java15 IO装饰设计模式
2015-09-23 21:47
381 查看
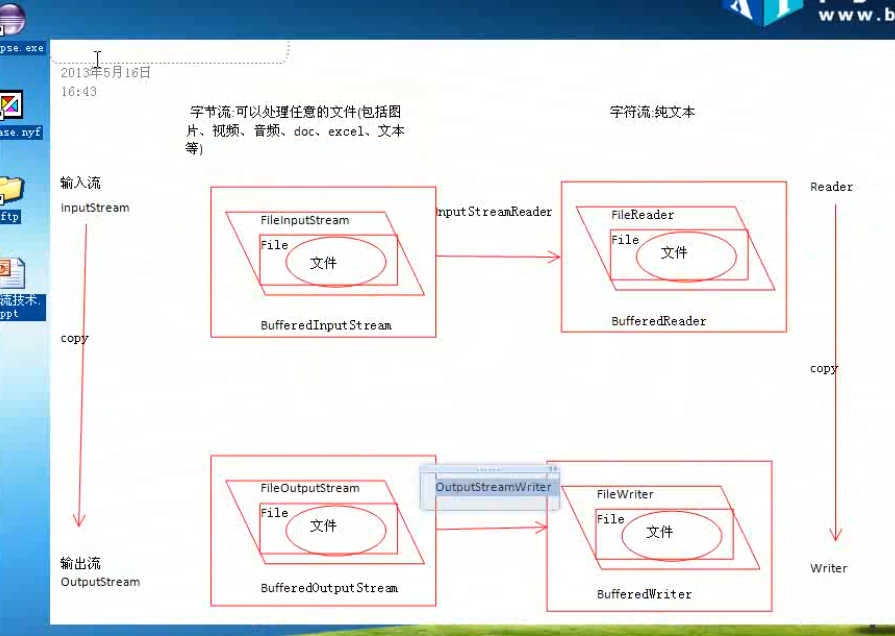
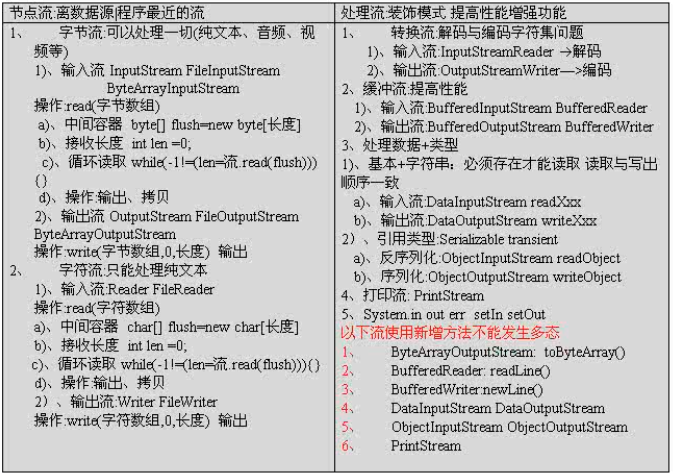
IO装饰设计模式:(IO中使用了装饰设计模式)
节点流可以直接从源读取数据,处理流就是对节点流的包装,这就是装饰,装饰就是对原有的流的性能的提升。比如买的车,马力不够,就进行装饰,使其马力增大。
装饰模式:
扩音器对声音进行了扩大。
类与类之间的关系(6种): 1、依赖:一个对象是形参或者局部变量,只有调用方法的时候才会依赖这个类。
2、关联:一个对象是属性。关联分为:
聚合:是属性 整体与部分关系, 不一致的生命周期, 人与手
组合:是属性 整体与部分关系, 一致的生命周期, 人与大脑
3、继承:父子类关系。
4、实现: 接口与实现类关系
public class Voice {
private int voice =10;
public Voice() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public int getVoice() {
return voice;
}
public void setVoice(int voice) {
this.voice = voice;
}
public void say(){
System.out.println(voice);
}
}
/**
* 扩音器
* 类与类之间的关系:
* 1、依赖:一个对象是形参或者局部变量,只有调用方法的时候才会依赖这个类。
* 2、关联:一个对象是属性。关联分为:
* 聚合:是属性 整体与部分关系, 不一致的生命周期, 人与手
* 组合:是属性 整体与部分关系, 一致的生命周期, 人与大脑
* 3、继承:父子类关系。
* 4、实现: 接口与实现类关系。
*/
public class Amplifier {
private Voice voice;
public Amplifier() {
}
public Amplifier(Voice voice) {
super();
this.voice = voice;
}
public void say(){
System.out.println(voice.getVoice()*1000);
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Voice v =new Voice();
v.say();
Amplifier am =new Amplifier(v);
am.say();
}
}
4.不能父目录拷贝到子目录中。
if(dest.getAbsolutePath().contains(src.getAbsolutePath())){
System.out.println("父目录不能拷贝到子目录中");
return;
}
/**
* 文件的分割思路
* 1、分割的块数 size n块
* 2、每一块的大小 blockSize
* 最后:总的文件大小 -(n-1)*blockSize
*/
public class RndDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rnd =new RandomAccessFile(new File("E:/xp/test/a.txt"),"r");
rnd.seek(30);//跳过30字节再开始。一个数字是4个字节
//定义缓冲大小
byte[] flush =new byte[10];
//接收长度
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=rnd.read(flush))){
if(len>=20){
System.out.println(new String(flush,0,20));
break;
}else{
System.out.println(new String(flush,0,len));
}
}
FileUtil.close(rnd);
}
}
文件的分割与合并:
public class SplitFile {
//原始文件的路径
private String filePath;
//原始文件名
private String fileName;
//原始文件大小
private long length;
//根据每块的大小,确定分多少块
private int size;
//每块的大小
private long blockSize;
//分割后的存放目录
private String destBlockPath;
//每块的名称
private List<String> blockPath;
public SplitFile(){
blockPath = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath){
this(filePath,destBlockPath,1024);
}
public SplitFile(String filePath,String destBlockPath,long blockSize){//方法里面一个个调用另一个方法,这是面向过程的思路。
this();
this.filePath= filePath;
this.destBlockPath =destBlockPath;
this.blockSize=blockSize;
init();
}
/**
* 初始化操作 计算 块数、确定文件名
*/
public void init(){
File src =null;
//健壮性
if(null==filePath ||!(((src=new File(filePath)).exists()))){
return;
}
if(src.isDirectory()){
return ;
}
//文件名
this.fileName =src.getName();
//计算块数 实际大小 与每块大小
this.length = src.length();
//修正 每块大小
if(this.blockSize>length){
this.blockSize =length;
}
//确定块数
size= (int)(Math.ceil(length*1.0/this.blockSize));
//确定文件的路径
initPathName();
}
private void initPathName(){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
this.blockPath.add(destBlockPath+"/"+this.fileName+".part"+i);
}
}
/**
* 文件的分割
* 0)、第几块
* 1、起始位置
* 2、实际大小
* @param destPath 分割文件存放目录
*/
public void split(){
long beginPos =0; //起始点
long actualBlockSize =blockSize; //实际大小
//计算所有块的大小、位置、索引
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(i==size-1){ //最后一块
actualBlockSize =this.length-beginPos;
}
spiltDetail(i,beginPos,actualBlockSize);
beginPos+=actualBlockSize; //本次的终点,下一次的起点
}
}
/**
* 文件的分割 输入 输出
* 文件拷贝
* @param idx 第几块
* @param beginPos 起始点
* @param actualBlockSize 实际大小
*/
private void spiltDetail(int idx,long beginPos,long actualBlockSize){
//1、创建源
File src = new File(this.filePath); //源文件
File dest = new File(this.blockPath.get(idx)); //目标文件
//2、选择流
RandomAccessFile raf = null; //输入流,随机访问流。
BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流
try {
raf=new RandomAccessFile(src,"r");
bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//读取文件,定位到起始位置。
raf.seek(beginPos);
//缓冲区
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
//接收长度
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=raf.read(flush))){
if(actualBlockSize-len>=0){ //查看是否足够
//写出
bos.write(flush, 0, len);
actualBlockSize-=len; //剩余量
}else{ //写出最后一次的剩余量
bos.write(flush, 0, (int)actualBlockSize);
break;
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
FileUtil.close(bos,raf);
}
}
/**
* 文件的合并
*/
public void merge(String destPath){
//创建源
File dest =new File(destPath);
//选择流
BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流
SequenceInputStream sis =null ;//输入流
//创建一个容器
Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<InputStream>();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) {
vi.add(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i)))));//把每块文件的流搞成一个集合。
}
bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加
sis=new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements()); //java.io.SequenceInputStream.SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e)
//public Enumeration<E> elements()
//缓冲区
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
//接收长度
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=sis.read(flush))){//读到程序里面来,所以是输入流。
bos.write(flush, 0, len);//输出到目的地文件,所以是输出流。
}
bos.flush();
FileUtil.close(sis);
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
FileUtil.close(bos);
}
}
/**
* 文件的合并
*/
public void merge1(String destPath){
//创建源
File dest =new File(destPath);
//选择流
BufferedOutputStream bos=null; //输出流
try {
bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest,true)); //追加
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
for (int i = 0; i < this.blockPath.size(); i++) {
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(this.blockPath.get(i))));
//缓冲区
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
//接收长度
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=bis.read(flush))){
bos.write(flush, 0, len);
}
bos.flush();
FileUtil.close(bis);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
FileUtil.close(bos);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SplitFile split = new SplitFile("E:/xp/20130502/test/学员设置(20130502).xls","E:/xp/20130502",51);
System.out.println(split.size);
split.split();
split.merge("E:/xp/20130502/test1.xls");
}
}
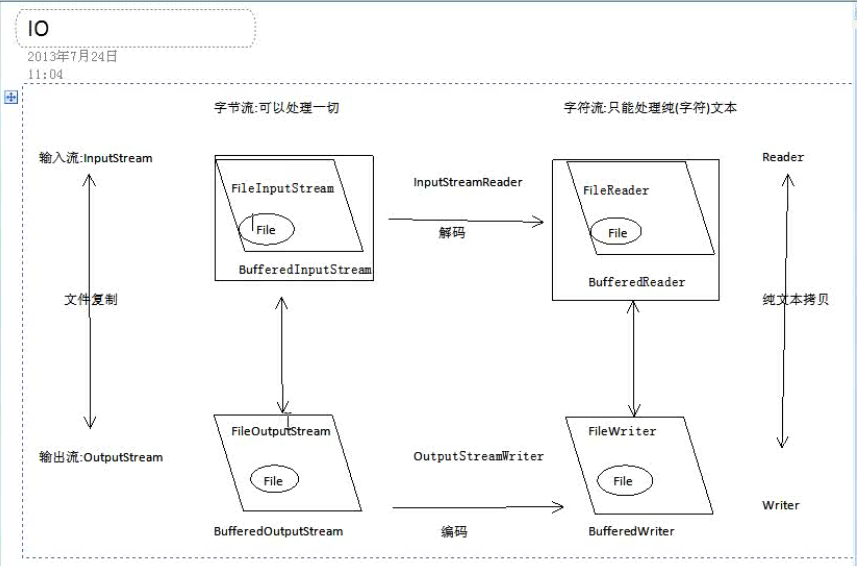
IO总结:
IO操作步骤:4步。创建源,选择流,操作,
如图
操作:递归打印,文件拷贝,关闭流的方法,文件的分割与合并。
相关文章推荐
- SpringMVC 的环境配置
- springMVC实现简单登录
- 在Struts2中使用ValueStack、ActionContext、ServletContext、request、session等
- 《2016展讯校招软开java笔试题》
- struts体系结构
- java hibernate +mysql demo
- java14 处理流
- java13 InputStream,Reader
- HDU1026 Ignatius and the Princess I(java)
- java12 File类
- java11 Guava:谷歌开发的集合库
- 在Eclipse中添加Servlet-api.jar的方法
- eclipse控制台输出重定向到…
- java10 WeakHashMap
- java08 Set
- java07 map
- Android studio导入eclipse项目且不改变目录结构
- 认识理解Java中native方法
- java06
- java05
