring的jdbctemplate的crud的基类dao
- 读取spring配置文件的方法(spring读取资源文件)
- Spring Bean基本管理实例详解
- java实现简单美女拼图游戏
- 详解Java的Spring框架中的事务管理方式
- 解析Java的Spring框架的BeanPostProcessor发布处理器
- Java开发框架spring实现自定义缓存标签
- java基本教程之线程休眠 java多线程教程
- JSP开发中在spring mvc项目中实现登录账号单浏览器登录
- spring boot实战之内嵌容器tomcat配置
