Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
2011-05-19 16:15
316 查看
Gallery组件主要用于横向显示图像列表,不过按常规做法。
Gallery组件只能有限地显示指定的图像。也就是说,如果为Gallery组件指定了10张图像,那么当Gallery组件显示到第10张时,就不会
再继续显示了。这虽然在大多数时候没有什么关系,但在某些情况下,我们希望图像显示到最后一张时再重第1张开始显示,也就是循环显示。要实现这种风格的
Gallery组件,就需要对Gallery的Adapter对象进行一番改进。
Gallery组件的传统用法
在实现可循环显示图像的Gallery组件之前先来回顾一下Gallery组件的传统用法。Gallery组件可以横向显示一个图像列表,当单击当前图像的后一个图像时,这个图像列表会向左
移动
一格,当单击当前图像的前一个图像时,这个图像列表会向右移动一样。也可以通过拖动的方式来向左和向右移动图像列表。当前显示的是第1个图像的效果如图1所示。Gallery组件显示到最后一个图像的效果如图2所示
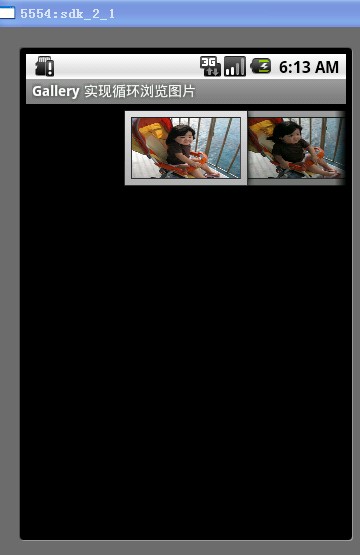
图1
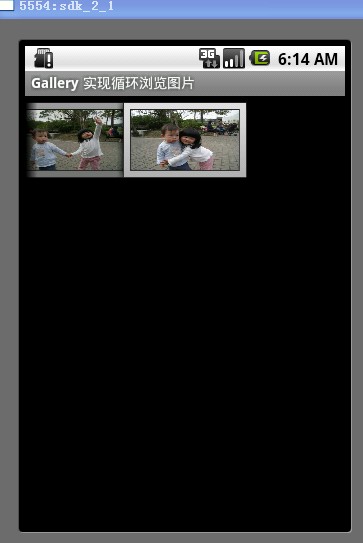
图2
从图2可以看出,当显示到最后一个图像时,列表后面就没有图像的,这也是Gallery组件的基本显示效果。在本文后面的部分将详细介绍如何使Gallery组件显示到最后一个图像时会从第1个图像开始显示。
好了,现在我们来看一下图1和图2的效果是如何做出来的吧。
Gallery既然用于显示图像,那第1步就必须要有一些图像文件用来显示。现在可以随意准备一些图像。在本文的例子中准备了6个jpg文件
(item1.jpg至item15.jpg)。将这些文件都放在res/drawable目录中
下面将这些图像的资源ID都保存在int数组中,代码如下:
private
int
[] myImageIds = {R.drawable.photo1,
R.drawable.photo2,
R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4,
R.drawable.photo5,
R.drawable.photo6,};
在本例的main.xml文件中配置了一个Gallery组件,代码如下:
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width=
"fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Gallery android:id="@+id/gallery"
android:layout_width=
"fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop=
"30dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
现在在onCreate方法中装载这个组件,代码如下:
public
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// 装载Gallery组件
Gallery gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gallery);
// 创建用于描述图像数据的ImageAdapter对象
ImageAdapter imageAdapter = new
ImageAdapter(
this
);
// 设置Gallery组件的Adapter对象
gallery.setAdapter(imageAdapter);
}
在上面的代码中涉及到一个非常重要的类:ImageAdapter。该类是android.widget.BaseAdapter的子类,用于描述图像信息。下面先看一下这个类的完整代码
public
class
ImageAdapter
extends
BaseAdapter
{
int
mGalleryItemBackground;
private
Context mContext;
public
ImageAdapter(Context context)
{
mContext = context;
// 获得Gallery组件的属性
TypedArray typedArray = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery);
mGalleryItemBackground = typedArray.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0
);
}
// 返回图像总数
public
int
getCount()
{
return
resIds.length;
}
public
Object getItem(
int
position)
{
return
position;
}
public
long
getItemId(
int
position)
{
return
position;
}
// 返回具体位置的ImageView对象
public
View getView(
int
position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
ImageView imageView = new
ImageView(mContext);
// 设置当前图像的图像(position为当前图像列表的位置)
imageView.setImageResource(myImageIds[position]);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new
Gallery.LayoutParams(
163
,
106
));
// 设置Gallery组件的背景风格
imageView.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground);
return
imageView;
}
}
在编写ImageAdapter类时应注意的两点:
1. 在ImageAdapter类的构造方法中获得了Gallery组件的属性信息。这些信息被定义在res/values/attrs.xml文件中,代码如下:
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="Gallery"
>
<attr name="android:galleryItemBackground"
/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
上面的属性信息用于设置Gallery的背景风格。
2. 在ImageAdapter类中有两个非常重要的方
法:getCount和getView。其中getCount方法用于返回图像总数,要注意的是,这个总数不能大于图像的实际数(可以小于图像的实际
数),否则会抛出越界异常。当Gallery组件要显示某一个图像时,就会调用getView方法,并将当前的图像索引(position参数)传入该方
法。一般getView方法用于返回每一个显示图像的组件(ImageView对象)。从这一点可以看出,Gallery组件是即时显示图像的,而不是一
下将所有的图像都显示出来。在getView方法中除了创建了ImageView对象,还用从resIds数组中获得了相应的图像资源ID来设置在
ImageView中显示的图像。最后还设置了Gallery组件的背景显示风格。
OK,现在来运行这个程序,来回拖动图像列表,就会看到如图1和图2所示的效果了。
循环显示图像的原理
循环显示有些类似于循环链表,最后一个结点的下一个结点又是第1个结点。循环显示图像也可以模拟这一点。
也许细心的读者从上一节实现的ImageAdapter类中会发现些什
么。对!就是getView方法中的position参数和getCount方法的关系。position参数的值是不可能超过getCount方法返回
的值的,也就是说,position参数值的范围是0至getCount() - 1。
如果这时Gallery组件正好显示到最后一个图像,position参数值正好为getCount() - 1。那么我们如何再让Gallery显示下一个图像呢?也就是说让position参数值再增1,对!将getCount()方法的返回值也增1。
那么这里还有一个问题,如果position参数值无限地增加,就意味着
myImageIds数组要不断地增大,这样会大大消耗系统的资源。想到这,就需要解决两个问题:既要position不断地增加,又让resIds数组
中保存的图像资源ID是有限的,该怎么做呢?对于getCount()方法非常好解决,可以让getCount方法返回一个很大的数,例
如,Integer.MAX_VALUE。这时position参数值就可以随着Gallery组件的图像不断向前移动而增大。现在myImageIds
数组只有6个元素,如果position的值超过数组边界,要想继续循环取得数组中的元素(也就是说,当position的值是6时,取
myImageIds数组的第0个元素,是6时取第1个元素),最简单的方法就是取余,代码如下:
myImageIds[position % myImageIds.length]
在本节对ImageAdapter类做了如下两个改进:
1. 使getCount方法返回一个很大的值。建议返回Integer.MAX_VALUE。
2. 在getView方法中通过取余来循环取得resIds数组中的图像资源ID。
通过上面两点改进,可以使图像列表在向右移动时会循环显示图像。当然,这
种方法从本质上说只是伪循环,也就是说,如果真把图像移动到getCount方法返回的值那里,那也就显示到最后一个图像的。不过在这里getCount
方法返回的是Integer.MAX_VALUE,这个值超过了20亿,除非有人真想把图像移动到第20亿的位置,否则Gallery组件看着就是一个循
环显示图像的组件。
实现循环显示图像的Gallery组件
在本节将组出与循环显示图像相关的ImageAdapter类的完整代
码。读者可以从中看到上一节介绍的两点改进。为了使界面看上去更丰满,本例还在单击某一个Gallery组件中的图像时在下方显示一个放大的图像(使用
ImageSwitcher组件)。本例的显示效果如图3所示。当不断向后移动图像时,图像可不断显示,读者可以自己运行本例来体验一下。
本例中Main类的完整代码如下:
package
irdc.EX04_10;
import
android.app.Activity;
import
android.os.Bundle;
/*本范例需使用到的class*/
import
android.content.Context;
import
android.content.res.TypedArray;
import
android.view.View;
import
android.view.ViewGroup;
import
android.widget.AdapterView;
import
android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import
android.widget.Gallery;
import
android.widget.ImageView;
import
android.widget.Toast;
import
android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
public
class
EX04_10
extends
Activity
{
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main); /* 透过findViewById取得 */
Gallery g = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.mygallery); /* 新增一ImageAdapter并设定给Gallery对象 */
g.setAdapter(new
ImageAdapter(
this
));
/* 设定一个itemclickListener并Toast被点选图片的位置 */
setTitle("Gallery 实现循环浏览图片"
);
g.setOnItemClickListener(new
OnItemClickListener()
{
public
void
onItemClick(AdapterView parent, View v,
int
position,
long
id)
{
Toast.makeText(EX04_10.this
, getString(R.string.my_gallery_text_pre) + position + getString(R.string.my_gallery_text_post), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
public
class
ImageAdapter
extends
BaseAdapter
/* 改写BaseAdapter自定义一ImageAdapter class */
{
int
mGalleryItemBackground;
private
Context mContext;
/* ImageAdapter的建构子 */
private
int
[] myImageIds = {R.drawable.photo1,
R.drawable.photo2,
R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4,
R.drawable.photo5,
R.drawable.photo6,};
public
ImageAdapter(Context c)
{
mContext = c;
TypedArray a = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery); /* 使用在res/values/attrs.xml中的定义 的Gallery属性. */
mGalleryItemBackground = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0
);
///*取得Gallery属性的Index
a.recycle();/* 让对象的styleable属性能够反复使用 */
}
public
int
getCount()
/* 一定要重写的方法getCount,传回图片数目总数 */
{
//return myImageIds.length;
return
Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public
Object getItem(
int
position)
/* 一定要重写的方法getItem,传回position */
{
return
position;
}
public
long
getItemId(
int
position)
/* 一定要重写的方法getItemId,传回position */
{
return
position;
}
public
View getView(
int
position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
/* 一定要重写的方法getView,传回一View对象 */
{
// if (position == getCount())
// {
// position = 0;
// }
ImageView i = new
ImageView(mContext);
i.setImageResource(myImageIds[position%myImageIds.length]); /* 设定图片给imageView对象 */
i.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY); /* 重新设定图片的宽高 */
i.setLayoutParams(new
Gallery.LayoutParams(
136
,
88
));
/* 重新设定Layout的宽高 */
i.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground); /* 设定Gallery背景图 */
return
i;
/* 传回imageView物件 */
}
}
}
Gallery组件只能有限地显示指定的图像。也就是说,如果为Gallery组件指定了10张图像,那么当Gallery组件显示到第10张时,就不会
再继续显示了。这虽然在大多数时候没有什么关系,但在某些情况下,我们希望图像显示到最后一张时再重第1张开始显示,也就是循环显示。要实现这种风格的
Gallery组件,就需要对Gallery的Adapter对象进行一番改进。
Gallery组件的传统用法
在实现可循环显示图像的Gallery组件之前先来回顾一下Gallery组件的传统用法。Gallery组件可以横向显示一个图像列表,当单击当前图像的后一个图像时,这个图像列表会向左
移动
一格,当单击当前图像的前一个图像时,这个图像列表会向右移动一样。也可以通过拖动的方式来向左和向右移动图像列表。当前显示的是第1个图像的效果如图1所示。Gallery组件显示到最后一个图像的效果如图2所示

图1

图2
从图2可以看出,当显示到最后一个图像时,列表后面就没有图像的,这也是Gallery组件的基本显示效果。在本文后面的部分将详细介绍如何使Gallery组件显示到最后一个图像时会从第1个图像开始显示。
好了,现在我们来看一下图1和图2的效果是如何做出来的吧。
Gallery既然用于显示图像,那第1步就必须要有一些图像文件用来显示。现在可以随意准备一些图像。在本文的例子中准备了6个jpg文件
(item1.jpg至item15.jpg)。将这些文件都放在res/drawable目录中
下面将这些图像的资源ID都保存在int数组中,代码如下:
private
int
[] myImageIds = {R.drawable.photo1,
R.drawable.photo2,
R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4,
R.drawable.photo5,
R.drawable.photo6,};
private int[] myImageIds = {R.drawable.photo1,
R.drawable.photo2,
R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4,
R.drawable.photo5,
R.drawable.photo6,};在本例的main.xml文件中配置了一个Gallery组件,代码如下:
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width=
"fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Gallery android:id="@+id/gallery"
android:layout_width=
"fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop=
"30dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <Gallery android:id="@+id/gallery" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="30dp" /> </LinearLayout>
现在在onCreate方法中装载这个组件,代码如下:
public
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// 装载Gallery组件
Gallery gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gallery);
// 创建用于描述图像数据的ImageAdapter对象
ImageAdapter imageAdapter = new
ImageAdapter(
this
);
// 设置Gallery组件的Adapter对象
gallery.setAdapter(imageAdapter);
}
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// 装载Gallery组件
Gallery gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gallery);
// 创建用于描述图像数据的ImageAdapter对象
ImageAdapter imageAdapter = new ImageAdapter(this);
// 设置Gallery组件的Adapter对象
gallery.setAdapter(imageAdapter);
}在上面的代码中涉及到一个非常重要的类:ImageAdapter。该类是android.widget.BaseAdapter的子类,用于描述图像信息。下面先看一下这个类的完整代码
public
class
ImageAdapter
extends
BaseAdapter
{
int
mGalleryItemBackground;
private
Context mContext;
public
ImageAdapter(Context context)
{
mContext = context;
// 获得Gallery组件的属性
TypedArray typedArray = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery);
mGalleryItemBackground = typedArray.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0
);
}
// 返回图像总数
public
int
getCount()
{
return
resIds.length;
}
public
Object getItem(
int
position)
{
return
position;
}
public
long
getItemId(
int
position)
{
return
position;
}
// 返回具体位置的ImageView对象
public
View getView(
int
position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
ImageView imageView = new
ImageView(mContext);
// 设置当前图像的图像(position为当前图像列表的位置)
imageView.setImageResource(myImageIds[position]);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new
Gallery.LayoutParams(
163
,
106
));
// 设置Gallery组件的背景风格
imageView.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground);
return
imageView;
}
}
public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter
{
int mGalleryItemBackground;
private Context mContext;
public ImageAdapter(Context context)
{
mContext = context;
// 获得Gallery组件的属性
TypedArray typedArray = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery);
mGalleryItemBackground = typedArray.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0);
}
// 返回图像总数
public int getCount()
{
return resIds.length;
}
public Object getItem(int position)
{
return position;
}
public long getItemId(int position)
{
return position;
}
// 返回具体位置的ImageView对象
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(mContext);
// 设置当前图像的图像(position为当前图像列表的位置)
imageView.setImageResource(myImageIds[position]);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new Gallery.LayoutParams(163, 106));
// 设置Gallery组件的背景风格
imageView.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground);
return imageView;
}
}在编写ImageAdapter类时应注意的两点:
1. 在ImageAdapter类的构造方法中获得了Gallery组件的属性信息。这些信息被定义在res/values/attrs.xml文件中,代码如下:
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="Gallery"
>
<attr name="android:galleryItemBackground"
/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="Gallery"> <attr name="android:galleryItemBackground" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
上面的属性信息用于设置Gallery的背景风格。
2. 在ImageAdapter类中有两个非常重要的方
法:getCount和getView。其中getCount方法用于返回图像总数,要注意的是,这个总数不能大于图像的实际数(可以小于图像的实际
数),否则会抛出越界异常。当Gallery组件要显示某一个图像时,就会调用getView方法,并将当前的图像索引(position参数)传入该方
法。一般getView方法用于返回每一个显示图像的组件(ImageView对象)。从这一点可以看出,Gallery组件是即时显示图像的,而不是一
下将所有的图像都显示出来。在getView方法中除了创建了ImageView对象,还用从resIds数组中获得了相应的图像资源ID来设置在
ImageView中显示的图像。最后还设置了Gallery组件的背景显示风格。
OK,现在来运行这个程序,来回拖动图像列表,就会看到如图1和图2所示的效果了。
循环显示图像的原理
循环显示有些类似于循环链表,最后一个结点的下一个结点又是第1个结点。循环显示图像也可以模拟这一点。
也许细心的读者从上一节实现的ImageAdapter类中会发现些什
么。对!就是getView方法中的position参数和getCount方法的关系。position参数的值是不可能超过getCount方法返回
的值的,也就是说,position参数值的范围是0至getCount() - 1。
如果这时Gallery组件正好显示到最后一个图像,position参数值正好为getCount() - 1。那么我们如何再让Gallery显示下一个图像呢?也就是说让position参数值再增1,对!将getCount()方法的返回值也增1。
那么这里还有一个问题,如果position参数值无限地增加,就意味着
myImageIds数组要不断地增大,这样会大大消耗系统的资源。想到这,就需要解决两个问题:既要position不断地增加,又让resIds数组
中保存的图像资源ID是有限的,该怎么做呢?对于getCount()方法非常好解决,可以让getCount方法返回一个很大的数,例
如,Integer.MAX_VALUE。这时position参数值就可以随着Gallery组件的图像不断向前移动而增大。现在myImageIds
数组只有6个元素,如果position的值超过数组边界,要想继续循环取得数组中的元素(也就是说,当position的值是6时,取
myImageIds数组的第0个元素,是6时取第1个元素),最简单的方法就是取余,代码如下:
myImageIds[position % myImageIds.length]
myImageIds[position % myImageIds.length]
在本节对ImageAdapter类做了如下两个改进:
1. 使getCount方法返回一个很大的值。建议返回Integer.MAX_VALUE。
2. 在getView方法中通过取余来循环取得resIds数组中的图像资源ID。
通过上面两点改进,可以使图像列表在向右移动时会循环显示图像。当然,这
种方法从本质上说只是伪循环,也就是说,如果真把图像移动到getCount方法返回的值那里,那也就显示到最后一个图像的。不过在这里getCount
方法返回的是Integer.MAX_VALUE,这个值超过了20亿,除非有人真想把图像移动到第20亿的位置,否则Gallery组件看着就是一个循
环显示图像的组件。
实现循环显示图像的Gallery组件
在本节将组出与循环显示图像相关的ImageAdapter类的完整代
码。读者可以从中看到上一节介绍的两点改进。为了使界面看上去更丰满,本例还在单击某一个Gallery组件中的图像时在下方显示一个放大的图像(使用
ImageSwitcher组件)。本例的显示效果如图3所示。当不断向后移动图像时,图像可不断显示,读者可以自己运行本例来体验一下。
本例中Main类的完整代码如下:
package
irdc.EX04_10;
import
android.app.Activity;
import
android.os.Bundle;
/*本范例需使用到的class*/
import
android.content.Context;
import
android.content.res.TypedArray;
import
android.view.View;
import
android.view.ViewGroup;
import
android.widget.AdapterView;
import
android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import
android.widget.Gallery;
import
android.widget.ImageView;
import
android.widget.Toast;
import
android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
public
class
EX04_10
extends
Activity
{
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main); /* 透过findViewById取得 */
Gallery g = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.mygallery); /* 新增一ImageAdapter并设定给Gallery对象 */
g.setAdapter(new
ImageAdapter(
this
));
/* 设定一个itemclickListener并Toast被点选图片的位置 */
setTitle("Gallery 实现循环浏览图片"
);
g.setOnItemClickListener(new
OnItemClickListener()
{
public
void
onItemClick(AdapterView parent, View v,
int
position,
long
id)
{
Toast.makeText(EX04_10.this
, getString(R.string.my_gallery_text_pre) + position + getString(R.string.my_gallery_text_post), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
public
class
ImageAdapter
extends
BaseAdapter
/* 改写BaseAdapter自定义一ImageAdapter class */
{
int
mGalleryItemBackground;
private
Context mContext;
/* ImageAdapter的建构子 */
private
int
[] myImageIds = {R.drawable.photo1,
R.drawable.photo2,
R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4,
R.drawable.photo5,
R.drawable.photo6,};
public
ImageAdapter(Context c)
{
mContext = c;
TypedArray a = obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.Gallery); /* 使用在res/values/attrs.xml中的定义 的Gallery属性. */
mGalleryItemBackground = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.Gallery_android_galleryItemBackground, 0
);
///*取得Gallery属性的Index
a.recycle();/* 让对象的styleable属性能够反复使用 */
}
public
int
getCount()
/* 一定要重写的方法getCount,传回图片数目总数 */
{
//return myImageIds.length;
return
Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public
Object getItem(
int
position)
/* 一定要重写的方法getItem,传回position */
{
return
position;
}
public
long
getItemId(
int
position)
/* 一定要重写的方法getItemId,传回position */
{
return
position;
}
public
View getView(
int
position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
/* 一定要重写的方法getView,传回一View对象 */
{
// if (position == getCount())
// {
// position = 0;
// }
ImageView i = new
ImageView(mContext);
i.setImageResource(myImageIds[position%myImageIds.length]); /* 设定图片给imageView对象 */
i.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY); /* 重新设定图片的宽高 */
i.setLayoutParams(new
Gallery.LayoutParams(
136
,
88
));
/* 重新设定Layout的宽高 */
i.setBackgroundResource(mGalleryItemBackground); /* 设定Gallery背景图 */
return
i;
/* 传回imageView物件 */
}
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- 【Android】使用Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- 【Android】使用Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Gallery组件基本用法以及实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- Android Gallery组件传统用法实现循环显示图像
- Gallery组件实现循环显示图像
- 可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件
- Android可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件用法实例
- 可循环显示图像的Gallery组件
- 可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件
- 可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件
- 可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件
- Android Gallery实现循环显示图像
- 可循环显示图像的Android Gallery组件
