Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记13:Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历
2015-10-02 09:21
1041 查看
1. Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历:
需求:存储自定义对象并遍历Student(name,age)
分析:
(1)创建学生类
(2)创建集合对象
(3)创建学生对象
(4)把学生对象添加到集合对象中
(5)遍历集合
2. 代码示例:
Student.java,如下:
再次编写一个测试类CollectionTest2,如下:
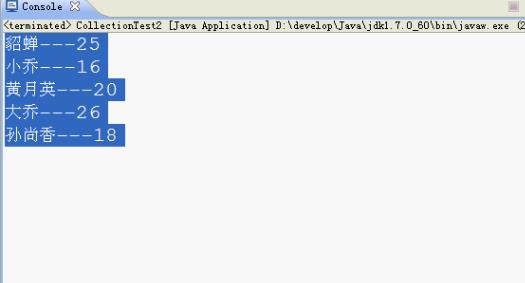
运行效果如下:
需求:存储自定义对象并遍历Student(name,age)
分析:
(1)创建学生类
(2)创建集合对象
(3)创建学生对象
(4)把学生对象添加到集合对象中
(5)遍历集合
2. 代码示例:
Student.java,如下:
package cn.itcast_04;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}再次编写一个测试类CollectionTest2,如下:
package cn.itcast_04;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
* 需求:存储自定义对象并遍历Student(name,age)
*
* 分析:
* A:创建学生类
* B:创建集合对象
* C:创建学生对象
* D:把学生对象添加到集合对象中
* E:遍历集合
*/
public class CollectionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
Collection c = new ArrayList();
// 创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("貂蝉", 25);
Student s2 = new Student("小乔", 16);
Student s3 = new Student("黄月英", 20);
Student s4 = new Student();
s4.setName("大乔");
s4.setAge(26);
// 把学生对象添加到集合对象中
c.add(s1);
c.add(s2);
c.add(s3);
c.add(s4);
c.add(new Student("孙尚香", 18)); // 匿名对象
// 遍历集合
Iterator it = c.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Student s = (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
}运行效果如下:

相关文章推荐
- Spring中EmptyResultDataAccessException异常产生的原理及处理方法
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记12:Collection集合存储字符串并遍历
- Java 集合就是比数组好(为什么有了数组还需要集合?)
- Java Statement和PreparedStatement性能测试
- java14:玩彩票
- 多项式输出-Java
- Eclipse快捷键详细解析
- JAVA native 本地方法
- spring的配置模式与注解模式基础
- javaCode的数组2
- struts2+easyui实现根据条件检索信息
- java环境变量的作用与配置
- struts2+easyui的datagrid显示列表信息
- java中多态性与动态绑定
- JVM之旅--GC探秘
- Java中的enum枚举类
- 使用Spring + quartz集群持久化时注意事项
- java篇 【10】类设计分析
- JAVA_SE基础——35.static修饰成员函数
- j2ee开发环境的建立(按需更新)
