(4) 利用 Setter方式实现 【第一种方式】 依赖注入,编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
2012-06-09 15:20
991 查看
import cn.itm.dao.PersonDao;
public class PersonDaoBean implements PersonDao {
public void add(){
System.out.println("执行PersonDaoBean的add方法。。。");
}
}package cn.itm.dao;
public interface PersonDao {
public abstract void add();
}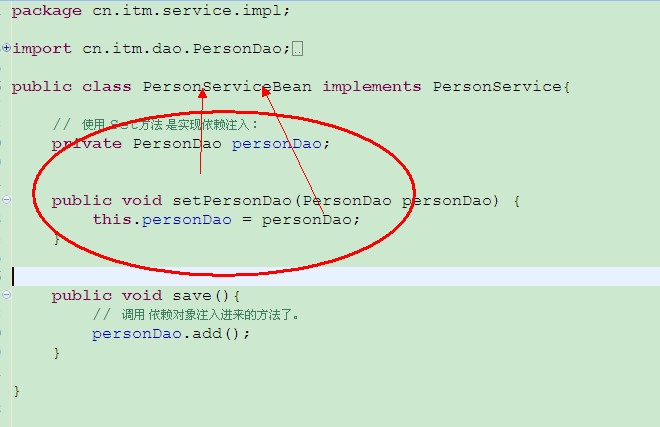
package cn.itm.service.impl;
import cn.itm.dao.PersonDao;
import cn.itm.service.PersonService;
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService{
// 使用 Set方法 是实现依赖注入:
private PersonDao personDao;
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
public void save(){
// 调用 依赖对象注入进来的方法了。
personDao.add();
}
}package cn.itm.service;
public interface PersonService {
public abstract void save();
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.itm.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itm.service.impl.PersonServiceBean" >
<!-- 实现 注入 -->
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>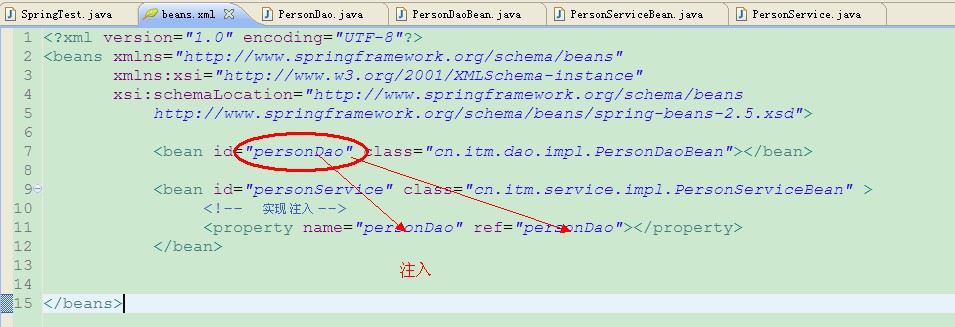
测试类:
package junit.test;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.itm.service.PersonService;
public class SpringTest {
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception {
}
// 专门用来实例化 Spring 容器的。
@Test public void instanceSpring(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
personService.save();
}
}成功。
利用setter方式的好处:可以被多个bean使用。
下面利用编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理:
package junit.test;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.XPath;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class ItmClassPathXMLApplicationContext {
private List<BeanDefinition> beanDefines = new ArrayList<BeanDefinition>();
// 存放实例
private Map<String,Object> sigletons = new HashMap<String,Object>();
public ItmClassPathXMLApplicationContext(String fileName){
this.readXML(fileName);
this.instanceBeans();
this.injectObject();
}
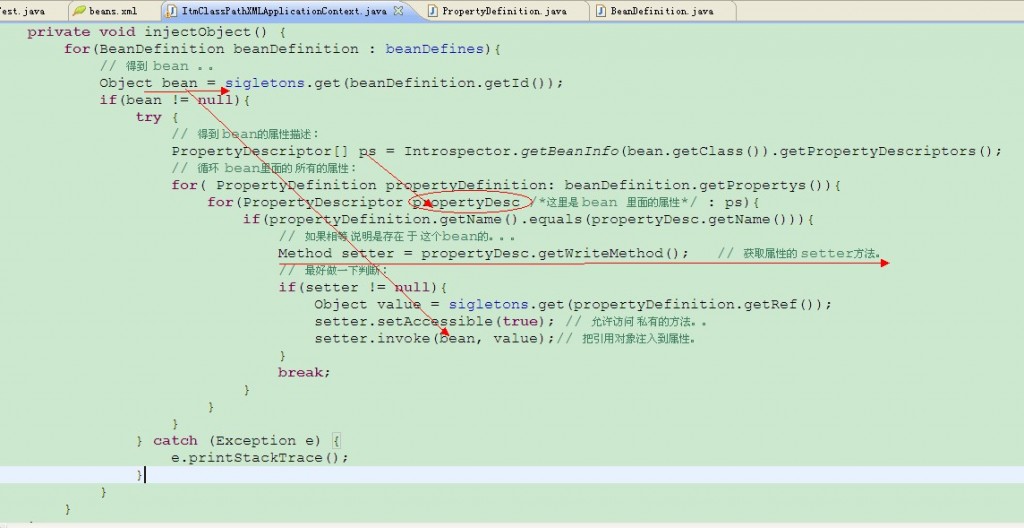
private void injectObject() {
for(BeanDefinition beanDefinition : beanDefines){
// 得到 bean 。。
Object bean = sigletons.get(beanDefinition.getId());
if(bean != null){
try {
// 得到 bean的属性描述:
PropertyDescriptor[] ps = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass()).getPropertyDescriptors();
// 循环 bean里面的 所有的属性:
for( PropertyDefinition propertyDefinition: beanDefinition.getPropertys()){
for(PropertyDescriptor propertyDesc /*这里是 bean 里面的属性*/ : ps){
if(propertyDefinition.getName().equals(propertyDesc.getName())){
// 如果相等 说明是存在 于 这个bean的。。。
Method setter = propertyDesc.getWriteMethod(); // 获取属性的 setter方法。
// 最好做一下判断:
if(setter != null){
Object value = sigletons.get(propertyDefinition.getRef());
setter.setAccessible(true); // 允许访问 私有的方法。。
setter.invoke(bean, value);// 把引用对象注入到属性。
}
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 通过反射技术,完成 bean 的实例化:
*/
private void instanceBeans() {
for(BeanDefinition beanDefinition : beanDefines){
try {
if(beanDefinition.getClassName() != null && !"".equals(beanDefinition.getClassName().trim())){
sigletons.put(beanDefinition.getId(), Class.forName(beanDefinition.getClassName()).newInstance());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 读取 XML 的配置文件:
* @param fileName
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readXML(String fileName) {
// 创建读取器:
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = null;
try{
URL xmlPath = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(fileName);
document = saxReader.read(xmlPath); // 读取文件的内容。。。
Map<String,String> nsMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
nsMap.put("ns", "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"); // 加入命名空间
// 创建beans/bean 查询路径。
XPath xsub = document.createXPath("//ns:beans/ns:bean");
// 设置命名空间。
xsub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap);
// 获取文档下 所有bean节点:
List<Element> beans = xsub.selectNodes(document);
for(Element element : beans){
String id = element.attributeValue("id"); // 获取id属性值。
String clazz = element.attributeValue("class"); // 获取 class 属性值。
BeanDefinition beanDefine = new BeanDefinition(id, clazz);
// 查询的相对路径:
XPath propertysub = element.createXPath("ns:property");
propertysub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap);// 设置命名空间。
List<Element> propertys = propertysub.selectNodes(element);
for(Element property : propertys){
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
String propertyRef = property.attributeValue("ref");
System.out.println(propertyName + "==" + propertyRef);
PropertyDefinition propertyDefinition = new PropertyDefinition(propertyName, propertyRef);
// 放到 bean里面去:
beanDefine.getPropertys().add(propertyDefinition);
}
beanDefines.add(beanDefine);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取 bean实例
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public Object getBean(String beanName){
return this.sigletons.get(beanName);
}
}
本文源自:学习 传智播客黎活明老师的视频 自己总结而至。
相关文章推荐
- (3) 利用 Setter方式实现 【第一种方式】 依赖注入,编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- (4) 编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理【附加:注入依赖对象的两种方式】
- (5) 编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理【附加:注入依赖对象的两种方式】
- 编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- Spring、Spring依赖注入与编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- 传智播客Spring2.5视频教程_编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理 1
- (转)编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- Spring第七弹—依赖注入之注解方式注入及编码解析@Resource原理
- Spring、Spring依赖注入与编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- 编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
- Spring源码剖析——依赖注入实现原理
- Spring源码剖析——依赖注入实现原理
- spring学习笔记整理--05(编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理)
- Spring源码剖析——依赖注入实现原理
- SSH深度历险(八) 剖析SSH核心原理+Spring依赖注入的三种方式
- 利用SPring实现bean属性setter方式注入
- ITCAST视频-Spring学习笔记(编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理)
- SSH深度历险(八) 剖析SSH核心原理+Spring依赖注入的三种方式
- 传智播客Spring2.5视频教程_编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理 2
- 7.编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理
