Java注解
2015-09-02 22:28
375 查看
注解定义
用一个词就可以描述注解,那就是元数据,即一种描述数据的数据。所以,可以说注解就是源代码的元数据。Annotation是一种应用于类、方法、参数、变量、构造器及包声明中的特殊修饰符。它是一种由JSR-175标准选择用来描述元数据的一种工具
注解有什么用?
使用Annotation之前(甚至在使用之后),XML被广泛的应用于描述元数据。XML配置其实就是为了分离代码和配置而引入的,而很多时候,希望使用一些和代码紧耦合的东西,比如想把某个方法声明为服务,那么使用Annotation会更好一些,因为这种情况下需要注解和方法紧密耦合起来。Annotations仅仅是元数据,和业务逻辑无关
注解分类
按照运行机制分类
源码注解 :只在源码中存在,编译成.class中不存在编译时注解 :在.class文件中也存在
运行时注解 :在运行阶段还会有逻辑作用的注解
按照来源分
JDK自带注解(比如:@Override,@Deprecated)
第三方注解
自定义注解
自定义注解
使用@interface关键字声明注解
成员以无参无异常的方式声明
可以指定默认值
成员是受限的,仅限于基本数据类型和String,Class,Annotation, Enumeration等类型。
如果注解只有一个成员,成员名只能叫
value(),在使用时可以忽略成员名和赋值号
可以没有成员,没有成员的注解称为标识注解
元注解
package com.weixuan.annotationtest;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @ClassName: Description
* @Description: 注解的作用域
* @author 韦轩
* @date 2015年9月2日 下午6:28:36
*/
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
/**
* @ClassName: Description
* @Description: 注解的生命周期
* @author 韦轩
* @date 2015年9月2日 下午6:28:54
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
/**
* @ClassName: Description
* @Description: 继承
* @author 韦轩
* @date 2015年9月2日 下午6:29:21
*
*/
@Inherited
/**
*
* @ClassName: Description
* @Description: Java doc
* @author 韦轩
* @date 2015年9月2日 下午6:29:49
*
*/
@Documented
public @interface Description {
String Desc();
String author();
int age() default 18;
}使用自定义注解
@注解名(<成员1>= “”,<成员2>=”“)@Description(desc="This is a test!",author="weixuan",age=22)
public void test() {
}解析注解
通过反射获取类、函数或成员上的运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑。package com.weixuan.annotationtest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
/**
* 使用类加载器加载类
*/
Class c = Class.forName("com.weixuan.annotationtest.TestAnnotation");
/**
* 找到类上面的注解
*/
boolean isExist = c.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class);
if (isExist) {
/**
* 拿到注解实例
*/
Description desc = (Description) c.getAnnotation(Description.class);
System.out.println(desc.desc());
System.out.println(desc.age());
System.out.println(desc.author());
}
/**
* 拿到方法上的注解
*/
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
for (Method ms : methods) {
boolean isMExist = ms.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class);
if (isMExist) {
Description d = ms.getAnnotation(Description.class);
System.out.println(d.desc());
}
}
}
}demo
为一个实体生成相应的SQLTable.java
package com.weixuan.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Table {
String value();
}Column.java
package com.weixuan.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Column {
String value();
}User.java
package com.weixuan.demo;
@Table("user")
public class User {
@Column("user_ID")
private Integer userID;
@Column("user_Name")
private String userName;
@Column("nick_Name")
private String nickName;
@Column("user_Age")
private Integer userAge;
@Column("city")
private String city;
@Column("email")
private String email;
public Integer getUserID() {
return userID;
}
public void setUserID(Integer userID) {
this.userID = userID;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public Integer getUserAge() {
return userAge;
}
public void setUserAge(Integer userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public User(Integer userID, String userName, String nickName, Integer userAge, String city, String email) {
super();
this.userID = userID;
this.userName = userName;
this.nickName = nickName;
this.userAge = userAge;
this.city = city;
this.email = email;
}
public User() {
super();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [userID=" + userID + ", userName=" + userName + ", nickName=" + nickName + ", userAge=" + userAge
+ ", city=" + city + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}Test.java
package com.weixuan.demo;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
private static String query(User user) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
Class c = user.getClass();
boolean isExist = c.isAnnotationPresent(Table.class);
if (!isExist)
return null;
Table table = (Table) c.getAnnotation(Table.class);
//获取表明=名
String tableName = table.value();
stringBuilder.append("select * from ").append(tableName).append(" where 1=1");
// 遍历所有字段
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
boolean isEt = field.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class);
if (!isEt)
continue;
Column column = field.getAnnotation(Column.class);
String fieldName = field.getName();
// 拿到字段对应的值,先拿到get方法
String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
Object fieldValue = null;
try {
Method method = c.getMethod(getMethodName);
fieldValue = method.invoke(user);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException | IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException
| InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!(fieldValue == null)) {
if (fieldValue instanceof String)
stringBuilder.append(" and ").append(fieldName).append(" like '").append(fieldValue).append("'");
else {
stringBuilder.append(" and ").append(fieldName).append(" = ").append(fieldValue);
}
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUserID(1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setCity("ChengDu");
User user3 = new User();
user3.setEmail("test@test.com");
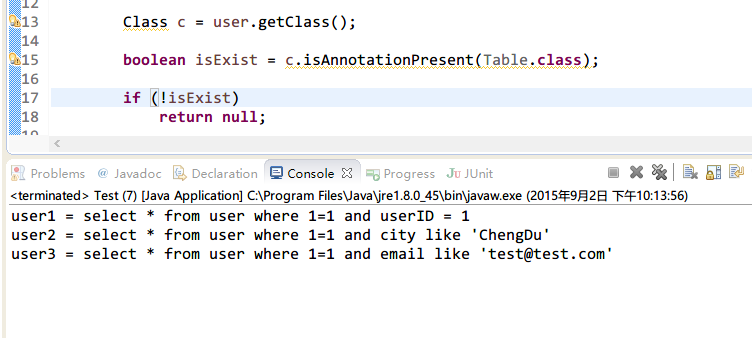
String sql1 = query(user1);
System.out.println("user1 = " + sql1);
String sql2 = query(user2);
System.out.println("user2 = " + sql2);
String sql3 = query(user3);
System.out.println("user3 = " + sql3);
}
}结果
相关文章推荐
- java对世界各个时区(TimeZone)的通用转换处理方法(转载)
- java-注解annotation
- java-模拟tomcat服务器
- java-用HttpURLConnection发送Http请求.
- java-WEB中的监听器Lisener
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- 介绍一款信息管理系统的开源框架---jeecg
- 聚类算法之kmeans算法java版本
- java实现 PageRank算法
- PropertyChangeListener简单理解
- 插入排序
- 冒泡排序
- 堆排序
- 快速排序
- 二叉查找树
- [原创]java局域网聊天系统
