spring DI/IOC核心模拟程序
2016-01-22 16:05
507 查看
DI/IOC概述:
依赖注入/控制反转。某一个类中需要使用其他类中的方法来实现业务时,一般采用在前者中声明后者并实例化,然后用后者的实例在前者中调用后者的方法,这种情形下,前者依赖后者,被依赖类的对象生灭由依赖类控制,这种做法耦合度较高。在使用spring的情形下,通过反射机制,类统一在spring中注册,被依赖对象统一由spring注入到依赖对象中。依赖注入和控制反转是站在不同的角度对同一动作的不同描述,DI,被依赖对象由spring容器实例化并注入到依赖对象中,IOC,被依赖对象的生灭由依赖对象控制转换为spring容器。案例:
有三个类,Iron(铁),Axe(斧子),HumanBeing(人类),人类类依赖斧子类,斧子类依赖铁类。Iron:
package com.sunsharing.di;/**
* Created by baich on 2016/1/22.
*/
public class Iron {
public void useage() {
System.out.println("Iron used to make tools");
}
}
Axe:
package com.sunsharing.di;
/**
* Created by baich on 2016/1/22.
*/
public class Axe {
private Iron iron;
public Iron getIron() {
return iron;
}
public void setIron(Iron iron) {
this.iron = iron;
}
public void cut() {
iron.useage();
System.out.println("cut tree!");
}
}HumanBeing:
package com.sunsharing.di;
/**
* Created by baich on 2016/1/22.
*/
public class HumanBeing {
private Axe axe;
public Axe getAxe() {
return axe;
}
public void setAxe(Axe axe) {
this.axe = axe;
}
public void useAxe() {
axe.cut();
}
}配置文件bean.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans> <bean id="Iron" class="com.sunsharing.di.Iron"></bean> <bean id="Axe" class="com.sunsharing.di.Axe"> <property name="Iron" ref="Iron"/> </bean> <bean id="HumanBeing" class="com.sunsharing.di.HumanBeing"> <property name="Axe" ref="Axe"/> </bean> </beans>
spring引擎SpringEngin:
package com.sunsharing.di;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by baich on 2016/1/22.
*/
public class SpringEngin {
/**
* 递归获取对象
* @param ele 父节点
* @param className bean id值
* @return
*/
public Object getObj(Element ele, String className) throws Exception {
List<Element> elements = ele.elements("bean");
for (Element element : elements) {
Attribute atb = element.attribute("id");
String idV = atb.getValue();
if(idV.equals(className)) {
Attribute atb02 = element.attribute("class");
String classV = atb02.getValue();
Object obj = Class.forName(classV).newInstance();
List<Element> eleList = element.elements("property");
for (Element el : eleList) {
Attribute atb03 = el.attribute("name");
String nV = atb03.getValue();
Attribute atb04 = el.attribute("ref");
String refV = atb04.getValue();
Object ob = getObj(ele, refV);
Method mt = obj.getClass().getMethod("set" + nV, ob.getClass());
mt.invoke(obj, ob);
}
return obj;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
*
* @param className 待实例化的类
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public Object getObj(String className) throws Exception {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
File file = new File("bean.xml");
Document document = reader.read(file);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
Object obj = getObj(root, className);
return obj;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringEngin se = new SpringEngin();
HumanBeing hb = (HumanBeing) se.getObj("HumanBeing");
hb.useAxe();
}
}执行效果:
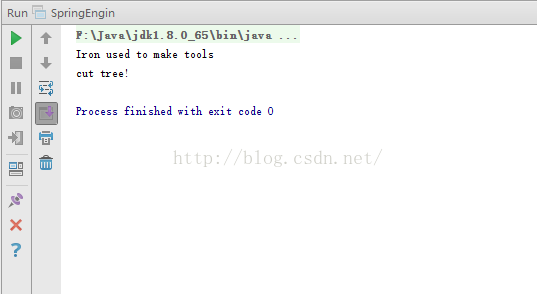
相关文章推荐
- java中ThreadLocal类的使用
- 深入Synchronized和java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock的区别详解
- java string为null时的字符串拼接
- 一Java设计模式——需要遵守的六个原则
- spring bean的scope属性
- Spring核心AOP的工作流程
- 补充:枫之逆的“Eclipse启动时fail to create Java Virtual Machine问题的解决”
- 图像的均值滤波、中值滤波_JAVA
- java 校验文件头 判断虚假文件
- JAVA多线程
- 小白学Java json解析~~
- Spring AOP 5种通知与java动态代理
- 登陆成功后返回前一个页面
- spring mvc --xml
- &#26159 类似编码用Java转换成字符串
- java运算符及二进制、八进制、十六进制
- java调用外部webservice的实例
- java中&和&&的区别
- SpringMVC学习笔记(1)之入门篇
- HDU-3887-Counting Offspring-dfs序+树状数组
