Java Exception和Error的区别
2015-07-19 16:47
507 查看
Java中异常的抽象类是Throwable,在此基础上,派生出两大类:Error和Exception。
Error是程序中的严重错误,不应该用try…catch包括。Javadoc的说明如下:
An Error is a subclass of Throwable that indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. Most such errors are abnormal conditions.
常见的Error有:AssertionError、OutOfMemoryError、StackOverflowError。
Exception分两类:Checked Exception和Unchecked Exception。
Unchecked Exception的基类是RuntimeException,所有继承自RuntimeException的Exception都属于Unchecked Exception, 如:NullPointerException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。
Checked Exception直接继承自Exception,所有不继承RuntimeException的Exception都属于Checked Exception,如:FileNotFoundException。
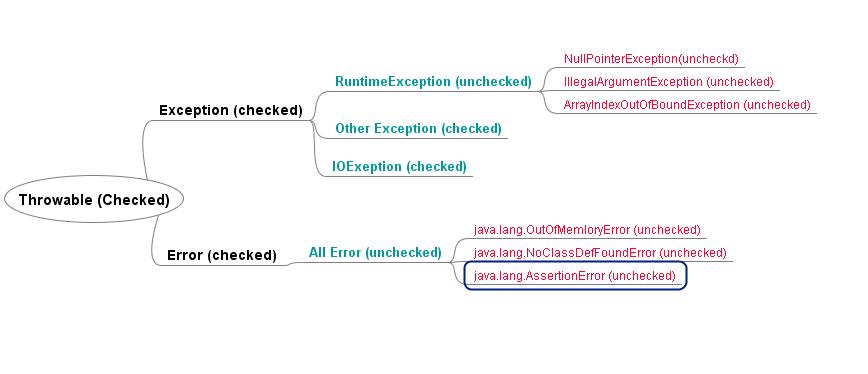
Checked Exception和Unchecked Exception都可以用try…catch包含。其中,Checked Exception在编译时检查是否有想要的catch处理,因此必要有try…catch包含,或者方法签名处抛出相应的异常。而Unchecked Exception在运行时判断,所以不一定要try…catch包含。而且,Unchecked Exception往往是程序本身存在bug,一般不catch这样的错误。
备注1:
在try中执行return语句,依然会执行finally语句块,除非在try语句中结束JVM进程(system.exit(0))
备注2:
不要在finally语句块调用return,否则的话,在try语句块中抛出的异常无法被调用者捕获,如下:
备注3:
throw与throws的区别:
throw是在语句块,程序员主动抛出一个异常。
throws是在方法的签名处,说明该方法可能抛出的异常。当有多个异常抛出时,用逗号分隔。
备注4:
从JDK7开始,同一个try对应的多个catch可以写在一起。
Error是程序中的严重错误,不应该用try…catch包括。Javadoc的说明如下:
An Error is a subclass of Throwable that indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. Most such errors are abnormal conditions.
常见的Error有:AssertionError、OutOfMemoryError、StackOverflowError。
Exception分两类:Checked Exception和Unchecked Exception。
Unchecked Exception的基类是RuntimeException,所有继承自RuntimeException的Exception都属于Unchecked Exception, 如:NullPointerException、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。
Checked Exception直接继承自Exception,所有不继承RuntimeException的Exception都属于Checked Exception,如:FileNotFoundException。
Checked Exception和Unchecked Exception都可以用try…catch包含。其中,Checked Exception在编译时检查是否有想要的catch处理,因此必要有try…catch包含,或者方法签名处抛出相应的异常。而Unchecked Exception在运行时判断,所以不一定要try…catch包含。而且,Unchecked Exception往往是程序本身存在bug,一般不catch这样的错误。
备注1:
在try中执行return语句,依然会执行finally语句块,除非在try语句中结束JVM进程(system.exit(0))
public class Hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
System.out.println("in try");
return;
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
//输出
in try
finally备注2:
不要在finally语句块调用return,否则的话,在try语句块中抛出的异常无法被调用者捕获,如下:
try {
doSomething();
System.out.println("No Exception Caught!");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("got it.");
}
}
public static void doSomething() {
try {
throw new RuntimeException();
} finally {
return;
}
}
//输出
No Exception Caught!备注3:
throw与throws的区别:
throw是在语句块,程序员主动抛出一个异常。
throws是在方法的签名处,说明该方法可能抛出的异常。当有多个异常抛出时,用逗号分隔。
备注4:
从JDK7开始,同一个try对应的多个catch可以写在一起。
相关文章推荐
- 访问Nginx发生SSL connection error的一种情况
- 星外虚拟主机访问被控出现Unspecified error解决方法
- IIS 错误 Server Application Error 详细解决方法
- On Error Resume Next 语句
- IIS运行错误 Server Application Error 错误代码 Error: 8004的解决方法
- Lua编程示例(一):select、debug、可变参数、table操作、error
- 收集整理的http/1.1 500 server error错误的解决方法
- SQL 2005 ERROR:3145 解决办法(备份集中的数据库备份与现有的数据库不同)
- VBScript中On Error语句用法小结
- MySQL抛出Incorrect string value异常分析
- Ajax Throws Sys.WebForms.PageRequestManagerErrorException with Response.Redirect的解决方法
- PHP函数之error_reporting(E_ALL ^ E_NOTICE)详细说明
- node.js使用npm 安装插件时提示install Error: ENOENT报错的解决方法
- 详解JavaScript中的异常处理方法
- java程序中的延时加载异常及解决方案
- .NET(C#):Emit创建异常处理的方法
- PHP 5.3和PHP 5.4出现FastCGI Error解决方法
- 解决mysql ERROR 1017:Can't find file: '/xxx.frm' 错误
- MYSQL ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user (using password: YES)问题的解决
- vs2012 error c4996: This function or variable may be unsafe
