Windows编程之最简单窗口程序
2015-07-20 16:21
513 查看
一、一些基本知识介绍
一些windows编程的https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff381404(v=vs.85).aspx
p代表“指针”
lp代表“长指针
DWORD_PTR
INT_PTR
LONG_PTR
ULONG_PTR
UINT_PTR
头文件WinNT.h定义了如下typedef (基于UTF-16编码,即是16bit),为了支持Unicode
一般来说,会经常看到如下编码的宽字符,即是前面加个L:
其他一些相关的typedef
windows支持unicode与ANSI,较新的则只支持Unicode
SetWindowTextA takes an ANSI string.
SetWindowTextW takes a Unicode string.
通过宏UNICODE来控制
示范例子:
二、windows窗口编程
1、窗口句柄
HWND,通常来自以下两个函数的返回值
CreateWindow and CreateWindowEx.
要操作窗口通常需要使用HWND作为参数传入函数使用,例如移动窗口MoveWindow:
另外句柄不是指针,不存在
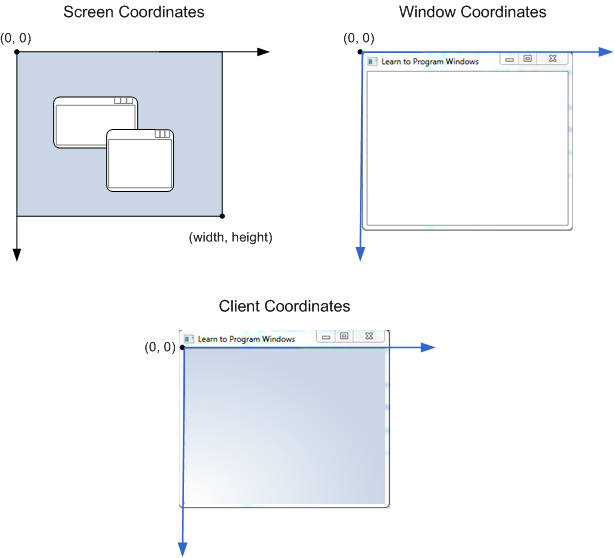
2、屏幕和窗口坐标
一般来说,windows的窗口都是以左上角为原点(0,0),另外一些坐标定义如图(图片来自msdn):
3、windows编程的入口点
WinMain or wWinMain
以wWinMain为例子
hInstance:标识executable
hPrevInstance:现在已经没有使用,始终为0,以前用在16位的windows中。
pCmdLine:包含Unicode字符串的命令行参数
nCmdShow:一个flag,表示应用程序窗口的显示如:最大化,最小化或者正常。
4、创建一个窗口的过程
(1)注册一个窗口类
lpfnWndProc:窗口过程,定义了绝多部分的动作
hInstance:来自wWinMain,实例句柄
lpszClassName:标识窗口类的字符串
传递WNDCLASS结构的地址给RegisterClass函数,注册窗口类到操作系统。
(2)创建窗口新实例
调用CreateWindowEx
第一个参数:
设定窗口中的一些可选行为(例如透明窗口),默认为0。
第二个参数:
定义窗口所创建的类型
第三个参数:
窗口标题,如果窗口存在标题栏则显示在其中。
第四个参数:
窗口的风格,定义了一些窗口外观和表现的标志组合,WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDO是几个标志结合的位或,包含最小化,最大化按钮,边框,标题栏等等
第五个参数:
位置和大小 CW_USEDEFAULT 使用默认值
第六个参数:
父窗口。
第七个参数:
菜单
第八个参数:
实例句柄
第九个参数:
指向void*的任意数据结构,传递数据所用
最后CreateWindowEx 返回句柄创建新窗口,如果失败返回0.
(3)显示窗口
要显示窗口则将窗口句柄传递给ShowWindow函数
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
hwnd 参数来自CreateWindowEx
nCmdShow参数用于最大化或者最小化窗口。操作系统将通过wWinMain函数传递该参数给程序
(4)窗口消息
窗口消息
MSG msg;GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0);
提取消息使用以下两个函数
TranslateMessage(&msg); DispatchMessage(&msg);
退出提取消息循环
退出提取消息循环
WM_QUIT是一个特殊的消息,它会令消息循环结束。消息循环的示例:
(4)窗口过程
The [b]DispatchMessage function
calls the window procedure of the window that is the target of the message. The window procedure has the following signature.[/b]
hwnd:窗口句柄
uMSg:消息代码
wParam、lParam:消息的其他数据
典型的窗口过程如下:
一个典型的窗口过程可能需要处理几十条消息,因此它可能会变得非常长,这样可以将每个消息的逻辑处理封装到一个单独的函数中n,
然后再在switch中处理。
假如不处理窗口过程特定的消息,可以直接返回默认的DefWindowProc函数,
(4)绘制窗口内容
更新绘图有两种选择:
*只更新一部分
*更新全部区域
下面代码是更新整个区域,使用单一颜色,采用系统默认的COLOR_WINDOW,颜色取决于系统的配色方案
完成绘图后,需要调用EndPaint,清除更新区域,表示绘图已经完成
三、最后的完整代码
[cpp] view
plaincopy


#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#include <Windows.h>
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE, PWSTR pCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
//Register the window class
const wchar_t CLASS_NAME[] = L"Sample Window Class";
WNDCLASS wc = { };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WindowProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpszClassName = CLASS_NAME;
RegisterClass(&wc);
//Create the window.
HWND hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, //Optional window styles.
CLASS_NAME, //Window class
L"Learn to Program Windows", //Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, //Window style
//Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, //Parent window
NULL, //Menu
hInstance, //Instance handle
NULL //Additional application data
);
if(hwnd == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
//Run the message loop.
MSG msg = { };
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
FillRect(hdc, &ps.rcPaint, (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1));
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
}
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
一些windows编程的https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff381404(v=vs.85).aspx
| Data type | Size | Signed? |
|---|---|---|
| BYTE | 8 bits | Unsigned |
| DWORD | 32 bits | Unsigned |
| INT32 | 32 bits | Signed |
| INT64 | 64 bits | Signed |
| LONG | 32 bits | Signed |
| LONGLONG | 64 bits | Signed |
| UINT32 | 32 bits | Unsigned |
| UINT64 | 64 bits | Unsigned |
| ULONG | 32 bits | Unsigned |
| ULONGLONG | 64 bits | Unsigned |
| WORD | 16 bits | Unsigned |
WinDef.h中定义了BOOL值
#define FALSE 0 #define TRUE 1
p代表“指针”
lp代表“长指针
DWORD_PTR
INT_PTR
LONG_PTR
ULONG_PTR
UINT_PTR
头文件WinNT.h定义了如下typedef (基于UTF-16编码,即是16bit),为了支持Unicode
typedef wchar_t WCHAR;
一般来说,会经常看到如下编码的宽字符,即是前面加个L:
wchar_t a = L'a'; wchar_t *str = L"hello";
其他一些相关的typedef
| Typedef | Definition |
|---|---|
| CHAR | char |
| PSTR or LPSTR | char* |
| PCSTR or LPCSTR | const char* |
| PWSTR or LPWSTR | wchar_t* |
| PCWSTR or LPCWSTR | const wchar_t* |
SetWindowTextA takes an ANSI string.
SetWindowTextW takes a Unicode string.
#ifdef UNICODE #define SetWindowText SetWindowTextW #else #define SetWindowText SetWindowTextA #endif
通过宏UNICODE来控制
| Macro | Unicode | ANSI |
|---|---|---|
| TCHAR | wchar_t | char |
| TEXT("x") | L"x" | "x" |
SetWindowTextW(L"My Application"); // Unicode function with wide-character string.
SetWindowTextA("My Application"); // ANSI function.#ifdef _UNICODE #define _tcslen wcslen #else #define _tcslen strlen #endif
二、windows窗口编程
1、窗口句柄
HWND,通常来自以下两个函数的返回值
CreateWindow and CreateWindowEx.
要操作窗口通常需要使用HWND作为参数传入函数使用,例如移动窗口MoveWindow:
BOOL MoveWindow(HWND hWnd, int X, int Y, int nWidth, int nHeight, BOOL bRepaint);
另外句柄不是指针,不存在
*hwnd
2、屏幕和窗口坐标
一般来说,windows的窗口都是以左上角为原点(0,0),另外一些坐标定义如图(图片来自msdn):

3、windows编程的入口点
WinMain or wWinMain
以wWinMain为例子
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, PWSTR pCmdLine, int nCmdShow);
hInstance:标识executable
hPrevInstance:现在已经没有使用,始终为0,以前用在16位的windows中。
pCmdLine:包含Unicode字符串的命令行参数
nCmdShow:一个flag,表示应用程序窗口的显示如:最大化,最小化或者正常。
4、创建一个窗口的过程
(1)注册一个窗口类
// Register the window class.
const wchar_t CLASS_NAME[] = L"Sample Window Class";
WNDCLASS wc = { };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WindowProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpszClassName = CLASS_NAME;lpfnWndProc:窗口过程,定义了绝多部分的动作
hInstance:来自wWinMain,实例句柄
lpszClassName:标识窗口类的字符串
传递WNDCLASS结构的地址给RegisterClass函数,注册窗口类到操作系统。
RegisterClass(&wc);
(2)创建窗口新实例
调用CreateWindowEx
HWND hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, // Optional window styles.
CLASS_NAME, // Window class
L"Learn to Program Windows", // Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, // Window style
// Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, // Parent window
NULL, // Menu
hInstance, // Instance handle
NULL // Additional application data
);
if (hwnd == NULL)
{
return 0;
}第一个参数:
Optional window styles.
设定窗口中的一些可选行为(例如透明窗口),默认为0。
第二个参数:
Window class
定义窗口所创建的类型
第三个参数:
Window text
窗口标题,如果窗口存在标题栏则显示在其中。
第四个参数:
Window style
窗口的风格,定义了一些窗口外观和表现的标志组合,WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDO是几个标志结合的位或,包含最小化,最大化按钮,边框,标题栏等等
第五个参数:
Size and position
位置和大小 CW_USEDEFAULT 使用默认值
第六个参数:
Parent window
父窗口。
第七个参数:
Menu
菜单
第八个参数:
Instance handle
实例句柄
第九个参数:
Additional application data
指向void*的任意数据结构,传递数据所用
最后CreateWindowEx 返回句柄创建新窗口,如果失败返回0.
(3)显示窗口
要显示窗口则将窗口句柄传递给ShowWindow函数
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
hwnd 参数来自CreateWindowEx
nCmdShow参数用于最大化或者最小化窗口。操作系统将通过wWinMain函数传递该参数给程序
(4)窗口消息
窗口消息
MSG msg;GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0);
提取消息使用以下两个函数
TranslateMessage(&msg); DispatchMessage(&msg);
退出提取消息循环
退出提取消息循环
PostQuitMessage(0);
WM_QUIT是一个特殊的消息,它会令消息循环结束。消息循环的示例:
// Correct.
MSG msg = { };
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}(4)窗口过程
The [b]DispatchMessage function
calls the window procedure of the window that is the target of the message. The window procedure has the following signature.[/b]
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
hwnd:窗口句柄
uMSg:消息代码
wParam、lParam:消息的其他数据
典型的窗口过程如下:
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_SIZE: // Handle window resizing
// etc
}一个典型的窗口过程可能需要处理几十条消息,因此它可能会变得非常长,这样可以将每个消息的逻辑处理封装到一个单独的函数中n,
然后再在switch中处理。
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_SIZE:
{
int width = LOWORD(lParam); // Macro to get the low-order word.
int height = HIWORD(lParam); // Macro to get the high-order word.
// Respond to the message:
OnSize(hwnd, (UINT)wParam, width, height);
}
break;
}
}
void OnSize(HWND hwnd, UINT flag, int width, int height);
{
// Handle resizing
}假如不处理窗口过程特定的消息,可以直接返回默认的DefWindowProc函数,
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);hui
(4)绘制窗口内容
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
// All painting occurs here, between BeginPaint and EndPaint.
FillRect(hdc, &ps.rcPaint, (HBRUSH) (COLOR_WINDOW+1));
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
}
return 0;
}更新绘图有两种选择:
*只更新一部分
*更新全部区域
下面代码是更新整个区域,使用单一颜色,采用系统默认的COLOR_WINDOW,颜色取决于系统的配色方案
FillRect(hdc, &ps.rcPaint, (HBRUSH) (COLOR_WINDOW+1));
完成绘图后,需要调用EndPaint,清除更新区域,表示绘图已经完成
三、最后的完整代码
[cpp] view
plaincopy

#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#include <Windows.h>
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE, PWSTR pCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
//Register the window class
const wchar_t CLASS_NAME[] = L"Sample Window Class";
WNDCLASS wc = { };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WindowProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpszClassName = CLASS_NAME;
RegisterClass(&wc);
//Create the window.
HWND hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, //Optional window styles.
CLASS_NAME, //Window class
L"Learn to Program Windows", //Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, //Window style
//Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, //Parent window
NULL, //Menu
hInstance, //Instance handle
NULL //Additional application data
);
if(hwnd == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
//Run the message loop.
MSG msg = { };
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
FillRect(hdc, &ps.rcPaint, (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1));
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
}
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
相关文章推荐
- java各种算法排序图解以及原码实现
- Java 的 Excel 导入功能实现
- Spring事务配置的五种方式
- ——JAVASE-集合(下)
- java.net.JarURLConnection示例
- Maven+eclipse创建JavaWeb项目
- java读取xml文件
- python中的os.path.dirname(__file__)的使用
- windows下java使用Sigar的配置
- Java synchronized 同步原语 详解
- Spring依赖注入
- 使用栈实现进制转换(java大数进制转换)
- Java魔法堂:String.format详解
- JAVA使用aspose.word 实现html转换word
- Java list foreach 修改元素
- 代码静态管理
- 解决Eclipse里项目名有红叉,但是底下的每一个文件都没有红叉
- Java并发编程的艺术
- 深入浅出 Java Concurrency (15): 锁机制 part 10 锁的一些其它问题
- Java中volatile关键字详解
