程序间的通信
2015-09-18 22:39
495 查看
程序见的通信,是对于两个程序间的传送数据的操作.下面是在AppDelegate里实现的方法,总共建立两个工程 步骤一模一样.
考虑到有的童鞋对xcode接触不久,我将整个.m文件全部复制了,对照者打就可以了.
@property (nonatomic , retain) UITextField *field;
@property (nonatomic , retain) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation AppDelegate
(BOOL)application:(UIApplication )application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary )launchOptions {
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
UIButton *button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeCustom];
button.frame = CGRectMake(100, 400, 100, 30);
button.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[self.window addSubview:button];
self.label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 300, 222, 30)];
self.label.backgroundColor = [UIColor grayColor];
[self.window addSubview:self.label];
self.field = [[UITextField alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 200, 222, 30)];
self.field.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.468 green:0.500 blue:0.470 alpha:1.000];
self.field.placeholder = @”shuruxinxi”;
[self.window addSubview:self.field];
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(button:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
return YES;
}
(void)button:(UIButton *)button
{
NSString *string = [self.field.text stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
if ([[UIApplication sharedApplication] canOpenURL:[NSURL URLWithString:str]]) {
}
else{
}
}
(BOOL)application:(UIApplication )application openURL:(NSURL )url sourceApplication:(NSString *)sourceApplication annotation:(id)annotation
{
self.label.text = [[url host] stringByReplacingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
return YES;
}
(void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application {
// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.
// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and throttle down OpenGL ES frame rates. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}
(void)applicationDidEnterBackground:(UIApplication *)application {
// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later.
// If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}
(void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application {
// Called as part of the transition from the background to the inactive state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}
(void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application {
// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}
(void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
// Saves changes in the application’s managed object context before the application terminates.
[self saveContext];
}
@synthesize managedObjectModel = _managedObjectModel;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator = _persistentStoreCoordinator;
(NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory {
// The directory the application uses to store the Core Data store file. This code uses a directory named “com.Try.__” in the application’s documents directory.
return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
}
(NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@”__” withExtension:@”momd”];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}
(NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and return a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@”__.sqlite”];
NSError *error = nil;
NSString *failureReason = @”There was an error creating or loading the application’s saved data.”;
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @”Failed to initialize the application’s saved data”;
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@”YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN” code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@”Unresolved error %@, %@”, error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
(NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext {
// Returns the managed object context for the application (which is already bound to the persistent store coordinator for the application.)
if (_managedObjectContext != nil) {
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSPersistentSt
4000
oreCoordinator *coordinator = [self persistentStoreCoordinator];
if (!coordinator) {
return nil;
}
_managedObjectContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] init];
[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = self.managedObjectContext;
if (managedObjectContext != nil) {
NSError *error = nil;
if ([managedObjectContext hasChanges] && ![managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@”Unresolved error %@, %@”, error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
}
}
@end
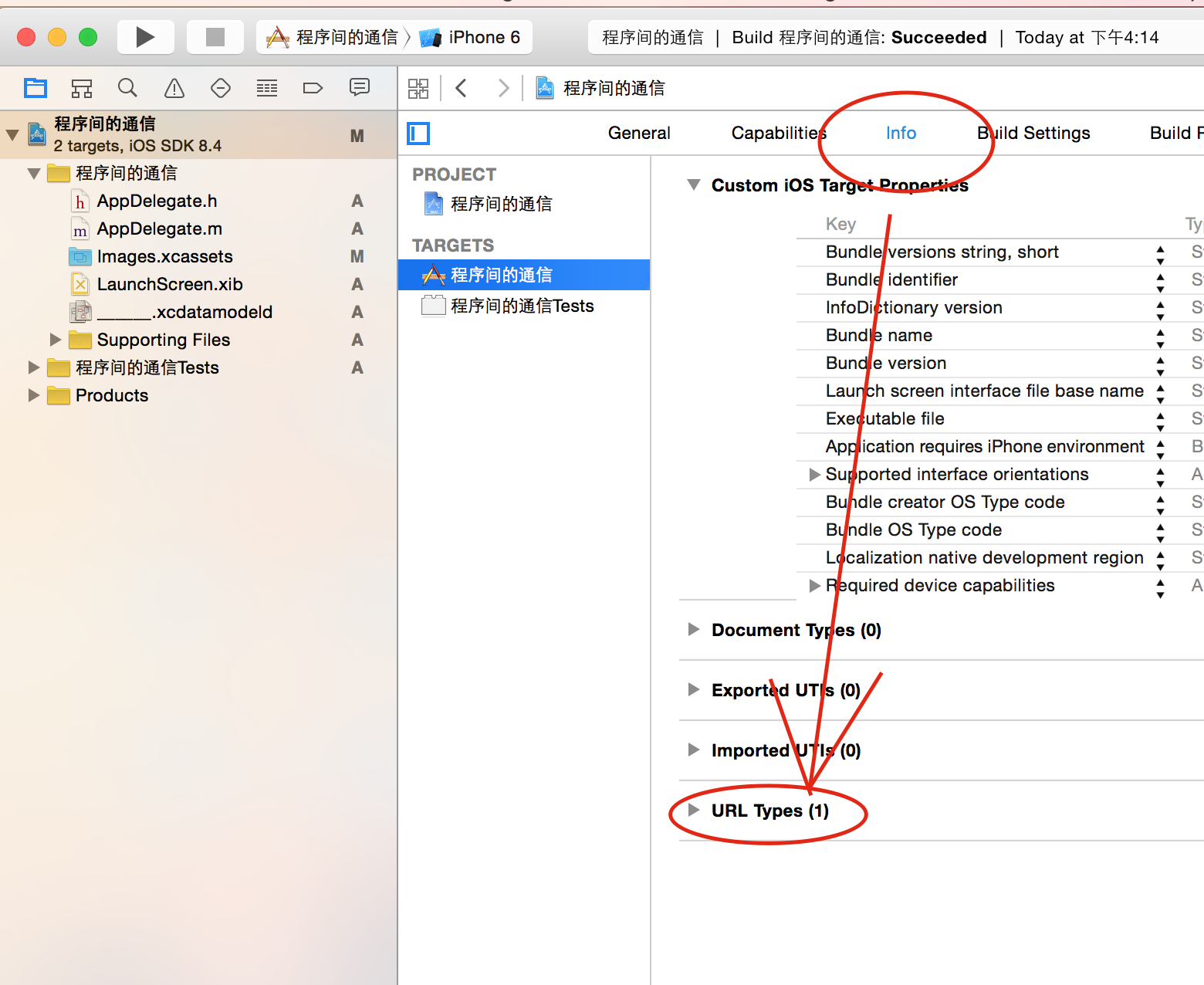
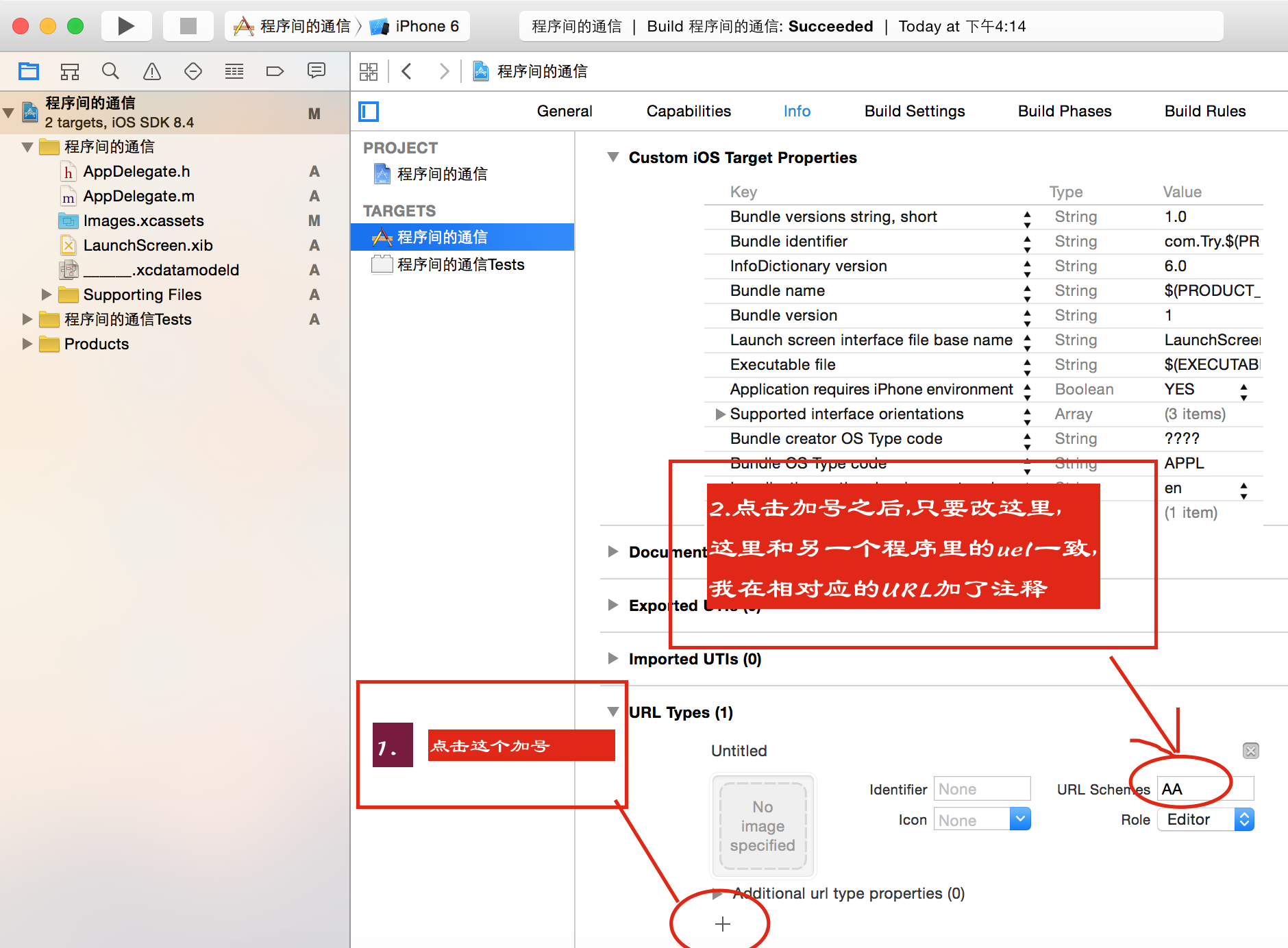
考虑到有的童鞋对xcode接触不久,我将整个.m文件全部复制了,对照者打就可以了.
记得实现的时候先让两个都运行一遍
import “AppDelegate.h”
@interface AppDelegate ()@property (nonatomic , retain) UITextField *field;
@property (nonatomic , retain) UILabel *label;
@end
@implementation AppDelegate
(BOOL)application:(UIApplication )application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary )launchOptions {
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
UIButton *button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeCustom];
button.frame = CGRectMake(100, 400, 100, 30);
button.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[self.window addSubview:button];
self.label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 300, 222, 30)];
self.label.backgroundColor = [UIColor grayColor];
[self.window addSubview:self.label];
self.field = [[UITextField alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 200, 222, 30)];
self.field.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.468 green:0.500 blue:0.470 alpha:1.000];
self.field.placeholder = @”shuruxinxi”;
[self.window addSubview:self.field];
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(button:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
return YES;
}
(void)button:(UIButton *)button
{
NSString *string = [self.field.text stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
这里就是我在下面改的东西.用它找到另一个工程,进行通信(BB就是另一个工程的,这个工程我起名叫AA)
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@”BB://%@”,string];if ([[UIApplication sharedApplication] canOpenURL:[NSURL URLWithString:str]]) {
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:str]];
}
else{
NSLog(@"faile");
}
}
(BOOL)application:(UIApplication )application openURL:(NSURL )url sourceApplication:(NSString *)sourceApplication annotation:(id)annotation
{
self.label.text = [[url host] stringByReplacingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
return YES;
}
(void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application {
// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.
// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and throttle down OpenGL ES frame rates. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}
(void)applicationDidEnterBackground:(UIApplication *)application {
// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later.
// If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}
(void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application {
// Called as part of the transition from the background to the inactive state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}
(void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application {
// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}
(void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
// Saves changes in the application’s managed object context before the application terminates.
[self saveContext];
}
pragma mark - Core Data stack
@synthesize managedObjectContext = _managedObjectContext;@synthesize managedObjectModel = _managedObjectModel;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator = _persistentStoreCoordinator;
(NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory {
// The directory the application uses to store the Core Data store file. This code uses a directory named “com.Try.__” in the application’s documents directory.
return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
}
(NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@”__” withExtension:@”momd”];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}
(NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and return a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@”__.sqlite”];
NSError *error = nil;
NSString *failureReason = @”There was an error creating or loading the application’s saved data.”;
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @”Failed to initialize the application’s saved data”;
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@”YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN” code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@”Unresolved error %@, %@”, error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
(NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext {
// Returns the managed object context for the application (which is already bound to the persistent store coordinator for the application.)
if (_managedObjectContext != nil) {
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSPersistentSt
4000
oreCoordinator *coordinator = [self persistentStoreCoordinator];
if (!coordinator) {
return nil;
}
_managedObjectContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] init];
[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];
return _managedObjectContext;
}
pragma mark - Core Data Saving support
(void)saveContext {NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = self.managedObjectContext;
if (managedObjectContext != nil) {
NSError *error = nil;
if ([managedObjectContext hasChanges] && ![managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@”Unresolved error %@, %@”, error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
}
}
@end
完成以上代码还有一个关键地方




相关文章推荐
- 峰回路转,Firefox 浏览器即将重返 iOS 平台
- 峰回路转,Firefox 浏览器即将重返 iOS 平台
- 我是运营,我没有假期
- 不可修补的 iOS 漏洞可能导致 iPhone 4s 到 iPhone X 永久越狱
- iOS 12.4 系统遭黑客破解,漏洞危及数百万用户
- 每日安全资讯:NSO,一家专业入侵 iPhone 的神秘公司
- [转][源代码]Comex公布JailbreakMe 3.0源代码
- DB2数据库的安装
- C#实现把指定数据写入串口
- “传奇”图象数据存储方式
- C#实现子窗体与父窗体通信方法实例总结
- 修复mysql数据库
- SQLServer 数据导入导出的几种方法小结
- MySQL数据备份之mysqldump的使用详解
- C#实现窗体间传递数据实例
- 给你的数据库文件减肥
- Oracle数据更改后出错的解决方法
- C#将Sql数据保存到Excel文件中的方法
- java和c#使用hessian通信的方法
