连接查询详解
2014-03-27 08:24
176 查看
在查询多个表时,我们经常会用“连接查询”。连接是关系数据库模型的主要特点,也是它区别于其它类型数据库管理系统的一个标志。
目的:实现多个表查询操作。
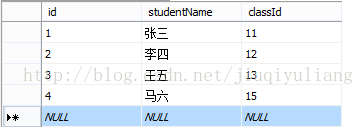
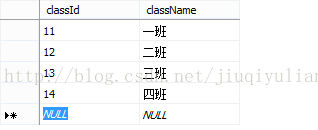
T_student T_class
FROM join_table join_type join_table[ON (join_condition)]
其中join_table指出参与连接操作的表名,连接可以对同一个表操作,也可以对多表操作,对同一个表操作的连接又称做自连接。join_type 指出连接类型。join_condition指连接条件。
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s,T_class c
where s.classId = c.classId
等于
select * from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId <> c.classId</span></span>
查询语句同等值连接基本相同:
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select s.*,c.className from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
与等值连接对比:结果是少一个一列classId:
总结:内连接是只显示满足条件的!
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
left join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
总结:左连接显示左表全部行,和右表与左表相同行。
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
right join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
总结:右连接恰与左连接相反,显示右表全部行,和左表与右表相同行。
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
full join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
总结:返回左表和右表中的所有行。
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select *from T_student
cross join T_class
‘等于
select *from T_student, T_class</span></span>
总结:相当与笛卡尔积,左表和右表组合。
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-family: System;"> <span style="font-size: 18px;">
select * from T_student s
cross join T_class c
where s.classId = c.classId
(注:cross join后加条件只能用where,不能用on)</span></span>
查询结果跟等值连接的查询结果是一样。
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
什么是连接查询呢?
概念:根据两个表或多个表的列之间的关系,从这些表中查询数据。目的:实现多个表查询操作。
知道了连接查询的概念之后,什么时候用连接查询呢?
一般是用作关联两张或两张以上的数据表时用的。看起来有点抽象,我们举个例子,做两张表:学生表(T_student)和班级表(T_class)。T_student T_class


连接标准语法格式:
SQL-92标准所定义的FROM子句的连接语法格式为:FROM join_table join_type join_table[ON (join_condition)]
其中join_table指出参与连接操作的表名,连接可以对同一个表操作,也可以对多表操作,对同一个表操作的连接又称做自连接。join_type 指出连接类型。join_condition指连接条件。
连接类型:
连接分为三种:内连接、外连接、交叉连接。内连接(INNER JOIN)
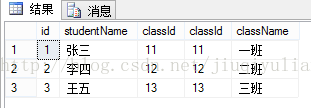
使用比较运算符(包括=、>、<、<>、>=、<=、!>和!<)进行表间的比较操作,查询与连接条件相匹配的数据。根据比较运算符不同,内连接分为等值连接、自然连接和不等连接三种。1、等值连接
概念:在连接条件中使用等于号(=)运算符,其查询结果中列出被连接表中的所有列,包括其中的重复列。[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s,T_class c
where s.classId = c.classId
等于
select * from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
select * from T_student s,T_class c where s.classId = c.classId 等于 select * from T_student s inner join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId结果是:

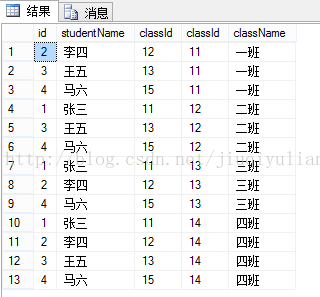
2、不等连接
概念:在连接条件中使用除等于号之外运算符(>、<、<>、>=、<=、!>和!<)[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId <> c.classId</span></span>
select * from T_student s inner join T_class c on s.classId <> c.classId结果是:

3、自然连接
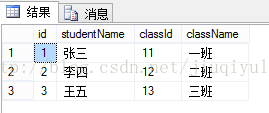
概念:连接条件和等值连接相同,但是会删除连接表中的重复列。查询语句同等值连接基本相同:
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select s.*,c.className from T_student s
inner join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
select s.*,c.className from T_student s inner join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId
与等值连接对比:结果是少一个一列classId:

总结:内连接是只显示满足条件的!
外连接
外连接分为左连接(LEFT JOIN)或左外连接(LEFT OUTER JOIN)、右连接(RIGHT JOIN)或右外连接(RIGHT OUTER JOIN)、全连接(FULL JOIN)或全外连接(FULL OUTER JOIN)。我们就简单的叫:左连接、右连接和全连接。1、左连接:
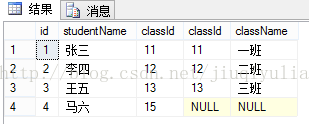
概念:返回左表中的所有行,如果左表中行在右表中没有匹配行,则结果中右表中的列返回空值。[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
left join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
select * from T_student s left join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId结果是:

总结:左连接显示左表全部行,和右表与左表相同行。
2、右连接:
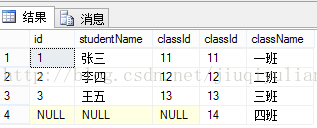
概念:恰与左连接相反,返回右表中的所有行,如果右表中行在左表中没有匹配行,则结果中左表中的列返回空值。[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
right join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
select * from T_student s right join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId结果是:

总结:右连接恰与左连接相反,显示右表全部行,和左表与右表相同行。
3、全连接:
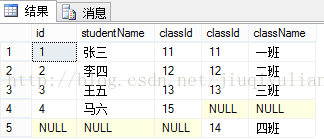
概念:返回左表和右表中的所有行。当某行在另一表中没有匹配行,则另一表中的列返回空值[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select * from T_student s
full join T_class c
on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
select * from T_student s full join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId结果是:

总结:返回左表和右表中的所有行。
交叉连接(CROSS JOIN):也称迪卡尔积
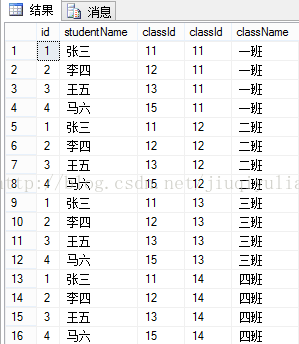
概念:不带WHERE条件子句,它将会返回被连接的两个表的笛卡尔积,返回结果的行数等于两个表行数的乘积(例如:T_student和T_class,返回4*4=16条记录),如果带where,返回或显示的是匹配的行数。1、不带where:
[sql]view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size: 18px;"><span style="font-family: System;">
select *from T_student
cross join T_class
‘等于
select *from T_student, T_class</span></span>
select *from T_student cross join T_class ‘等于 select *from T_student, T_class结果是:

总结:相当与笛卡尔积,左表和右表组合。
2、有where子句,往往会先生成两个表行数乘积的数据表,然后才根据where条件从中选择。
[sql]view plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-family: System;"> <span style="font-size: 18px;">
select * from T_student s
cross join T_class c
where s.classId = c.classId
(注:cross join后加条件只能用where,不能用on)</span></span>
select * from T_student s cross join T_class c where s.classId = c.classId (注:cross join后加条件只能用where,不能用on)
查询结果跟等值连接的查询结果是一样。
[sql]
view plaincopyprint?
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
<pre></pre>
相关文章推荐
- 详解MySQL中的分组查询与连接查询语句
- Hibernate_查询_HQL详解(二)_聚集函数、分组、连接查询、查询时使用参数的HQL语法
- 数据库多表连接查询详解
- 【Oracle】多表连接查询详解
- 用JDBC连接MySQL数据库(包括查询,操作数据库 详解)
- 详解MySql基本查询、连接查询、子查询、正则表达查询
- sql表的连接查询详解
- Oracle连接查询详解
- MyBatis:关联查询——一对多 多表连接、单独查询(详解resultMap)
- MySQL高级查询——连接查询实例详解
- SQL各种连接查询详解(左连接、右连接..)
- SQL各种连接查询详解
- SQL各种连接查询详解
- SQL各种连接查询详解(左连接、右连接..)
- sql表的连接查询详解
- SQL各种连接查询详解(左连接、右连接..)
- T-SQL根据查询详解--多表连接查询
- MySQL基础(三)多表查询(各种join连接详解)
- SQL各种连接查询详解(左连接、右连接..)
- SQL各种连接查询详解(左连接、右连接..)
