数据结构-堆实现优先队列(java)
2015-12-19 15:56
615 查看
队列的特点是先进先出。通常都把队列比喻成排队买东西,大家都很守秩序,先排队的人就先买东西。但是优先队列有所不同,它不遵循先进先出的规则,而是根据队列中元素的优先权,优先权最大的先被取出。这就很像堆的特征:总是移除优先级最高的根节点。
重点:优先级队列,是要看优先级的,谁的优先级更高,谁就先得到权限。不分排队的顺序!
上篇文章解释了堆的概念实现,现在用堆实现优先队列:
//最大堆
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Heap<E extends Comparable>{
private ArrayList<E> list=new ArrayList<E>();//用数组实现堆
public Heap(){}
public Heap(E[] objects){
for(int i=0;i<objects.length;i++){
add(objects[i]);
}
}
public void add(E newObject){//添加一个元素
list.add(newObject);
int currentIndex=list.size()-1;
while(currentIndex>0){
int parentIndex=(currentIndex-1)/2;//找到该结点的父结点
if(list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(parentIndex))>0){//与父节点比较
//如果当前结点的值大于父结点就交换位置
E temp=list.get(currentIndex);
list.set(currentIndex, list.get(parentIndex));
list.set(parentIndex, temp);
}
else
break;
currentIndex=parentIndex;
}
}
public E remove(){//删除并返回根结点,堆的特点是移除了根结点后还是堆
if(list.size()==0) return null;
E removeObject=list.get(0);
list.set(0, list.get(list.size()-1));//把最后一个结点放在根结点的位置
list.remove(list.size()-1);
int currentIndex=0;
while(currentIndex<list.size()){
int leftChildIndex=2*currentIndex+1;
int rightChildIndex=2*currentIndex+2;//左右孩子结点的坐标
if(leftChildIndex>=list.size())break;
//比较左右孩子的值,使maxIndex指向值大的结点
int maxIndex=leftChildIndex;
if(rightChildIndex<list.size()){
if(list.get(maxIndex).compareTo(list.get(rightChildIndex))<0){
maxIndex=rightChildIndex;
}
}
//如果当前结点的值小于其左右孩子中的大的值,就交换两个结点
if(list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(maxIndex))<0){
E temp=list.get(maxIndex);
list.set(maxIndex, list.get(currentIndex));
list.set(currentIndex, temp);
currentIndex=maxIndex;
}
else
break;
}
return removeObject;
}
public int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
}MyPriorityQueue.java
public class MyPriorityQueue<E extends Comparable> {
private Heap<E> heap=new Heap<E>();//用堆实现优先队列
//入队列
public void enqueue(E e){
heap.add(e); //这个add以后,堆会自己调整成一个新堆
}
//出队列
public E dequeue(){
return heap.remove();//这移除出之后,堆会自己调整,还是一个新堆
}
public int getSize(){
return heap.getSize();
}
}
TestMyPriorityQueueMainClass.java
public class TestMyPriorityQueueMainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Patient p1=new Patient("John",2);
Patient p2=new Patient("Tom",9);
Patient p3=new Patient("Jack",4);
Patient p4=new Patient("Michael",6);
MyPriorityQueue<Patient> priorityQueue=new MyPriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.enqueue(p1);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p2);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p3);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p4);
while(priorityQueue.getSize()>0){
System.out.print(priorityQueue.dequeue()+" ");
}
}
static class Patient implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int priority;
public Patient(String name,int priority){
this.name=name;
this.priority=priority;
}
public String toString(){
return name+"(priority:"+priority+")";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object oo) {//比较优先级
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.priority-((Patient)oo).priority;
}
}
}
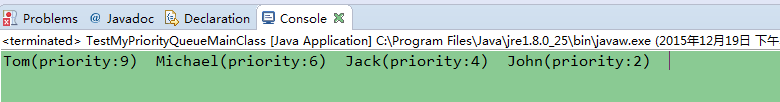
测试结果:优先级高的先输出,优先级最高的就是堆的根节点
重点:优先级队列,是要看优先级的,谁的优先级更高,谁就先得到权限。不分排队的顺序!
上篇文章解释了堆的概念实现,现在用堆实现优先队列:

//最大堆
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Heap<E extends Comparable>{
private ArrayList<E> list=new ArrayList<E>();//用数组实现堆
public Heap(){}
public Heap(E[] objects){
for(int i=0;i<objects.length;i++){
add(objects[i]);
}
}
public void add(E newObject){//添加一个元素
list.add(newObject);
int currentIndex=list.size()-1;
while(currentIndex>0){
int parentIndex=(currentIndex-1)/2;//找到该结点的父结点
if(list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(parentIndex))>0){//与父节点比较
//如果当前结点的值大于父结点就交换位置
E temp=list.get(currentIndex);
list.set(currentIndex, list.get(parentIndex));
list.set(parentIndex, temp);
}
else
break;
currentIndex=parentIndex;
}
}
public E remove(){//删除并返回根结点,堆的特点是移除了根结点后还是堆
if(list.size()==0) return null;
E removeObject=list.get(0);
list.set(0, list.get(list.size()-1));//把最后一个结点放在根结点的位置
list.remove(list.size()-1);
int currentIndex=0;
while(currentIndex<list.size()){
int leftChildIndex=2*currentIndex+1;
int rightChildIndex=2*currentIndex+2;//左右孩子结点的坐标
if(leftChildIndex>=list.size())break;
//比较左右孩子的值,使maxIndex指向值大的结点
int maxIndex=leftChildIndex;
if(rightChildIndex<list.size()){
if(list.get(maxIndex).compareTo(list.get(rightChildIndex))<0){
maxIndex=rightChildIndex;
}
}
//如果当前结点的值小于其左右孩子中的大的值,就交换两个结点
if(list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(maxIndex))<0){
E temp=list.get(maxIndex);
list.set(maxIndex, list.get(currentIndex));
list.set(currentIndex, temp);
currentIndex=maxIndex;
}
else
break;
}
return removeObject;
}
public int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
}MyPriorityQueue.java
public class MyPriorityQueue<E extends Comparable> {
private Heap<E> heap=new Heap<E>();//用堆实现优先队列
//入队列
public void enqueue(E e){
heap.add(e); //这个add以后,堆会自己调整成一个新堆
}
//出队列
public E dequeue(){
return heap.remove();//这移除出之后,堆会自己调整,还是一个新堆
}
public int getSize(){
return heap.getSize();
}
}
TestMyPriorityQueueMainClass.java
public class TestMyPriorityQueueMainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Patient p1=new Patient("John",2);
Patient p2=new Patient("Tom",9);
Patient p3=new Patient("Jack",4);
Patient p4=new Patient("Michael",6);
MyPriorityQueue<Patient> priorityQueue=new MyPriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.enqueue(p1);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p2);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p3);
priorityQueue.enqueue(p4);
while(priorityQueue.getSize()>0){
System.out.print(priorityQueue.dequeue()+" ");
}
}
static class Patient implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int priority;
public Patient(String name,int priority){
this.name=name;
this.priority=priority;
}
public String toString(){
return name+"(priority:"+priority+")";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object oo) {//比较优先级
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.priority-((Patient)oo).priority;
}
}
}
测试结果:优先级高的先输出,优先级最高的就是堆的根节点

相关文章推荐
- java对世界各个时区(TimeZone)的通用转换处理方法(转载)
- java-注解annotation
- java-模拟tomcat服务器
- java-用HttpURLConnection发送Http请求.
- java-WEB中的监听器Lisener
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- 介绍一款信息管理系统的开源框架---jeecg
- 聚类算法之kmeans算法java版本
- java实现 PageRank算法
- PropertyChangeListener简单理解
- c++11 + SDL2 + ffmpeg +OpenAL + java = Android播放器
- 插入排序
- 冒泡排序
- 堆排序
- 快速排序
- 二叉查找树
