C++编程中时间使用总结
2014-11-07 09:43
155 查看
各种时间类/数据结构
与时间相关的类和数据结构有:1. CTime
2. CTimeSpan
3. __time64_t和time_t
4. struct tm
5. SYSTEMTIME
6. FILETIME
7. DBTIMESTAMP
一. CTime
// 微软文档http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/78zb0ese.aspx
1.1 定义
class CTime
{
public:
static CTime WINAPI GetCurrentTime() throw();
static BOOL WINAPI IsValidFILETIME(_In_ const FILETIME& ft) throw();
CTime() throw();
CTime(_In_ __time64_t time) throw();
CTime(_In_ int nYear, _In_ int nMonth, _In_ int nDay, _In_ int nHour, _In_ int nMin, _In_ int nSec, _In_ int nDST = -1);
CTime(_In_ WORD wDosDate, _In_ WORD wDosTime, _In_ int nDST = -1);
CTime(_In_ const SYSTEMTIME& st, _In_ int nDST = -1);
CTime(_In_ const FILETIME& ft, _In_ int nDST = -1);
CTime(_In_ const DBTIMESTAMP& dbts, _In_ int nDST = -1) throw();
CTime& operator=(_In_ __time64_t time) throw();
CTime& operator+=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) throw();
CTime& operator-=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) throw();
CTimeSpan operator-(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
CTime operator-(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
CTime operator+(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator==(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
bool operator!=(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
bool operator<(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
bool operator>(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
bool operator<=(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
bool operator>=(_In_ CTime time) const throw();
struct tm* GetGmtTm(_Out_ struct tm* ptm) const;
struct tm* GetLocalTm(_Out_ struct tm* ptm) const;
bool GetAsSystemTime(_Out_ SYSTEMTIME& st) const throw();
bool GetAsDBTIMESTAMP(_Out_ DBTIMESTAMP& dbts) const throw();
__time64_t GetTime() const throw();
int GetYear() const throw();
int GetMonth() const throw();
int GetDay() const throw();
int GetHour() const throw();
int GetMinute() const throw();
int GetSecond() const throw();
int GetDayOfWeek() const throw();
// formatting using "C" strftime
CString Format(_In_z_ LPCTSTR pszFormat) const;
CString FormatGmt(_In_z_ LPCTSTR pszFormat) const;
CString Format(_In_ UINT nFormatID) const;
CString FormatGmt(_In_ UINT nFormatID) const;
#if defined(_AFX) && defined(_UNICODE)
// for compatibility with MFC 3.x
CString Format(_In_z_ LPCSTR pFormat) const;
CString FormatGmt(_In_z_ LPCSTR pFormat) const;
#endif
#ifdef _AFX
CArchive& Serialize64(_In_ CArchive& ar);
#endif
private:
__time64_t m_time;
};1.2 使用
1.2.1 构造
// 1993年3月19日22:15:00 (年月日, 时分秒)CTime t(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0);
nYear 1970–3000
nMonth 1–12
nDay 1–31
nHour 0-23
nMin 0-59
nSec 0-59
1.2.2 格式化成字符串
CTime t(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0);// "Friday, March 19, 1999"
CString s = t.Format(_T("%A, %B %d, %Y"));
CTime::Format的参数
%a 缩写的星期名称
%A 完整星期名称
%b 缩写的月份名称
%B 完整的月份名称。
%c 日期和时间表示恰当的区域设置
%d 日期为十进制数字 (01 - 31) 的月份
%H 以 24 小时格式 (00 - 23) 的点
%I 以 12 小时格式 (01 - 12) 的点
%j 日期为十进制数字 (001 - 366)。
%m 为十进制数字 (01 - 12) 的月份
%M 为十进制数字 (00 - 59) 的分钟
%p 12 小时时钟的当前区域设置的 A.M/P.M. 指示器
%S 其次为十进制数字 (00 - 59)
%U 周为十进制数字的年份,周日为一周的第一天 (00 - 53)
%w 周为十进制数字 (0 - 6 ;0 是星期天)
%W 周为十进制数字的年份,星期一为一周的第一天 (00 - 53)
%x 当前区域设置的日期显示
%X 当前区域设置的时间显示
%y 无世纪年,为十进制数字 (00 - 99)
%Y 世纪年,为十进制数字
%z, %Z 根据注册表设置,无论是时区名称或时区缩写,如果时区未知,则没有字符
%% 百分号
1.2.3 获取当前时间
CTime tm = CTime::GetCurrentTime();__time64_t CTime::GetTime( ) const throw( );
// 返回1970年一月1日到CTime对象之间的秒数
1.2.4 获取 年月日, 时分秒
// 10:15 PM March 19, 1999CTime t(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0);
ATLASSERT(t.GetYear() == 1999);
ATLASSERT(t.GetMonth() == 3);
ATLASSERT(t.GetDay() == 19);
ATLASSERT(t.GetHour() == 22);
ATLASSERT(t.GetMinute() == 15);
ATLASSERT(t.GetSecond() == 0);
ATLASSERT(t.GetDayOfWeek() == 1);
ATLASSERT(t.GetDayOfWeek() == 7);
1.2.5 CTime转tm; CTime转time_t; CTime转SYSTEMTIME;
struct tm* CTime::GetGmtTm(struct tm* ptm) const;struct tm* CTime::GetLocalTm(struct tm* ptm) const;
__time64_t CTime::GetTime( ) const throw( ); // 返回1970年一月1日到CTime对象之间的秒数
bool GetAsSystemTime(_Out_ SYSTEMTIME& st) const throw();
bool GetAsDBTIMESTAMP(_Out_ DBTIMESTAMP& dbts) const throw();
1.2.6 举例
CTime time1 = CTime::GetCurrentTime(); // 获取当前时间CTime time2(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0); // 构造一个时间
CTime time3(1999, 3, 18, 22, 14, 30); // 构造一个时间
// time2与time3 时间相差1天0小时0分钟30秒(1 * 24 * 60 * 60 + 30)
CTimeSpan timeSpan = time2 - time3;
int nTemp = 0;
nTemp = timeSpan.GetDays(); // 1
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalHours(); // 24
nTemp = timeSpan.GetHours(); // 0
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalMinutes(); // 1440
nTemp = timeSpan.GetMinutes(); // 0
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalSeconds(); // 86430
nTemp = timeSpan.GetSeconds(); // 30
CString strTemp = time2.Format(_T("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %A")); // 输出格式: 1999-03-19 22:15:00 Friday
nTemp = time2.GetYear(); // 1999
nTemp = time2.GetMonth(); // 3
nTemp = time2.GetDay(); // 19
nTemp = time2.GetHour(); // 22
nTemp = time2.GetMinute(); // 15
nTemp = time2.GetSecond(); // 0
nTemp = time2.GetDayOfWeek(); // 6
二. CTimeSpan
用于表示时间范围2.1 定义
class CTimeSpan
{
public:
CTimeSpan() throw();
CTimeSpan(_In_ __time64_t time) throw();
CTimeSpan(_In_ LONG lDays, _In_ int nHours, _In_ int nMins, _In_ int nSecs) throw();
LONGLONG GetDays() const throw();
LONGLONG GetTotalHours() const throw();
LONG GetHours() const throw();
LONGLONG GetTotalMinutes() const throw();
LONG GetMinutes() const throw();
LONGLONG GetTotalSeconds() const throw();
LONG GetSeconds() const throw();
__time64_t GetTimeSpan() const throw();
CTimeSpan operator+(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
CTimeSpan operator-(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
CTimeSpan& operator+=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) throw();
CTimeSpan& operator-=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) throw();
bool operator==(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator!=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator<(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator>(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator<=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
bool operator>=(_In_ CTimeSpan span) const throw();
public:
CString Format(_In_z_ LPCTSTR pszFormat) const;
CString Format(_In_ UINT nID) const;
#if defined(_AFX) && defined(_UNICODE)
// for compatibility with MFC 3.x
CString Format(_In_z_ LPCSTR pFormat) const;
#endif
#ifdef _AFX
CArchive& Serialize64(_In_ CArchive& ar);
#endif
private:
__time64_t m_timeSpan;
};2.2 举例
CTime time1 = CTime::GetCurrentTime(); // 获取当前时间CTime time2(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0); // 构造一个时间
CTime time3(1999, 3, 18, 22, 14, 30); // 构造一个时间
// time2与time3 时间相差1天0小时0分钟30秒(1 * 24 * 60 * 60 + 30)
CTimeSpan timeSpan = time2 - time3;
int nTemp = 0;
nTemp = timeSpan.GetDays(); // 1
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalHours(); // 24
nTemp = timeSpan.GetHours(); // 0
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalMinutes(); // 1440
nTemp = timeSpan.GetMinutes(); // 0
nTemp = timeSpan.GetTotalSeconds(); // 86430
nTemp = timeSpan.GetSeconds(); // 30
CString strTemp = time2.Format(_T("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %A")); // 输出格式: 1999-03-19 22:15:00 Friday
nTemp = time2.GetYear(); // 1999
nTemp = time2.GetMonth(); // 3
nTemp = time2.GetDay(); // 19
nTemp = time2.GetHour(); // 22
nTemp = time2.GetMinute(); // 15
nTemp = time2.GetSecond(); // 0
nTemp = time2.GetDayOfWeek(); // 6
三. __time64_t和time_t
就是一个64位的整形, 可以表示秒数typedef __time64_t time_t; /* time value */
typedef __int64 __time64_t; /* 64-bit time value */
time_t now;
time(&now); // 获取当前时间
四. struct tm
struct tm {int tm_sec; /* seconds after the minute - [0,59] */
int tm_min; /* minutes after the hour - [0,59] */
int tm_hour; /* hours since midnight - [0,23] */
int tm_mday; /* day of the month - [1,31] */
int tm_mon; /* months since January - [0,11] */
int tm_year; /* years since 1900 */
int tm_wday; /* days since Sunday - [0,6] */
int tm_yday; /* days since January 1 - [0,365] */
int tm_isdst; /* daylight savings time flag 夏令时标识符,实行夏令时的时候,tm_isdst为正。 */
/* 不实行夏令时的进候,tm_isdst为0;不了解情况时,tm_isdst()为负*/
};
4.1 CTime与tm
CTime有函数可以填充tm;struct tm* CTime::GetGmtTm(struct tm* ptm) const; // 获取CTime对象的时间
struct tm* CTime::GetLocalTm(struct tm* ptm) const; // 获取当前时间
4.2 CTime转tm
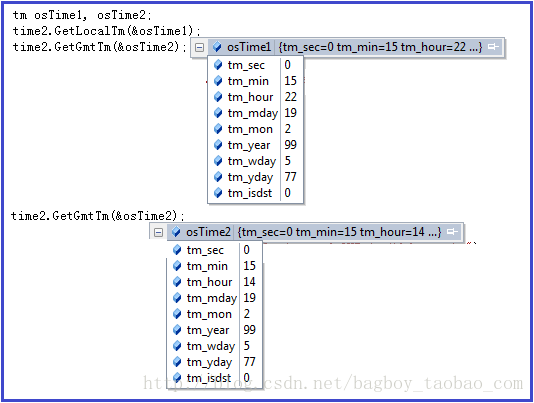
CTime time2(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0); // 构造一个时间tm osTime1, osTime2;
time2.GetLocalTm(&osTime1);
time2.GetGmtTm(&osTime2);
ATLTRACE(_T("Difference between local time and GMT is %d hours.\n"), osTime1.tm_hour - osTime2.tm_hour);
4.3 time_t与tm互转
4.3.1 time_t转tm
time_t tt = time2.GetTime();struct tm tm1;
localtime_s(&tm1, &tt);
struct tm temptm = *localtime(&t1);
// 这个函数也可以, 但是返回的是一个指针, 尽量不使用
4.3.2 tm转time_t
struct tm tm1;......
time_t tt2 = mktime(&tm1);
五. SYSTEMTIME
5.1 定义
typedef struct _SYSTEMTIME {WORD wYear; // The current year.
WORD wMonth; // The current month; January is 1.
WORD wDayOfWeek; // The current day of the week; Sunday is 0, Monday is 1, and so on.
WORD wDay; // The current day of the month.
WORD wHour; // The current hour.
WORD wMinute; // The current minute.
WORD wSecond; // The current second.
WORD wMilliseconds; // The current millisecond.
};
SYSTEMTIME是属于Window上的结构
5.2 例子
SYSTEMTIME systime;GetSystemTime(&systime);5.3 tm与SYSTEMTIME 互转
5.3.1 tm转SYSTEMTIME
struct tm tm1;......
SYSTEMTIME st = {1900 + tm1.tm_year, 1 + tm1.tm_mon, tm1.tm_wday, tm1.tm_mday, tm1.tm_hour, tm1.tm_min, tm1.tm_sec, 0};
5.3.2 SYSTEMTIME转tm
// 四年一闰, 百年不闰, 四百年再闰.
bool IsLeapYear(int nYear)
{
// 闰年: 能被400整除的是闰年; 能被4整除并且不被100整除的也是闰年;
return (0 == (nYear % 400)) || ((0 == (nYear % 4)) && (0 != (nYear % 100)));
}
int GetYearDay(int nYear, int nMonth, int nMDay)
{
int nMonthDaysLeap[12] = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int nMonthDaysNonLeap[12] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int* pDays = 0;
// 简单校验
if(1 > nMonth || 12 < nMonth || 1 > nMDay)
{
return 0;
}
// 是否闰年
pDays = IsLeapYear(nYear) ? nMonthDaysLeap : nMonthDaysNonLeap;
if(nMDay > pDays[nMonth - 1])
{
return 0;
}
int nYearDay = nMDay;
--nMonth;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < nMonth; ++i)
{
nYearDay += pDays[i];
}
return nYearDay;
}
SYSTEMTIME st;
......
int nYearDay = GetYearDay(st.wYear, st.wMonth, st.wDay);
struct tm tm2 = {st.wSecond, st.wMinute, st.wHour, st.wDay, st.wMonth-1, st.wYear-1900, st.wDayOfWeek, nYearDay - 1, 0};六. FILETIME
typedef struct _FILETIME {DWORD dwLowDateTime;
DWORD dwHighDateTime;
} FILETIME
6.1 相关函数
BOOL SystemTimeToFileTime(CONST SYSTEMTIME *lpSystemTime, LPFILETIME lpFileTime);BOOL FileTimeToSystemTime(CONST FILETIME *lpFileTime, LPSYSTEMTIME lpSystemTime);
6.2 FILETIME和SYSTEMTIME互转
BOOL SystemTimeToFileTime(CONST SYSTEMTIME *lpSystemTime, LPFILETIME lpFileTime);BOOL FileTimeToSystemTime(CONST FILETIME *lpFileTime, LPSYSTEMTIME lpSystemTime);
七. 时间的格式化
8.1 CTime::Format
CTime t(1999, 3, 19, 22, 15, 0);// "Friday, March 19, 1999"
CString s = t.Format(_T("%A, %B %d, %Y"));
8.2 strftime
size_t strftime(char *strDest, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *timeptr);%a 星期几的简写
%A 星期几的全称
%b 月分的简写
%B 月份的全称
%c 标准的日期的时间串
%C 年份的后两位数字
%d 十进制表示的每月的第几天
%D 月/天/年
%e 在两字符域中,十进制表示的每月的第几天
%F 年-月-日
%g 年份的后两位数字,使用基于周的年
%G 年分,使用基于周的年
%h 简写的月份名
%H 24小时制的小时
%I 12小时制的小时
%j 十进制表示的每年的第几天
%m 十进制表示的月份
%M 十时制表示的分钟数
%n 新行符
%p 本地的AM或PM的等价显示
%r 12小时的时间
%R 显示小时和分钟:hh:mm
%S 十进制的秒数
%t 水平制表符
%T 显示时分秒:hh:mm:ss
%u 每周的第几天,星期一为第一天 (值从0到6,星期一为0)
%U 第年的第几周,把星期日做为第一天(值从0到53)
%V 每年的第几周,使用基于周的年
%w 十进制表示的星期几(值从0到6,星期天为0)
%W 每年的第几周,把星期一做为第一天(值从0到53)
%x 标准的日期串
%X 标准的时间串
%y 不带世纪的十进制年份(值从0到99)
%Y 带世纪部分的十制年份
%z,%Z 时区名称,如果不能得到时区名称则返回空字符。
%% 百分号
八. 小结
1. 在上面的结果中, SYSTEMTIME结构可以提高毫秒信息.2. CTime, struct tm, time_t, SYSTEMTIME之间都可以直接或者间接的互转.
相关文章推荐
- Java日期时间使用总结
- C/C++时间函数使用方法总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、MySQL时间类型使用总结
- Java日期时间使用总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- Sql常见问题总结二(Sql语句怎么样查询IP,游标去重复,各种函数使用,各种取时间格式,字符串精确排序,超时锁问题)
- Java日期时间使用总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- 关于SQL SERVER时间格式使用的一些总结 综合整理
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- MySQL日期数据类型、时间类型使用总结
- c++编程之时间使用
- Sql常见问题总结二(Sql语句怎么样查询IP,游标去重复,各种函数使用,各种取时间格式,字符串精确排序,超时锁问题)
- MySQL日期数据类型、MySQL时间类型使用总结
- [转]MySQL:MySQL日期数据类型、MySQL时间类型使用总结
- MySQL:MySQL日期数据类型、MySQL时间类型使用总结
- 使用 NSDate,NSCalendar, NSDateComponents 获得时间之差总结 .
- SAP 使用较频繁的日期时间处理函数总结
