HttpClient之POST、GET
2016-01-09 00:00
429 查看
摘要: Apache的httpComponents 项目是专注于http协议的的java组件。原生的URLConnection如果需要和server通信,表单和文件传送支持不好,于是就有了新的HttpClient,并且在新的httpclient里面加入了NIO为基础实现的非阻塞的I/O实现。本章内容只讲解常用的get、post通信。
HttpClient之GET、POST
一、概述
1.1 简述
Apache的httpComponents 项目是专注于http协议的的java组件。原生的URLConnection和server通信,表单和文件传送支持不好。于是就有了新的HttpClient,并且在新的httpclient里面加入了以NIO为基础实现的非阻塞的I/O实现。本章内容只设计常用的get、post通信。
http响应包括内容:响应行、响应头、响应体:
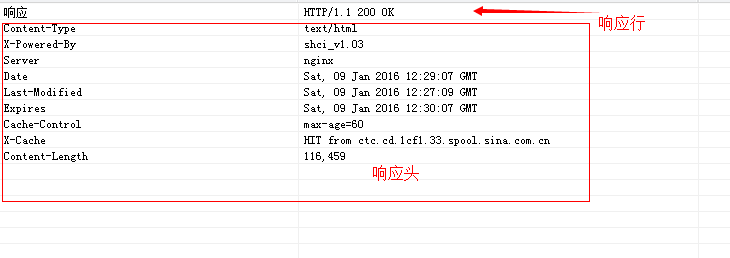
tips:详细的http协议,请大家自行百度。这里使用的IE9来访问是http://www.sina.com.cn/展示
1.3 组成模块
以4.5.1 发布版为准:
a)httpComponents core
HttpCore 是一组基础的http通信组件,能在客服端和服务器之间传送数据。支持:I/O模块:阻塞I/O和非阻塞I/O(以JAVA的NIO为基础)。
b)httpComponents client
HttpClient是一个在httpcore的基础实现的以http/1.1 协议设置的http代理。提供了可重复利用的组件:客服端身份验证、地址管理、http连接管理。HttpComponents Client代替了HttpClient 3.x的的使用,建议用户都升级。
c)httpComponents asynclient
异步HttpClient是以NIO和httpClient为基础并遵从http/1.1协议的代理。在那些需要大量连接、重要数据通过的使用,有很好的表现。
2.2 get请求
2.3 post请求
2.4 response处理
2.5 其它实现
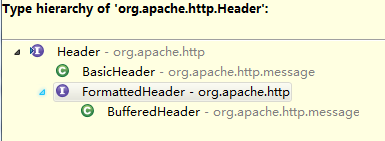
b)Header接口:实现请求和响应头数据设置(key-value)
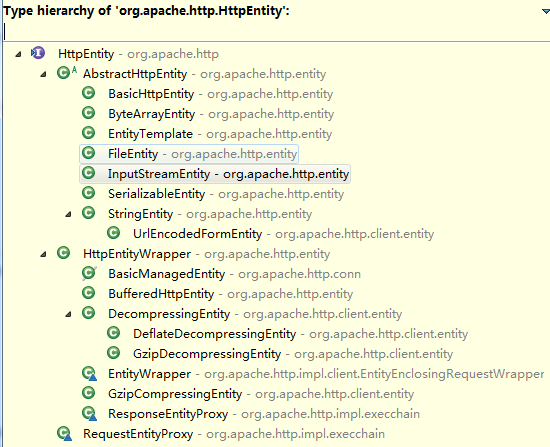
b)HttpEntity接口:实现响应体和请求体。原理都是一样在模型上都是用了策略模式。
HttpClient之GET、POST
一、概述
1.1 简述
Apache的httpComponents 项目是专注于http协议的的java组件。原生的URLConnection和server通信,表单和文件传送支持不好。于是就有了新的HttpClient,并且在新的httpclient里面加入了以NIO为基础实现的非阻塞的I/O实现。本章内容只设计常用的get、post通信。1.2 名词:
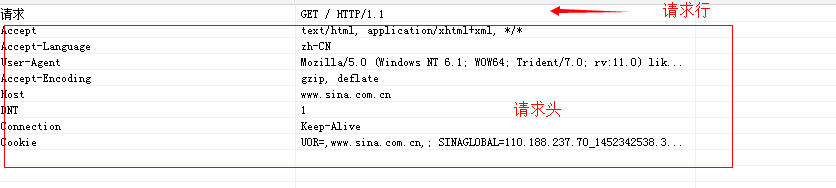
http请求包括内容: 请求行、请求头、请求体:
http响应包括内容:响应行、响应头、响应体:

tips:详细的http协议,请大家自行百度。这里使用的IE9来访问是http://www.sina.com.cn/展示
1.3 组成模块
以4.5.1 发布版为准:
a)httpComponents core
HttpCore 是一组基础的http通信组件,能在客服端和服务器之间传送数据。支持:I/O模块:阻塞I/O和非阻塞I/O(以JAVA的NIO为基础)。
b)httpComponents client
HttpClient是一个在httpcore的基础实现的以http/1.1 协议设置的http代理。提供了可重复利用的组件:客服端身份验证、地址管理、http连接管理。HttpComponents Client代替了HttpClient 3.x的的使用,建议用户都升级。
c)httpComponents asynclient
异步HttpClient是以NIO和httpClient为基础并遵从http/1.1协议的代理。在那些需要大量连接、重要数据通过的使用,有很好的表现。
二、实例
2.1 模版
这个模版是官方提供,所有的Httpclient实现方式都是这样开始
public void FunctionTemplate() throws ClientProtocolException, IOException {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); //固定开始
//请求方式处理:请求类型(get/post),uri,请求头、参数类型和数据(请求体)
//HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://localhost/");
HttpPost httpget = new HttpPost("http://localhost/");
//响应处理:响应行
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
try {
// 响应数据处理
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
response.close();
}
} 2.2 get请求
1.get的参数传递可以在uri中
//uri处理
public void TestUrl() throws URISyntaxException {
// get--url:"http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&q=httpclient&btnG=Google+Search&aq=f&oq="
// 方法一:贴全连接
// HttpGet httpGet = new
// HttpGet("http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&q=httpclient&btnG=Google+Search&aq=f&oq=");
// 方法二:通过URI来组装
URI uri = new URIBuilder().setScheme("http")// 协议
.setHost("www.google.com")// 主机
.setPath("/search")// 路径
.setParameter("q", "httpclient")// ?后面的参数
.setParameter("btnG", "Google Search")// ?后面的参数
.setParameter("aq", "f")// ?后面的参数
.setParameter("oq", "")// ?后面的参数
.build();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
}
//处理请求头
public void requestHeader() throws IOException {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();// 创建httpclient
// 请求处理(主要是自己生成的请求头和请求体)
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://localhost/");
// 请求头
Header header = new BasicHeader("Accpet-Encoiding", "gzip, deflate, sdch");
httpget.setHeader(header);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);// 响应处理
// 数据处理
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
response.close();
}
} 2.3 post请求
1.post发送数据需要用到HttpClient接口的总结
//传送文件
public void fileEntity() throws IOException {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();// 创建httpclient
// 请求处理(主要是自己生成的请求头和请求体)
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost/");
// 请求头
Header header = new BasicHeader("Accpet-Encoiding", "gzip, deflate, sdch");
httpPost.setHeader(header);
// 文件
File file = new File("test.txt");
FileEntity entity = new FileEntity(file, ContentType.create("text/plain", "UTF-8"));
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
response = httpclient.execute(httpPost);// 响应处理
// 数据处理
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
response.close();
}
}
//传送form数据
public void formEntity() throws IOException {
// 创建httpclient
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 请求处理(主要是自己生成的请求头和请求体)
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost/");
// 表单
List<NameValuePair> formparams = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("param1", "value1"));
formparams.add(new BasicNameValuePair("param2", "value2"));
// 格式化成 param1=value¶m2=value2
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(formparams);
// 当请求数据大小不定的时候可以设置chunk为true
entity.setChunked(true);
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 响应处理
response = httpclient.execute(httpPost);
// 数据处理
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
response.close();
}
} 2.4 response处理
public void testResponseEntity() {
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 所有的网络传送需要网络协议
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://www.baidu.com");
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
System.out.println(entity.getContentType());
// 利用inputstream-->BufferedReader---->string
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
try {
String temp = null;
BufferedReader r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(instream));
while ((temp = r.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
instream.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
response = null;
}
}
} 2.5 其它实现
//1.响应行设置,就是
public void TestResponse() {
// 响应行参数:Http/1.1 200 ok
HttpResponse response = new BasicHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpStatus.SC_OK, "OK");
System.out.println(response.getProtocolVersion());// 协议
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode());
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getReasonPhrase());
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().toString());
}
//2.头数据处理:key-value(请求/响应是通过h)
public void TestHeader() {
// 响应头
HttpResponse response = new BasicHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpStatus.SC_OK, "OK");
// 响应头
response.addHeader("Set-Cookie", "c1=a; path=/; domain=localhost");
response.addHeader("Set-Cookie", "c2=a; path=\"/\"; domain=\"localhost\"");
// 迭代
HeaderIterator it = response.headerIterator("Set-Cookie");
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
//3. Entity数据处理:
public void TestEntity() throws ParseException, IOException {
// 这里是stirng类型
// content:important message 传送的数据
// ContentType:数据类型
StringEntity myEntity = new StringEntity("important message", ContentType.create("text/plain", "UTF-8"));
System.out.println(myEntity.getContentType());
System.out.println(myEntity.getContentLength());
System.out.println(myEntity.getContent());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(myEntity));
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toByteArray(myEntity).length);
}2.6 HttpMessage、Header、HttpEntity
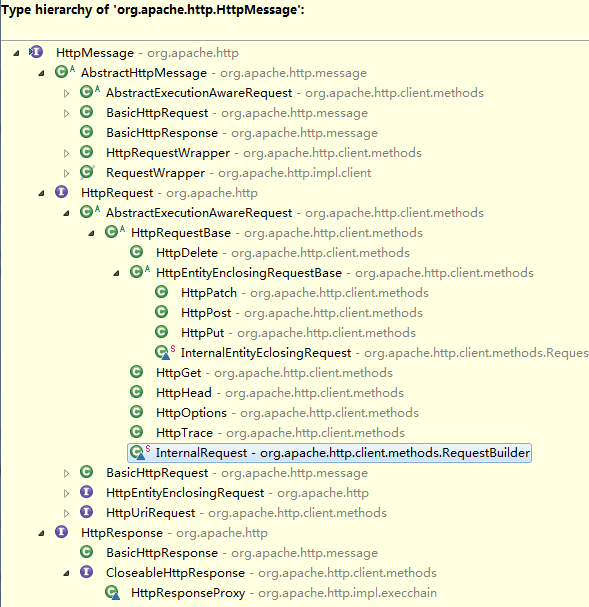
a)HttpMessage接口:HttpGet、HttpPost:
b)Header接口:实现请求和响应头数据设置(key-value)

b)HttpEntity接口:实现响应体和请求体。原理都是一样在模型上都是用了策略模式。

相关文章推荐
- java对世界各个时区(TimeZone)的通用转换处理方法(转载)
- java-注解annotation
- java-模拟tomcat服务器
- java-用HttpURLConnection发送Http请求.
- java-WEB中的监听器Lisener
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- 介绍一款信息管理系统的开源框架---jeecg
- 聚类算法之kmeans算法java版本
- java实现 PageRank算法
- PropertyChangeListener简单理解
- c++11 + SDL2 + ffmpeg +OpenAL + java = Android播放器
- 插入排序
- 冒泡排序
- 堆排序
- 快速排序
- 二叉查找树
