数据结构基础温故-1.线性表(中)
2015-07-01 01:23
549 查看
在上一篇中,我们学习了线性表最基础的表现形式-顺序表,但是其存在一定缺点:必须占用一整块事先分配好的存储空间,在插入和删除操作上需要移动大量元素(即操作不方便),于是不受固定存储空间限制并且可以进行比较快捷地插入和删除操作的链表横空出世,所以我们就来复习一下链表。
View Code
测试结果如下图所示。

ListDictionary位于System.Collection.Specialized下,它是基于键值对(Key/Value)的集合,微软给出的建议是:通常用于包含10个或10个以下项的集合。

它的节点的数据域是一个键值对,而不是一个简单的value。
在.NET中,LinkedList<T>是使用地比较多的链表实现类,它位于System.Collections.Generic下,是一个通用的双向链表类,它不支持随机访问(即索引访问),但它实现了很多的新增节点的方法,例如:AddAfter、AddBefore、AddFirst以及AddLast等。其中,AddFirst是在现有节点之后添加新节点,AddBefore则是在现有节点之前添加新节点,AddFirst是在开头处添加,而AddLast则是在末尾处添加。
(2)陈广,《数据结构(C#语言描述)》
(3)段恩泽,《数据结构(C#语言版)》
(4)率辉,《数据结构高分笔记(2015版)》
作者:周旭龙
出处:http://edisonchou.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。
一、单链表基础
1.1 单链表的节点结构
/// <summary>
/// 双链表的模拟实现
/// </summary>
public class MyDoubleLinkedList<T>
{
private int count; // 字段:当前链表节点个数
private DbNode<T> head; // 字段:当前链表的头结点
// 属性:当前链表节点个数
public int Count
{
get
{
return this.count;
}
}
// 索引器
public T this[int index]
{
get
{
return this.GetNodeByIndex(index).Item;
}
set
{
this.GetNodeByIndex(index).Item = value;
}
}
public MyDoubleLinkedList()
{
this.count = 0;
this.head = null;
}
// Method01:根据索引获取节点
private DbNode<T> GetNodeByIndex(int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("index", "索引超出范围");
}
DbNode<T> tempNode = this.head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
tempNode = tempNode.Next;
}
return tempNode;
}
// Method02:在尾节点后插入新节点
public void AddAfter(T value)
{
DbNode<T> newNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
if (this.head == null)
{
// 如果链表当前为空则置为头结点
this.head = newNode;
}
else
{
DbNode<T> lastNode = this.GetNodeByIndex(this.count - 1);
// 调整插入节点与前驱节点指针关系
lastNode.Next = newNode;
newNode.Prev = lastNode;
}
this.count++;
}
// Method03:在尾节点前插入新节点
public void AddBefore(T value)
{
DbNode<T> newNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
if (this.head == null)
{
// 如果链表当前为空则置为头结点
this.head = newNode;
}
else
{
DbNode<T> lastNode = this.GetNodeByIndex(this.count - 1);
DbNode<T> prevNode = lastNode.Prev;
// 调整倒数第2个节点与插入节点的关系
prevNode.Next = newNode;
newNode.Prev = prevNode;
// 调整倒数第1个节点与插入节点的关系
lastNode.Prev = newNode;
newNode.Next = lastNode;
}
this.count++;
}
// Method04:在指定位置后插入新节点
public void InsertAfter(int index, T value)
{
DbNode<T> tempNode;
if (index == 0)
{
if (this.head == null)
{
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
this.head = tempNode;
}
else
{
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
tempNode.Next = this.head;
this.head.Prev = tempNode;
this.head = tempNode;
}
}
else
{
DbNode<T> prevNode = this.GetNodeByIndex(index); // 获得插入位置的节点
DbNode<T> nextNode = prevNode.Next; // 获取插入位置的后继节点
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
// 调整插入节点与前驱节点指针关系
prevNode.Next = tempNode;
tempNode.Prev = prevNode;
// 调整插入节点与后继节点指针关系
if (nextNode != null)
{
tempNode.Next = nextNode;
nextNode.Prev = tempNode;
}
}
this.count++;
}
// Method05:在指定位置前插入新节点
public void InsertBefore(int index, T value)
{
DbNode<T> tempNode;
if (index == 0)
{
if (this.head == null)
{
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
this.head = tempNode;
}
else
{
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
tempNode.Next = this.head;
this.head.Prev = tempNode;
this.head = tempNode;
}
}
else
{
DbNode<T> nextNode = this.GetNodeByIndex(index); // 获得插入位置的节点
DbNode<T> prevNode = nextNode.Prev; // 获取插入位置的前驱节点
tempNode = new DbNode<T>(value);
// 调整插入节点与前驱节点指针关系
prevNode.Next = tempNode;
tempNode.Prev = prevNode;
// 调整插入节点与后继节点指针关系
tempNode.Next = nextNode;
nextNode.Prev = tempNode;
}
this.count++;
}
// Method06:移除指定位置的节点
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
if (index == 0)
{
this.head = this.head.Next;
}
else
{
DbNode<T> prevNode = this.GetNodeByIndex(index - 1);
if (prevNode.Next == null)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("index", "索引超出范围");
}
DbNode<T> deleteNode = prevNode.Next;
DbNode<T> nextNode = deleteNode.Next;
prevNode.Next = nextNode;
if(nextNode != null)
{
nextNode.Prev = prevNode;
}
deleteNode = null;
}
this.count--;
}
}View Code
4.4 双链表模拟实现的简单测试
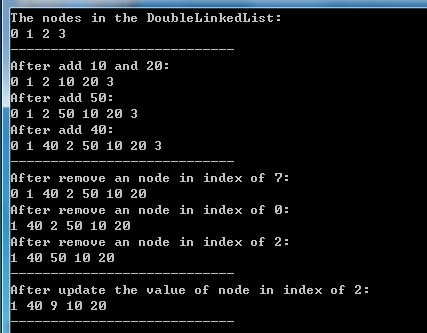
这里跟单链表一样,进行几个简单的测试:一是顺序插入(默认在尾节点之后)4个新节点,二是在尾节点之前和在指定索引位置插入新节点,三是移除指定索引位置的节点,四是修改某个节点的Item值。测试代码如下所示。static void MyDoubleLinkedListTest()
{
MyDoubleLinkedList<int> linkedList = new MyDoubleLinkedList<int>();
// Test1:顺序插入4个节点
linkedList.AddAfter(0);
linkedList.AddAfter(1);
linkedList.AddAfter(2);
linkedList.AddAfter(3);
Console.WriteLine("The nodes in the DoubleLinkedList:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
// Test2.1:在尾节点之前插入2个节点
linkedList.AddBefore(10);
linkedList.AddBefore(20);
Console.WriteLine("After add 10 and 20:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Test2.2:在索引为2(即第3个节点)的位置之后插入单个节点
linkedList.InsertAfter(2, 50);
Console.WriteLine("After add 50:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Test2.3:在索引为2(即第3个节点)的位置之前插入单个节点
linkedList.InsertBefore(2, 40);
Console.WriteLine("After add 40:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
// Test3.1:移除索引为7(即最后一个节点)的位置的节点
linkedList.RemoveAt(7);
Console.WriteLine("After remove an node in index of 7:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Test3.2:移除索引为0(即第一个节点)的位置的节点的值
linkedList.RemoveAt(0);
Console.WriteLine("After remove an node in index of 0:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Test3.3:移除索引为2(即第3个节点)的位置的节点
linkedList.RemoveAt(2);
Console.WriteLine("After remove an node in index of 2:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
// Test4:修改索引为2(即第3个节点)的位置的节点的值
linkedList[2] = 9;
Console.WriteLine("After update the value of node in index of 2:");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(linkedList[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
}测试结果如下图所示。

五、.NET中的ListDictionary与LinkedList<T>
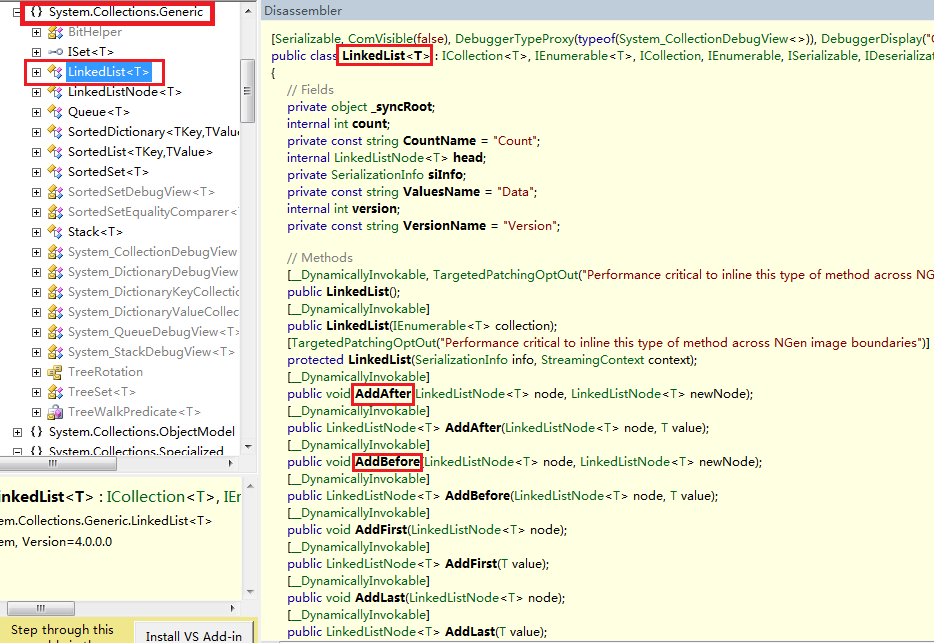
在.NET中,已经为我们提供了单链表和双链表的实现,它们分别是ListDictionary与LinkedList<T>。从名称可以看出,单链表的实现ListDictionary不是泛型实现,而LinkedList是泛型实现,它们又到底有什么区别呢,借助Reflector去看看吧。5.1 ListDictionary—基于key/value的单链表

ListDictionary位于System.Collection.Specialized下,它是基于键值对(Key/Value)的集合,微软给出的建议是:通常用于包含10个或10个以下项的集合。

它的节点的数据域是一个键值对,而不是一个简单的value。
5.2 LinkedList—神奇的泛型双向链表

在.NET中,LinkedList<T>是使用地比较多的链表实现类,它位于System.Collections.Generic下,是一个通用的双向链表类,它不支持随机访问(即索引访问),但它实现了很多的新增节点的方法,例如:AddAfter、AddBefore、AddFirst以及AddLast等。其中,AddFirst是在现有节点之后添加新节点,AddBefore则是在现有节点之前添加新节点,AddFirst是在开头处添加,而AddLast则是在末尾处添加。
参考资料
(1)程杰,《大话数据结构》(2)陈广,《数据结构(C#语言描述)》
(3)段恩泽,《数据结构(C#语言版)》
(4)率辉,《数据结构高分笔记(2015版)》
作者:周旭龙
出处:http://edisonchou.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。
相关文章推荐
- 常见数据结构算法边学边记
- 数据结构-中序转后序
- sizzle.js学习笔记利用闭包模拟实现数据结构:字典(Map)
- 【数据结构】链表
- get(index) set(index value), setAll(value)都为O(1)的数据结构
- 数据结构的基本概念
- 数据结构常见面试题
- java 数据结构
- 数据结构链表的操作集合(建立,遍历,插入,删除,排序,长度,空判断等)
- 数据结构顺序表的操作全集(创建,遍历,插入,删除,排序等等)
- swift篇第一期:简单的数据结构
- 大话数据机构——第一张 数据结构绪论
- 经典算法研究系列:五、红黑树算法的实现与剖析
- 《数据结构与算法分析c++描述》读书笔记三——AVL树
- 《数据结构与算法分析c++描述》读书笔记一——表
- 数据结构和算法第一章
- 数据结构和算法系列 - AVL树
- 数据结构基础
- 数据结构--线性表
- BST数据结构题
