死磕Spring系列之三,XML解析相关
2015-12-24 21:17
691 查看
通过第2章的介绍,应该知道Spring如何从XML一步步解析成BD对象并注册到容器中,这一过程有个概要认识了。
接下来开始详细分析与XML相关的那些事。
首先看一下使用的XML文档。
首先需要知道,
XML 指可扩展标记语言.第一行是 XML 声明。它定义 XML 的版本 (1.0) 和所使用的编码 UTF-8)。
下一行描述文档的根元素<beans>,(像在说:“本文档包含一个多个Bean “):
接下来就是子元素<bean>了。具体标签含义就不说了。
我想说的是文档头部的xmlns=".*", xmlns:xsi=".*",xsi:schemaLocation=".*"类似字样的一坨代码含义。
这些就是命名空间。
命名空间
a)为什么要有命名空间?
XML 命名空间提供避免元素命名冲突的方法。
在 XML 中,元素名称是由开发者定义的,当两个不同的文档使用相同的元素名时,就会发生命名冲突。b)默认的命名空间(Default Namespaces)
为元素定义默认的命名空间可以让我们省去在所有的子元素中使用前缀的工作。
c)xsi:schemaLocation
schemaLocation 属性引用具有目标命名空间的 XML 架构文档。
xsi:schemaLocation属性的值由一个URI引用对组成,两个URI之间以空白符分隔。第一个URI是名称空间的名字,第二个URI给出模式文档的位置,模式处理器将从这个位置读取模式文档,该模式文档的目标名称空间必须与第一个URI相匹配
XSD (xml Schema Definition)
Xml Schema的用途1. 定义一个Xml文档中都有什么元素2. 定义一个Xml文档中都会有什么属性3. 定义某个节点的都有什么样的子节点,可以有多少个子节点,子节点出现的顺序4. 定义元素或者属性的数据类型5. 定义元素或者属性的默认值或者固定值
具体语法,就不讲了,有兴趣的可以搜索。
DTD(Document Type Definition文档类型定义)的作用是定义 XML 文档的合法构建模块。
功能和XSD类似。具体使用如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN" " http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd ">
XSD,知道即可,spring2.0中使用XSD验证。
解析XML需要关注点
1.XML文档如何转换为系统资源
2.使用什么引擎解析
3.解析文档元素,解析为数据载体对象
1.XML文档如何转换为系统资源
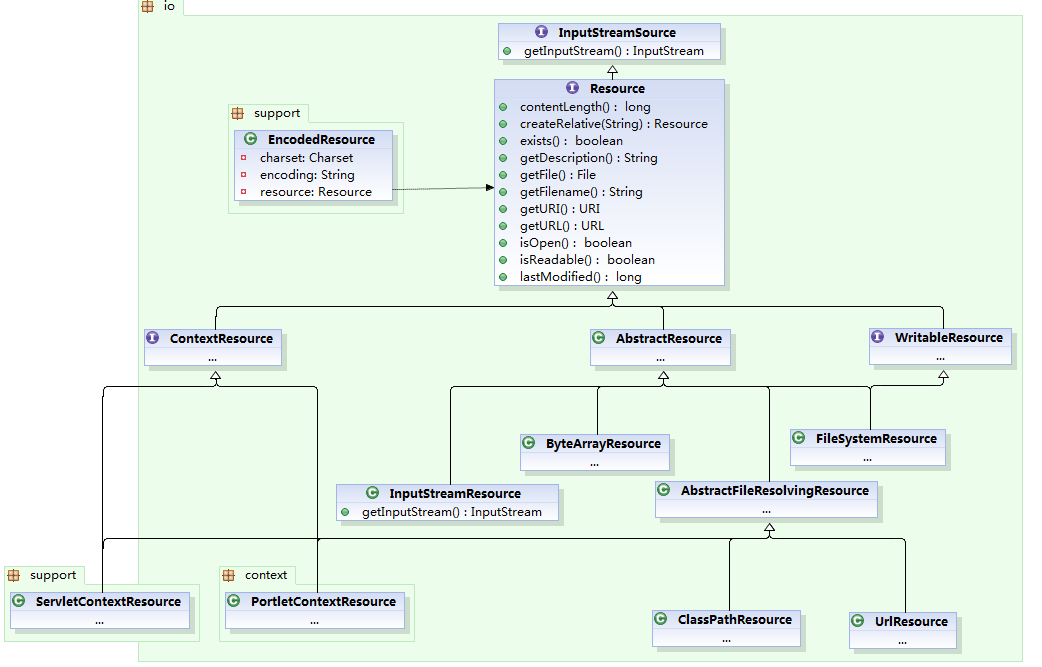
上图是Resource类图。通过Resouce接口,可以知道文件(xml)的名称,是否制度,内容长度,是否存在.....。我们非常熟悉的获取资源的几种方式,都能找到。ClasspathResource:根据类加载获取UrlResource:URL路径(远程)获取FileSystemResource:文件路径获取大家有兴趣可以仔细看一下。getInputStream()方法要重点关注。简单说一下 EncodedResource,他持有Resource接口引用,添加字符集支持。
2.使用什么引擎解析
2.1.准备输入(org.xml.sax.InputSource)
int org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException
2.2 生成Document
通过查看日志,最后我们得出我们想要的结果。
Using JAXP provider [com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl]
com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl
com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderImpl
3.解析文档元素,解析为数据载体对象
到了这里,Document对象我们已经拿到了,开始进行解析。
void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root)
3.1根据环境中profile参数,解析需要元素<beans>。
3.2 分别解析bean标签和自定义标签(对应于XML中元素)
void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)
parseCustomElement()方法暂时忽略,到自定义标签时,再进行分析。
此刻,我们需要关注的是parseDefaultElement()。
3.3具体分别处理import,alias,bean,beans子元素。
void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)
BeanDefinitionHolder org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean)
AbstractBeanDefinition org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean)
比较重要的对象。
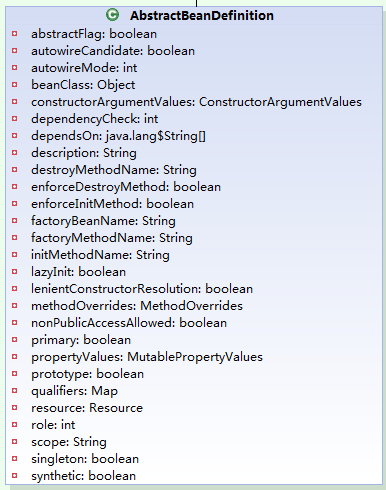
BeanDefinition为XML <bean>标签数据载体对象。通过分析,可以找到xml对应节点或属性,大部分都可以在AbstractBeanDefinition中找到。
BeanDefinition是支持层级的,在这儿就不重点分析了。
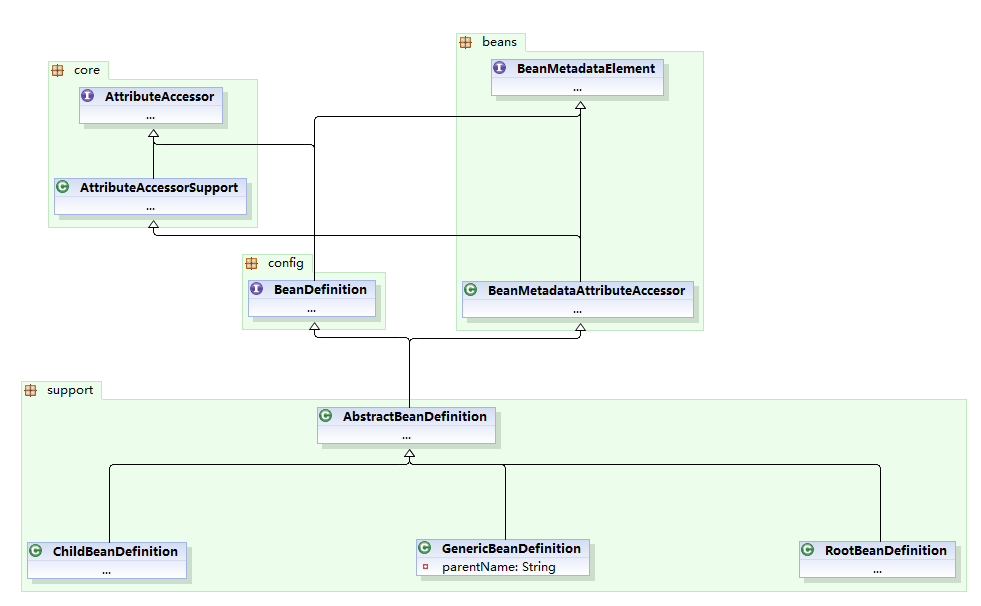
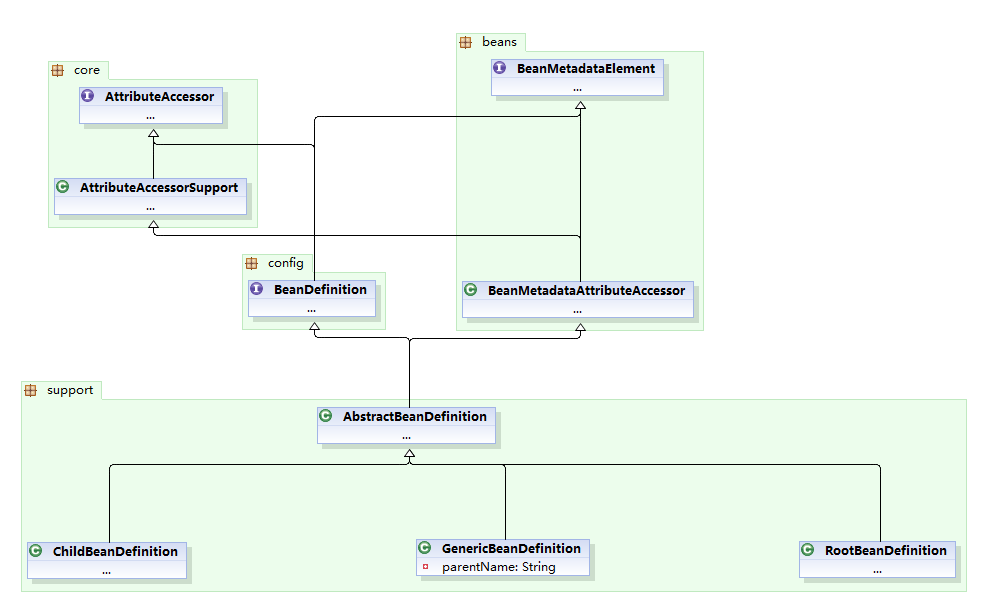
XML解析相关类图
本文出自 “简单” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://dba10g.blog.51cto.com/764602/1728020
接下来开始详细分析与XML相关的那些事。
首先看一下使用的XML文档。
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd"> <beanid="beijingCard"class="com.spring.examples.ioc.bean.Card" > <propertyname="cardNo"value="6220-52103-4123-456"></property> <propertyname="bank"value="北京银行"/> </bean> <beanid="jiansheCard"class="com.spring.examples.ioc.bean.Card"> <propertyname="cardNo"value="6227-52103-4123-456"></property> <propertyname="bank"value="建设银行"/> </bean> <beanid="miyue" class="com.spring.examples.ioc.bean.User"primary="true" scope="singleton"> <propertyname="userName"value="芈月"></property> <propertyname="email"value="miyue@daqin.com"></property> <propertyname="cardList"> <list> <refbean="beijingCard"/> <refbean="jiansheCard"/> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
首先需要知道,
XML 指可扩展标记语言.第一行是 XML 声明。它定义 XML 的版本 (1.0) 和所使用的编码 UTF-8)。
下一行描述文档的根元素<beans>,(像在说:“本文档包含一个多个Bean “):
接下来就是子元素<bean>了。具体标签含义就不说了。
我想说的是文档头部的xmlns=".*", xmlns:xsi=".*",xsi:schemaLocation=".*"类似字样的一坨代码含义。
这些就是命名空间。
命名空间
a)为什么要有命名空间?
XML 命名空间提供避免元素命名冲突的方法。
在 XML 中,元素名称是由开发者定义的,当两个不同的文档使用相同的元素名时,就会发生命名冲突。b)默认的命名空间(Default Namespaces)
为元素定义默认的命名空间可以让我们省去在所有的子元素中使用前缀的工作。
格式:xmlns="namespaceURI"
c)xsi:schemaLocation
<xsi:schemaLocation="list of anyURI" >
schemaLocation 属性引用具有目标命名空间的 XML 架构文档。
xsi:schemaLocation属性的值由一个URI引用对组成,两个URI之间以空白符分隔。第一个URI是名称空间的名字,第二个URI给出模式文档的位置,模式处理器将从这个位置读取模式文档,该模式文档的目标名称空间必须与第一个URI相匹配
XSD (xml Schema Definition)
Xml Schema的用途1. 定义一个Xml文档中都有什么元素2. 定义一个Xml文档中都会有什么属性3. 定义某个节点的都有什么样的子节点,可以有多少个子节点,子节点出现的顺序4. 定义元素或者属性的数据类型5. 定义元素或者属性的默认值或者固定值
具体语法,就不讲了,有兴趣的可以搜索。
DTD(Document Type Definition文档类型定义)的作用是定义 XML 文档的合法构建模块。
功能和XSD类似。具体使用如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN" " http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd ">
XSD,知道即可,spring2.0中使用XSD验证。
解析XML需要关注点
1.XML文档如何转换为系统资源
2.使用什么引擎解析
3.解析文档元素,解析为数据载体对象
1.XML文档如何转换为系统资源
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
} 首先看到这方,咱们关注到参数Resource,没错Spring提供Resource接口,将XML文件封装为资源对象。
上图是Resource类图。通过Resouce接口,可以知道文件(xml)的名称,是否制度,内容长度,是否存在.....。我们非常熟悉的获取资源的几种方式,都能找到。ClasspathResource:根据类加载获取UrlResource:URL路径(远程)获取FileSystemResource:文件路径获取大家有兴趣可以仔细看一下。getInputStream()方法要重点关注。简单说一下 EncodedResource,他持有Resource接口引用,添加字符集支持。
2.使用什么引擎解析
2.1.准备输入(org.xml.sax.InputSource)
int org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
thrownew BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
thrownew BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}开始构造XML InputSource.2.2 生成Document
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}2.3构造Document建造工厂protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory(int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware)
throws ParserConfigurationException {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware);
//根据获取的验证模式,决定为factory开启xsd开关
if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) {
factory.setValidating(true);
if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) {
// Enforce namespace aware for XSD...
factory.setNamespaceAware(true);
try {
factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
ParserConfigurationException pcex = new ParserConfigurationException(
"Unable to validate using XSD: Your JAXP provider [" + factory +
"] does not support XML Schema. Are you running on Java 1.4 with Apache Crimson? " +
"Upgrade to Apache Xerces (or Java 1.5) for full XSD support.");
pcex.initCause(ex);
throw pcex;
}
}
}
return factory;
}这时候一目了然了。通过查看日志,最后我们得出我们想要的结果。
Using JAXP provider [com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl]
com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl
com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderImpl
3.解析文档元素,解析为数据载体对象
到了这里,Document对象我们已经拿到了,开始进行解析。
void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root)
3.1根据环境中profile参数,解析需要元素<beans>。
protected BeanDefinitionParserDelegate createDelegate(
XmlReaderContext readerContext, Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parentDelegate) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parentDelegate);
if (delegate == null) {
delegate = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(readerContext, getEnvironment());
delegate.initDefaults(root, parentDelegate);
}
return delegate;
}/**
* 初始化默认参数:lazy-init, autowire, dependency check settings,
* init-method, destroy-method and merge settings.
*如果没有显示设置,使用上级默认参数。
*/
publicvoid initDefaults(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent) {
populateDefaults(this.defaults, (parent != null ? parent.defaults : null), root);
this.readerContext.fireDefaultsRegistered(this.defaults);
}下面正式进入正题,子元素的解析(如bean)3.2 分别解析bean标签和自定义标签(对应于XML中元素)
void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)
protectedvoid parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}parseCustomElement()方法暂时忽略,到自定义标签时,再进行分析。
此刻,我们需要关注的是parseDefaultElement()。
3.3具体分别处理import,alias,bean,beans子元素。
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
elseif (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
elseif (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
elseif (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}3.4处理import标签void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele)
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
//略:处理路径,获取资源
try {
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
//其他
}3.5处理alias标签protected void processAliasRegistration(Element ele) {
String name = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
String alias = ele.getAttribute(ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean valid = true;
//验证信息有效性
if (valid) {
try {
getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register alias '" + alias +
"' for bean with name '" + name + "'", ele, ex);
}
getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
}
}
void org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext.registerAlias(String beanName, String alias)
publicvoid registerAlias(String beanName, String alias) {
this.beanFactory.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
void org.springframework.core.SimpleAliasRegistry.registerAlias(String name, String alias)
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
Assert.hasText(name, "'name' must not be empty");
Assert.hasText(alias, "'alias' must not be empty");
if (alias.equals(name)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
}
else {
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
if (registeredName != null && !registeredName.equals(name)) {
thrownew IllegalStateException("Cannot register alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
}
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
}
}3.6解析bean,重中之重,每一步都进行分析。void org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}3.7BeanDefinitionHolder org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean)
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//处理别名
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
//设置名称
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
//判断名称,唯一性
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
//建立关系BD 与名称映射关系
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
returnnew BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}3.8AbstractBeanDefinition org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean)
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
//初始化bd
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//赋bd属性(scope,lazy-init,abstract...)
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
//lookup-method
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//replaced-method
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//qualifier
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
returnnull;
}到这里,就不继续探究了。下面就是逐次调用类似ele.getAttribute()从xml取值,bd.setXXX()赋值的过程。比较重要的对象。
BeanDefinition为XML <bean>标签数据载体对象。通过分析,可以找到xml对应节点或属性,大部分都可以在AbstractBeanDefinition中找到。
BeanDefinition是支持层级的,在这儿就不重点分析了。


XML解析相关类图

本文出自 “简单” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://dba10g.blog.51cto.com/764602/1728020
相关文章推荐
- java过滤特殊字符串
- Java邮件发送的简单实现
- java equals() 与‘==’区别
- java设计模式(四)--代理模式
- Java面向对象编程-第10章学习笔记
- Spark Hive在Eclipse代码中直接编译问题
- java常用数据,排序,链表等
- Springmvc访问静态资源
- 大话设计模式之原型模式(Java版) 拷贝也需要技术
- Java之美[从菜鸟到高手演变]之Java中static关键字
- Java中 FileReader的中文乱码问题
- Java之美[从菜鸟到高手演变]系列之博文阅读导航
- [java ] java.util.zip.ZipException: error in opening zip file
- java核心技术之内部类
- 终于和Java碰面了
- Java Web中资源的访问路径
- java并发控制:ReentrantLock Condition使用详解
- 设计模式——抽象工厂 Java源代码
- Echache整合Spring缓存实例讲解
- 如何切换eclipse中svn用户
