设计模式(c++)笔记之十七(Memento模式)
2013-10-24 15:44
417 查看
一、描述:
没有人想犯错误,但是没有人能够不犯错误。犯了错误一般只能改过,却很难改正(恢复)。世界上没有后悔药,但是我们在进行软件系统的设计时候是要给用户后悔的权利(实际上可能也是用户要求的权利:),我们对一些关键性的操作肯定需要提供诸如撤销(Undo) 的操作。那这个后悔药就是 Memento 模式提供的。Memento 模式的关键就是要在不破坏封装行的前提下,捕获并保存一个类的内部状态,这样就可以利用该保存的状态实施恢复操作。为了达到这个目标,可以在后面的实现中看到我们采取了一定语言支持的技术。
Memento 模式的典型结构图为:
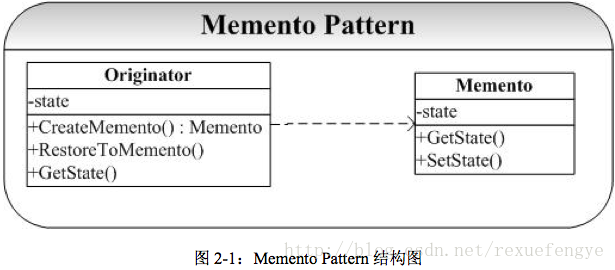
二、实例
我的工程目录:
注释:
备忘录:Memento
撤销返回操作:originator
主程序:main
备忘录:Memento类
Memento.h
#ifndef __Memento__Memento__
#define __Memento__Memento__
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Memento
{
public:
protected:
private:
//这是最关键的地方,将 Originator 为 friend 类,可以访问内部信息,但是其他类不能访问
friend class Originator; typedef string State;
Memento();
Memento(const State& sdt); ~Memento();
void SetState(const State& sdt); State GetState();
private:
State _sdt;
};
#endif /* defined(__Memento__Memento__) */Memento.cpp
#include "Memento.h"
typedef string State;
Memento::Memento()
{
}
Memento::Memento(const State& sdt)
{
this->_sdt = sdt;
}
State Memento::GetState()
{
return this->_sdt;
}
void Memento::SetState(const State& sdt)
{
this->_sdt = sdt;
}撤销返回操作:originator类
originator.h
#ifndef __Memento__Originator__
#define __Memento__Originator__
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Memento.h"
using namespace std;
class Originator
{
public:
typedef string State; Originator();
Originator(const State& sdt);
~Originator();
Memento* CreateMemento();
void SetMemento(Memento* men);
void RestoreToMemento(Memento* mt);
State GetState();
void SetState(const State& sdt);
void PrintState();
protected:
private:
State _sdt;
Memento* _mt;
};
#endif /* defined(__Memento__Originator__) */Originator.cpp
#include "Originator.h"
typedef string State;
Originator::Originator()
{
this->_sdt = "";
this->_mt = 0;
}
Originator::Originator(const State& sdt)
{
this->_sdt = sdt;
this->_mt = 0;
}
Originator::~Originator()
{
}
Memento* Originator::CreateMemento()
{
return new Memento(_sdt);
}
State Originator::GetState()
{
return this->_sdt;
}
void Originator::SetState(const State& sdt)
{
this->_sdt = sdt;
}
void Originator::PrintState()
{
cout<<this->_sdt<<"....."<<endl;
}
void Originator::SetMemento(Memento* men)
{
}
void Originator::RestoreToMemento(Memento* mt)
{
this->_sdt = mt->GetState();
}主程序:main
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Memento.h"
#include "Originator.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
// insert code here...
Originator *myOriginator = new Originator();
myOriginator->SetState("备忘状态old");//备忘前状态
myOriginator->PrintState();
Memento *myMemento = myOriginator->CreateMemento();//将状态备忘
myOriginator->SetState("修改状态new");//修改状态
myOriginator->PrintState();
myOriginator->RestoreToMemento(myMemento);//恢复修改前状态
myOriginator->PrintState();
std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
return 0;
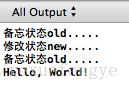
}结果如下:
Memento 模式的关键就是 friend class Originator;我们可以看到,Memento 的接口都声明为 private,而将 Originator 声明为 Memento 的友元类。我们将 Originator 的状态保存在 Memento 类中,而将 Memento 接口 private 起来,也就达到了封装的功效。
在 Originator 类中我们提供了方法让用户后悔:RestoreToMemento(Memento* mt);我们可以 通过这个接口让用户后悔。在测试程序中,我们演示了这一点:Originator 的状态由 old 变为 new 最 后又回到了 old。
参考文献:《GoF_23种设计模式解析》
相关文章推荐
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
- 设计模式学习笔记(十七)—Memento备忘录模式
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之七(AbstractFactory抽象工厂模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之一(Strategy策略模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之三(Singleton单例模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之八(Adapter适配器模式)
- 23种设计模式之十七(行为模式)Memento模式
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十四(Iterator迭代器模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十九(State状态模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之三(Singleton单例模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十四(Iterator迭代器模式)
- 设计模式学习笔记c++版——单例模式
- boolan——c++学习笔记之设计模式三
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十六(Observer观察者模式)
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之一(Strategy策略模式)
- 设计模式(c++)笔记之二十(Visitor模式)
