用一维数组实现栈(C++编程思想 p120)
2015-06-07 19:40
405 查看
1 实现思路
向栈中插入4个元素后的状态
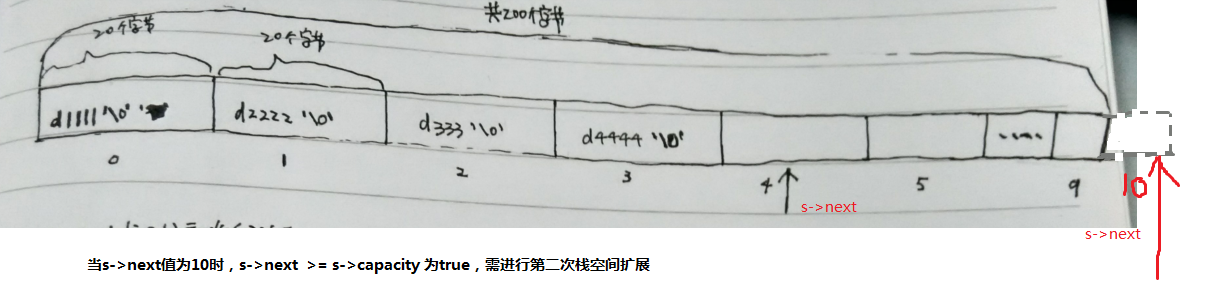
执行过程分析:

2 代码实现
clib.h 接口定义
2 Clib.cpp 函数实现
inflate increase 10
fetch result d3333
freeing storage
向栈中存放int型数据测试:
inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&intStash, 0) = 0
fetch(&intStash, 1) = 1
fetch(&intStash, 2) = 2
fetch(&intStash, 3) = 3
fetch(&intStash, 4) = 4
fetch(&intStash, 5) = 5
fetch(&intStash, 6) = 6
fetch(&intStash, 7) = 7
fetch(&intStash, 8) = 8
fetch(&intStash, 9) = 9
fetch(&intStash, 10) = 10
fetch(&intStash, 11) = 11
fetch(&intStash, 12) = 12
fetch(&intStash, 13) = 13
fetch(&intStash, 14) = 14
fetch(&intStash, 15) = 15
fetch(&intStash, 16) = 16
fetch(&intStash, 17) = 17
fetch(&intStash, 18) = 18
fetch(&intStash, 19) = 19
freeing storage
向栈中存放字符串(字符数组指针)测试:
inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&stringStash, 1) = typedef struct CStashTag
fetch(&stringStash, 2) = {
fetch(&stringStash, 3) = int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
fetch(&stringStash, 4) = int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 5) = int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 6) = unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
fetch(&stringStash, 7) = } CStash;
fetch(&stringStash, 8) =
fetch(&stringStash, 9) = void initalize(CStash* s, int size);
fetch(&stringStash, 10) = void cleanup(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 11) = int add(CStash* s, const void* element);
fetch(&stringStash, 12) = void* fetch(CStash* s, int index);
fetch(&stringStash, 13) = int count(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 14) = void inflate(CStash* s, int increase = 10);
freeing storage
附C++实现:
1)Stash.h头文件
2)Stash.cpp实现文件
3)main.cpp测试类
向栈中插入4个元素后的状态

执行过程分析:

2 代码实现
clib.h 接口定义
typedef struct CStashTag
{
int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
} CStash;
void initalize(CStash* s, int size);
void cleanup(CStash* s);
int add(CStash* s, const void* element);
void* fetch(CStash* s, int index);
int count(CStash* s);
void inflate(CStash* s, int increase = 10);2 Clib.cpp 函数实现
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include "clib.h"
using namespace std;
void initalize(CStash* s, int sz)
{
s->ele_size = sz;
s->capacity = 0;
s->next = 0;
s->storage = 0;
}
int add(CStash* s, const void* element)
{
if (s->next >= s->capacity)
{
inflate(s);
}
int startBytes = s->next * s->ele_size;
unsigned char* e = (unsigned char*)element;
for (int i=0; i<s->ele_size; i++)
s->storage[startBytes + i] = e[i];
s->next++;
return s->next - 1;
}
//取出索引index处的栈元素
void* fetch(CStash* s, int index)
{
assert(0 <= index);
if (index >= s->next)
{
return 0;
}
return &(s->storage[index * s->ele_size]);
}
//返回栈中元素的个数
int count(CStash* s)
{
return s->next;
}
//扩展栈空间,增加increase个元素空间
void inflate(CStash* s, int increase)
{
printf("inflate increase %d\n", increase);
assert(increase > 0);
//原栈长 + 增加的栈元素个数
int newCapacity = s->capacity + increase;
int newBytes = newCapacity * s->ele_size; //新的栈空间字节数
int oldBytes = s->capacity * s->ele_size; //旧的栈空间字节数
unsigned char* b = new unsigned char[newBytes]; //在堆上分配新的栈空间
if (oldBytes)
{
//拷贝旧的栈空间的内容到新的栈空间,并释放旧的栈空间
//把旧内存块中的数据拷贝到新分配的内存块
for (int i=0; i<oldBytes; i++)
b[i] = s->storage[i];
delete [] (s->storage); //释放旧的内存块
}
s->storage = b; //使栈存储空间字符指针s->storage指向新分配的内存块
s->capacity = newCapacity; //更新栈的容量
}
//清理栈存储空间字符指针
void cleanup(CStash* s)
{
if (s->storage != 0)
{
cout<<"freeing storage"<<endl;
delete []s->storage;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CStash stash;
char str1[] = "d1111";
char str2[] = "d2222";
char str3[] = "d3333";
char str4[] = "d4444";
initalize(&stash, 20);
add(&stash, str1);
add(&stash, str2);
add(&stash, str3);
add(&stash, str4);
unsigned char* result = (unsigned char*)fetch(&stash, 2);
printf("fetch result %s\n", result);
cleanup(&stash);
return 0;
};
输出:inflate increase 10
fetch result d3333
freeing storage
向栈中存放int型数据测试:
void intTest()
{
CStash intStash;
initalize(&intStash, sizeof(int)); //栈中存放int型数据,所以栈元素占用int--4个字节
int i;
for (i=0; i<20; i++)
add(&intStash, &i);
for (i=0; i<count(&intStash); i++)
cout<< "fetch(&intStash, " << i << ") = " << *(int *) fetch(&intStash, i) <<endl;
cleanup(&intStash);
}
输出:inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&intStash, 0) = 0
fetch(&intStash, 1) = 1
fetch(&intStash, 2) = 2
fetch(&intStash, 3) = 3
fetch(&intStash, 4) = 4
fetch(&intStash, 5) = 5
fetch(&intStash, 6) = 6
fetch(&intStash, 7) = 7
fetch(&intStash, 8) = 8
fetch(&intStash, 9) = 9
fetch(&intStash, 10) = 10
fetch(&intStash, 11) = 11
fetch(&intStash, 12) = 12
fetch(&intStash, 13) = 13
fetch(&intStash, 14) = 14
fetch(&intStash, 15) = 15
fetch(&intStash, 16) = 16
fetch(&intStash, 17) = 17
fetch(&intStash, 18) = 18
fetch(&intStash, 19) = 19
freeing storage
向栈中存放字符串(字符数组指针)测试:
void stringTest()
{
CStash stringStash;
ifstream in;
const int bufsize = 80;
initalize(&stringStash, sizeof(char) * bufsize);
in.open("clib.h");
assert(in);
string line;
while (getline(in, line))
{
add(&stringStash, line.c_str());
}
char *cp;
int i = 0;
while ((cp = (char *) fetch(&stringStash, i++)) != 0)
{
cout<< "fetch(&stringStash, " << i << ") = " << cp << endl;
}
cleanup(&stringStash);
}
输出:inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&stringStash, 1) = typedef struct CStashTag
fetch(&stringStash, 2) = {
fetch(&stringStash, 3) = int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
fetch(&stringStash, 4) = int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 5) = int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 6) = unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
fetch(&stringStash, 7) = } CStash;
fetch(&stringStash, 8) =
fetch(&stringStash, 9) = void initalize(CStash* s, int size);
fetch(&stringStash, 10) = void cleanup(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 11) = int add(CStash* s, const void* element);
fetch(&stringStash, 12) = void* fetch(CStash* s, int index);
fetch(&stringStash, 13) = int count(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 14) = void inflate(CStash* s, int increase = 10);
freeing storage
附C++实现:
1)Stash.h头文件
#ifndef STASH_H_INCLUDED
#define STASH_H_INCLUDED
class Stash
{
int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
void inflate(int increase = 10);
public:
void initalize(int sz);
int add(const void* element);
void* fetch(int index);
int count();
void cleanup();
};
#endif // STASH_H_INCLUDED2)Stash.cpp实现文件
#include "Stash.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
void Stash::initalize(int sz)
{
ele_size = sz;
capacity = 0;
next = 0;
storage = 0;
}
int Stash::add(const void *element)
{
if (next >= capacity)
{
inflate();
}
int startBytes = next * ele_size;
unsigned char *e = (unsigned char *) element;
for (int i=0; i<ele_size; i++)
{
storage[startBytes + i] = e[i];
}
next++;
return next-1;
}
void Stash::inflate(int increase)
{
cout << "inflate increase: " << increase << endl;
assert(increase > 0);
int newCapacity = capacity + increase;
int newBytes = newCapacity * ele_size;
int oldBytes = capacity * ele_size;
unsigned char *b = new unsigned char[newBytes];
if (oldBytes)
{
for (int i=0; i<oldBytes; i++)
b[i] = storage[i];
delete []storage;
}
storage = b;
capacity = newCapacity;
}
void* Stash::fetch(int index)
{
assert(index >= 0);
if (index > next)
return 0;
return &(storage[index * ele_size]);
}
int Stash::count()
{
return next;
}
void Stash::cleanup()
{
if (storage != 0)
{
cout << "freeing storage .... " << endl;
delete []storage;
}
}3)main.cpp测试类
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include "Stash.h"
using namespace std;
void intTest()
{
Stash intStash;
intStash.initalize(sizeof(int)); //栈中存放int型数据,所以栈元素占用int--4个字节
int i;
for (i=0; i<20; i++)
intStash.add(&i);
for (i=0; i<intStash.count(); i++)
cout<< "intStash.fetch(" << i << ") = " << *(int *) intStash.fetch(i) <<endl;
intStash.cleanup();
}
void stringTest()
{
Stash stringStash;
ifstream in;
const int bufsize = 80;
stringStash.initalize(sizeof(char) * bufsize);
in.open("Stash.h");
string line;
while (getline(in, line))
{
stringStash.add(line.c_str());
}
char *cp;
int i = 0;
while ((cp = (char *) stringStash.fetch(i++)) != 0)
{
cout<< "stringStash.fetch(" << i << ") = " << cp << endl;
}
stringStash.cleanup();
}
int main()
{
//intTest();
stringTest();
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- C++ tips: 类成员函数的参数默认值
- C语言里字符串的解析
- C++ 第8章 函数探幽
- C++ tips: std::stringstream 对象的复用
- C++ tips: throw和throw+对象的差别
- 【学习笔记】【C语言】逻辑运算符
- 类模板相互引用的问题(错误:缺少类型说明符-假定为int。注意:C++不支持默认int)
- chapter11test5
- 类模板相互引用的问题(错误:缺少类型说明符-假定为int。注意:C++不支持默认int)
- C++中的explicit关键字
- 黑马程序员——OC语言基础——面向对象三大特性之继承
- C++文件读写详解(ofstream,ifstream,fstream)
- 二值图像边缘提取算法C语言实现
- c++ --> 复制构造函数
- c语言编写贪吃蛇修改后最新版
- c++ --> 构造函数与析构函数
- C 链表
- 浅谈工作中使用过的几种C++界面库
- 初学c++之template <typename T>
- c++模板学习
