Mongodb源码分析--更新记录
2011-04-11 09:49
1006 查看
在之前的一篇文章中,介绍了assembleResponse函数(位于instance.cpp第224行),它会根据op操作枚举类型来调用相应的crud操作,枚举类型定义如下:
enum Operations {
opReply = 1, /* reply. responseTo is set. */
dbMsg = 1000, /* generic msg command followed by a string */
dbUpdate = 2001, /* 更新对象 */
dbInsert = 2002,
//dbGetByOID = 2003,
dbQuery = 2004,
dbGetMore = 2005,
dbDelete = 2006,
dbKillCursors = 2007
};
可以看到dbUpdate = 2001 为更新操作枚举值,下面我们看一下assembleResponse在确定是更新操作时调用的方法,如下:
//instance.cpp文件第224行
assembleResponse( Message &m, DbResponse &dbresponse, const SockAddr &client ) {
.....
try {
if ( op == dbInsert ) { //添加记录操作
receivedInsert(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbUpdate ) { //更新记录
receivedUpdate(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbDelete ) { //删除记录
receivedDelete(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbKillCursors ) { //删除Cursors(游标)对象
currentOp.ensureStarted();
logThreshold = 10;
ss << "killcursors ";
receivedKillCursors(m);
}
else {
mongo::log() << " operation isn't supported: " << op << endl;
currentOp.done();
log = true;
}
}
.....
}
}
从上面代码可以看出,系统在确定dbUpdate操作时,调用了receivedUpdate()方法(位于instance.cpp文件第570行),下面是该方法的定义:
void receivedUpdate(Message& m, CurOp& op) {
DbMessage d(m);//初始化数据库格式的消息
const char *ns = d.getns();//获取名空间,用于接下来insert数据
assert(*ns);
//因为CUD操作在主库中操作,所以这里断言名空间包含的db信息中是不是主库,即"master"
uassert( 10054 , "not master", isMasterNs( ns ) );
op.debug().str << ns << ' ';
//获取标志位信息(标识更新一条或多条等)关于消息结构体。有关消息结构参见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/02/2003335.html
int flags = d.pullInt();
//获取"更新消息"结构体中的selector(也就是要更新的数据条件,相关于where)
BSONObj query = d.nextJsObj();
assert( d.moreJSObjs() );
assert( query.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
BSONObj toupdate = d.nextJsObj();//要更新的记录
uassert( 10055 , "update object too large", toupdate.objsize() <= BSONObjMaxUserSize);
assert( toupdate.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
assert( query.objsize() + toupdate.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
//标识是否为upsert方式,即:如果存在就更新,如果不存在就插入
bool upsert = flags & UpdateOption_Upsert;
//是否更新所有满足条件(where)的记录
bool multi = flags & UpdateOption_Multi;
//是否更新所有节点(sharding状态)
bool broadcast = flags & UpdateOption_Broadcast;
{
string s = query.toString();
/* todo: we shouldn't do all this ss stuff when we don't need it, it will slow us down.
instead, let's just story the query BSON in the debug object, and it can toString()
lazily
*/
op.debug().str << " query: " << s;
op.setQuery(query);
}
writelock lk;
// 如果不更新所有节点(sharding)且当前物理结点是shard 状态时
if ( ! broadcast && handlePossibleShardedMessage( m , 0 ) )
return;
//if this ever moves to outside of lock, need to adjust check Client::Context::_finishInit
Client::Context ctx( ns );
UpdateResult res = updateObjects(ns, toupdate, query, upsert, multi, true, op.debug() );//更新对象
lastError.getSafe()->recordUpdate( res.existing , res.num , res.upserted ); // for getlasterror
}
上面的方法中,主要是对消息进行折包解析,找出要更新的数据记录及相应查询条件,以及更新方式(即upsert),然后再在“写锁”环境下执行更新数据操作。
最终上面代码会调用 updateObjects()方法,该方法定义如下:
//update.cpp 文件第1279行
UpdateResult updateObjects(const char *ns, const BSONObj& updateobj, BSONObj patternOrig, bool upsert, bool multi, bool logop , OpDebug& debug ) {
//断言记录的ns是否在"保留的$集合"中
uassert( 10155 , "cannot update reserved $ collection", strchr(ns, '$') == 0 );
if ( strstr(ns, ".system.") ) {
/* dm: it's very important that system.indexes is never updated as IndexDetails has pointers into it */
uassert( 10156 , str::stream() << "cannot update system collection: " << ns << " q: " << patternOrig << " u: " << updateobj , legalClientSystemNS( ns , true ) );
}
return _updateObjects(false, ns, updateobj, patternOrig, upsert, multi, logop, debug);
}
上面方法对要更新的ns进行判断,以避免因更新保留的集合而对系统结构造成损坏,如果一切正常,则调用 _updateObjects方法,如下:
//update.cpp 文件第1027行
UpdateResult _updateObjects(bool god, const char *ns, const BSONObj& updateobj, BSONObj patternOrig, bool upsert, bool multi, bool logop , OpDebug& debug, RemoveSaver* rs ) {
DEBUGUPDATE( "update: " << ns << " update: " << updateobj << " query: " << patternOrig << " upsert: " << upsert << " multi: " << multi );
Client& client = cc();
int profile = client.database()->profile;
StringBuilder& ss = debug.str;
if ( logLevel > 2 )
ss << " update: " << updateobj.toString();
/* idea with these here it to make them loop invariant for multi updates, and thus be a bit faster for that case */
/* NOTE: when yield() is added herein, these must be refreshed after each call to yield! */
NamespaceDetails *d = nsdetails(ns); // can be null if an upsert...
NamespaceDetailsTransient *nsdt = &NamespaceDetailsTransient::get_w(ns);
/* end note */
auto_ptr<ModSet> mods;//定义存储修改信息操作(如$inc, $set, $push,)的集合实例
bool isOperatorUpdate = updateobj.firstElement().fieldName()[0] == '$';
int modsIsIndexed = false; // really the # of indexes
if ( isOperatorUpdate ) {
if( d && d->indexBuildInProgress ) {//如果正在构建索引
set<string> bgKeys;
d->inProgIdx().keyPattern().getFieldNames(bgKeys);//获取当前对象的所有字段(field)信息
mods.reset( new ModSet(updateobj, nsdt->indexKeys(), &bgKeys));//为mods绑定操作信息
}
else {
mods.reset( new ModSet(updateobj, nsdt->indexKeys()) );//为mods绑定操作信息;
}
modsIsIndexed = mods->isIndexed();
}
//upsert:如果存在就更新,如果不存在就插入
if( !upsert && !multi && isSimpleIdQuery(patternOrig) && d && !modsIsIndexed ) {
int idxNo = d->findIdIndex();
if( idxNo >= 0 ) {
ss << " byid ";
//根据id更新记录信息
return _updateById(isOperatorUpdate, idxNo, mods.get(), profile, d, nsdt, god, ns, updateobj, patternOrig, logop, debug);
}
}
set<DiskLoc> seenObjects;
int numModded = 0;
long long nscanned = 0;
MatchDetails details;
//构造“更新操作”实例对象并用其构造游标操作(符)实例
shared_ptr< MultiCursor::CursorOp > opPtr( new UpdateOp( mods.get() && mods->hasDynamicArray() ) );
//构造MultiCursor查询游标(参见其构造方法中的 nextClause()语句)
shared_ptr< MultiCursor > c( new MultiCursor( ns, patternOrig, BSONObj(), opPtr, true ) );
auto_ptr<ClientCursor> cc;
while ( c->ok() ) {//遍历(下面的c->advance()调用)游标指向的记录信息
nscanned++;
bool atomic = c->matcher()->docMatcher().atomic();
// 并将其与更新操作中的条件进行匹配
if ( ! c->matcher()->matches( c->currKey(), c->currLoc(), &details ) ) {
c->advance();//将游标跳转到下一条记录
if ( nscanned % 256 == 0 && ! atomic ) {
if ( cc.get() == 0 ) {
shared_ptr< Cursor > cPtr = c;
cc.reset( new ClientCursor( QueryOption_NoCursorTimeout , cPtr , ns ) );
}
if ( ! cc->yield() ) {
cc.release();
// TODO should we assert or something?
break;
}
if ( !c->ok() ) {
break;
}
}
continue;
}
Record *r = c->_current();//游标当前所指向的记录
DiskLoc loc = c->currLoc();//游标当前所指向的记录所在地址
// TODO Maybe this is unnecessary since we have seenObjects
if ( c->getsetdup( loc ) ) {//判断当前记录是否是重复
c->advance();
continue;
}
BSONObj js(r);
BSONObj pattern = patternOrig;
if ( logop ) {//记录日志
BSONObjBuilder idPattern;
BSONElement id;
// NOTE: If the matching object lacks an id, we'll log
// with the original pattern. This isn't replay-safe.
// It might make sense to suppress the log instead
// if there's no id.
if ( js.getObjectID( id ) ) {
idPattern.append( id );
pattern = idPattern.obj();
}
else {
uassert( 10157 , "multi-update requires all modified objects to have an _id" , ! multi );
}
}
if ( profile )
ss << " nscanned:" << nscanned;
......
uassert( 10158 , "multi update only works with $ operators" , ! multi );
//查看更新记录操作的时间戳,本人猜测这么做可能因为mongodb会采用最后更新时间戳解决分布式系统
//一致性的问题,也就是通常使用的Last write wins准则,有关信息可参见这篇文章:
//http://blog.mongodb.org/post/520888030/on-distributed-consistency-part-5-many-writer
BSONElementManipulator::lookForTimestamps( updateobj );
checkNoMods( updateobj );
//更新记录
theDataFileMgr.updateRecord(ns, d, nsdt, r, loc , updateobj.objdata(), updateobj.objsize(), debug, god);
if ( logop ) {//记录日志操作
DEV if( god ) log() << "REALLY??" << endl; // god doesn't get logged, this would be bad.
logOp("u", ns, updateobj, &pattern );
}
return UpdateResult( 1 , 0 , 1 );//返回操作结果
}
if ( numModded )
return UpdateResult( 1 , 1 , numModded );
......
return UpdateResult( 0 , 0 , 0 );
}
上面的代码主要执行构造更新消息中的查询条件(selector)游标,并将“游标指向”的记录遍历出来与查询条件进行匹配,如果匹配命中,则进行更新。(有关游标的构造和继承实现体系,mongodb做的有些复杂,很难一句说清,我会在本系列后面另用篇幅进行说明)
注意上面代码段中的这行代码:
theDataFileMgr.updateRecord(ns, d, nsdt, r, loc , updateobj.objdata(), updateobj.objsize(), debug, god); 该方法会执行最终更新操作,其定义如下:
//pdfile.cpp 文件934行
const DiskLoc DataFileMgr::updateRecord(
const char *ns,
NamespaceDetails *d,
NamespaceDetailsTransient *nsdt,
Record *toupdate, const DiskLoc& dl,
const char *_buf, int _len, OpDebug& debug, bool god) {
StringBuilder& ss = debug.str;
dassert( toupdate == dl.rec() );
BSONObj objOld(toupdate);
BSONObj objNew(_buf);
DEV assert( objNew.objsize() == _len );
DEV assert( objNew.objdata() == _buf );
//如果_buf中不包含_id,但要更新的记录(toupdate)有_id
if( !objNew.hasElement("_id") && objOld.hasElement("_id") ) {
/* add back the old _id value if the update removes it. Note this implementation is slow
(copies entire object multiple times), but this shouldn't happen often, so going for simple
code, not speed.
*/
BSONObjBuilder b;
BSONElement e;
assert( objOld.getObjectID(e) );//获取对象objOld的ID并绑定到e
b.append(e); // 为了最好的性能,先放入_id
b.appendElements(objNew);
objNew = b.obj();
}
/*重复key检查*/
vector<IndexChanges> changes;
bool changedId = false;
//获取要修改的索引信息(包括要移除和添加的index key,并将结果返回给changes)
getIndexChanges(changes, *d, objNew, objOld, changedId);
//断言是否要修改_id索引
uassert( 13596 , str::stream() << "cannot change _id of a document old:" << objOld << " new:" << objNew , ! changedId );
dupCheck(changes, *d, dl);//重复key检查,如果重复则通过断言终止当前程序
//如果要更新的记录比最终要插入的记录尺寸小
if ( toupdate->netLength() < objNew.objsize() ) {
// 如不合适,则重新分配
uassert( 10003 , "failing update: objects in a capped ns cannot grow", !(d && d->capped));
d->paddingTooSmall();
if ( cc().database()->profile )
ss << " moved ";
//删除指定的记录(record),删除操作详见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/06/mongodb_delete_recode_source_code.html
deleteRecord(ns, toupdate, dl);
//插入新的BSONObj信息,插入操作详见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html
return insert(ns, objNew.objdata(), objNew.objsize(), god);
}
nsdt->notifyOfWriteOp();
d->paddingFits();
/* 如果有要修改的索引 */
{
unsigned keyUpdates = 0;
int z = d->nIndexesBeingBuilt();//获取索引(包括正在构建)数
for ( int x = 0; x < z; x++ ) {
IndexDetails& idx = d->idx(x);
//遍历当前更新记录要修改(移除)的索引键信息
for ( unsigned i = 0; i < changes[x].removed.size(); i++ ) {
try {
//移除当前记录在索引b树中相应信息(索引键)
idx.head.btree()->unindex(idx.head, idx, *changes[x].removed[i], dl);
}
catch (AssertionException&) {
ss << " exception update unindex ";
problem() << " caught assertion update unindex " << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
}
}
assert( !dl.isNull() );
//获取指定名称(key)下的子对象
BSONObj idxKey = idx.info.obj().getObjectField("key");
Ordering ordering = Ordering::make(idxKey);//生成排序方式
keyUpdates += changes[x].added.size();
//遍历当前更新记录要修改(插入)的索引键信息
for ( unsigned i = 0; i < changes[x].added.size(); i++ ) {
try {
//之前做了dupCheck()操作,所以这里不用担心重复key的问题
//在b树中添加索引键信息,有关该方法的定义参见我的这篇文章
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html
idx.head.btree()->bt_insert(
idx.head,
dl, *changes[x].added[i], ordering, /*dupsAllowed*/true, idx);
}
catch (AssertionException& e) {
ss << " exception update index ";
problem() << " caught assertion update index " << idx.indexNamespace() << " " << e << endl;
}
}
}
if( keyUpdates && cc().database()->profile )
ss << '\n' << keyUpdates << " key updates ";
}
// update in place
int sz = objNew.objsize();
//将新修改的记录信息复制到旧记录(toupdate)所在位置
memcpy(getDur().writingPtr(toupdate->data, sz), objNew.objdata(), sz);
return dl;
}
上面代码段主要先对B树索引进行修改(这里采用先移除再重建方式),之后直接更新旧记录在内存中的数据,最终完成了记录的更新操作。
最后,用一张时序图回顾一下更新记录时mongodb服务端代码的执行流程:
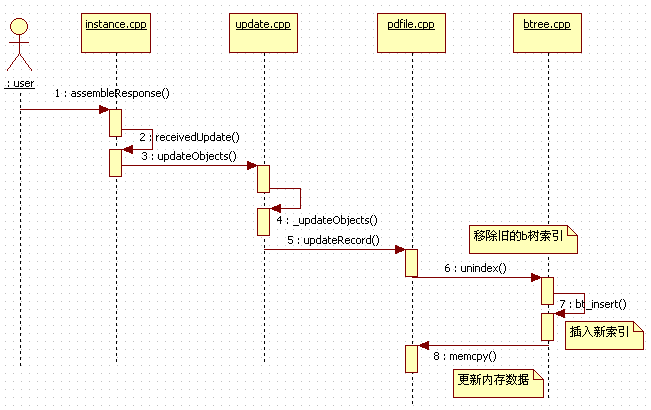
好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了,在接下来的文章中,将会介绍Mongodb的游标(cursor)设计体系和实现方式。
参考链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/06/mongodb_delete_recode_source_code.html http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/02/2003335.html http://blog.mongodb.org/post/520888030/on-distributed-consistency-part-5-many-writer
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/08/mongodb_update_recode_source_code.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
微博: http://t.sina.com.cn/daizhj Tags: mongodb,c++,source code
enum Operations {
opReply = 1, /* reply. responseTo is set. */
dbMsg = 1000, /* generic msg command followed by a string */
dbUpdate = 2001, /* 更新对象 */
dbInsert = 2002,
//dbGetByOID = 2003,
dbQuery = 2004,
dbGetMore = 2005,
dbDelete = 2006,
dbKillCursors = 2007
};
可以看到dbUpdate = 2001 为更新操作枚举值,下面我们看一下assembleResponse在确定是更新操作时调用的方法,如下:
//instance.cpp文件第224行
assembleResponse( Message &m, DbResponse &dbresponse, const SockAddr &client ) {
.....
try {
if ( op == dbInsert ) { //添加记录操作
receivedInsert(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbUpdate ) { //更新记录
receivedUpdate(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbDelete ) { //删除记录
receivedDelete(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbKillCursors ) { //删除Cursors(游标)对象
currentOp.ensureStarted();
logThreshold = 10;
ss << "killcursors ";
receivedKillCursors(m);
}
else {
mongo::log() << " operation isn't supported: " << op << endl;
currentOp.done();
log = true;
}
}
.....
}
}
从上面代码可以看出,系统在确定dbUpdate操作时,调用了receivedUpdate()方法(位于instance.cpp文件第570行),下面是该方法的定义:
void receivedUpdate(Message& m, CurOp& op) {
DbMessage d(m);//初始化数据库格式的消息
const char *ns = d.getns();//获取名空间,用于接下来insert数据
assert(*ns);
//因为CUD操作在主库中操作,所以这里断言名空间包含的db信息中是不是主库,即"master"
uassert( 10054 , "not master", isMasterNs( ns ) );
op.debug().str << ns << ' ';
//获取标志位信息(标识更新一条或多条等)关于消息结构体。有关消息结构参见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/02/2003335.html
int flags = d.pullInt();
//获取"更新消息"结构体中的selector(也就是要更新的数据条件,相关于where)
BSONObj query = d.nextJsObj();
assert( d.moreJSObjs() );
assert( query.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
BSONObj toupdate = d.nextJsObj();//要更新的记录
uassert( 10055 , "update object too large", toupdate.objsize() <= BSONObjMaxUserSize);
assert( toupdate.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
assert( query.objsize() + toupdate.objsize() < m.header()->dataLen() );
//标识是否为upsert方式,即:如果存在就更新,如果不存在就插入
bool upsert = flags & UpdateOption_Upsert;
//是否更新所有满足条件(where)的记录
bool multi = flags & UpdateOption_Multi;
//是否更新所有节点(sharding状态)
bool broadcast = flags & UpdateOption_Broadcast;
{
string s = query.toString();
/* todo: we shouldn't do all this ss stuff when we don't need it, it will slow us down.
instead, let's just story the query BSON in the debug object, and it can toString()
lazily
*/
op.debug().str << " query: " << s;
op.setQuery(query);
}
writelock lk;
// 如果不更新所有节点(sharding)且当前物理结点是shard 状态时
if ( ! broadcast && handlePossibleShardedMessage( m , 0 ) )
return;
//if this ever moves to outside of lock, need to adjust check Client::Context::_finishInit
Client::Context ctx( ns );
UpdateResult res = updateObjects(ns, toupdate, query, upsert, multi, true, op.debug() );//更新对象
lastError.getSafe()->recordUpdate( res.existing , res.num , res.upserted ); // for getlasterror
}
上面的方法中,主要是对消息进行折包解析,找出要更新的数据记录及相应查询条件,以及更新方式(即upsert),然后再在“写锁”环境下执行更新数据操作。
最终上面代码会调用 updateObjects()方法,该方法定义如下:
//update.cpp 文件第1279行
UpdateResult updateObjects(const char *ns, const BSONObj& updateobj, BSONObj patternOrig, bool upsert, bool multi, bool logop , OpDebug& debug ) {
//断言记录的ns是否在"保留的$集合"中
uassert( 10155 , "cannot update reserved $ collection", strchr(ns, '$') == 0 );
if ( strstr(ns, ".system.") ) {
/* dm: it's very important that system.indexes is never updated as IndexDetails has pointers into it */
uassert( 10156 , str::stream() << "cannot update system collection: " << ns << " q: " << patternOrig << " u: " << updateobj , legalClientSystemNS( ns , true ) );
}
return _updateObjects(false, ns, updateobj, patternOrig, upsert, multi, logop, debug);
}
上面方法对要更新的ns进行判断,以避免因更新保留的集合而对系统结构造成损坏,如果一切正常,则调用 _updateObjects方法,如下:
//update.cpp 文件第1027行
UpdateResult _updateObjects(bool god, const char *ns, const BSONObj& updateobj, BSONObj patternOrig, bool upsert, bool multi, bool logop , OpDebug& debug, RemoveSaver* rs ) {
DEBUGUPDATE( "update: " << ns << " update: " << updateobj << " query: " << patternOrig << " upsert: " << upsert << " multi: " << multi );
Client& client = cc();
int profile = client.database()->profile;
StringBuilder& ss = debug.str;
if ( logLevel > 2 )
ss << " update: " << updateobj.toString();
/* idea with these here it to make them loop invariant for multi updates, and thus be a bit faster for that case */
/* NOTE: when yield() is added herein, these must be refreshed after each call to yield! */
NamespaceDetails *d = nsdetails(ns); // can be null if an upsert...
NamespaceDetailsTransient *nsdt = &NamespaceDetailsTransient::get_w(ns);
/* end note */
auto_ptr<ModSet> mods;//定义存储修改信息操作(如$inc, $set, $push,)的集合实例
bool isOperatorUpdate = updateobj.firstElement().fieldName()[0] == '$';
int modsIsIndexed = false; // really the # of indexes
if ( isOperatorUpdate ) {
if( d && d->indexBuildInProgress ) {//如果正在构建索引
set<string> bgKeys;
d->inProgIdx().keyPattern().getFieldNames(bgKeys);//获取当前对象的所有字段(field)信息
mods.reset( new ModSet(updateobj, nsdt->indexKeys(), &bgKeys));//为mods绑定操作信息
}
else {
mods.reset( new ModSet(updateobj, nsdt->indexKeys()) );//为mods绑定操作信息;
}
modsIsIndexed = mods->isIndexed();
}
//upsert:如果存在就更新,如果不存在就插入
if( !upsert && !multi && isSimpleIdQuery(patternOrig) && d && !modsIsIndexed ) {
int idxNo = d->findIdIndex();
if( idxNo >= 0 ) {
ss << " byid ";
//根据id更新记录信息
return _updateById(isOperatorUpdate, idxNo, mods.get(), profile, d, nsdt, god, ns, updateobj, patternOrig, logop, debug);
}
}
set<DiskLoc> seenObjects;
int numModded = 0;
long long nscanned = 0;
MatchDetails details;
//构造“更新操作”实例对象并用其构造游标操作(符)实例
shared_ptr< MultiCursor::CursorOp > opPtr( new UpdateOp( mods.get() && mods->hasDynamicArray() ) );
//构造MultiCursor查询游标(参见其构造方法中的 nextClause()语句)
shared_ptr< MultiCursor > c( new MultiCursor( ns, patternOrig, BSONObj(), opPtr, true ) );
auto_ptr<ClientCursor> cc;
while ( c->ok() ) {//遍历(下面的c->advance()调用)游标指向的记录信息
nscanned++;
bool atomic = c->matcher()->docMatcher().atomic();
// 并将其与更新操作中的条件进行匹配
if ( ! c->matcher()->matches( c->currKey(), c->currLoc(), &details ) ) {
c->advance();//将游标跳转到下一条记录
if ( nscanned % 256 == 0 && ! atomic ) {
if ( cc.get() == 0 ) {
shared_ptr< Cursor > cPtr = c;
cc.reset( new ClientCursor( QueryOption_NoCursorTimeout , cPtr , ns ) );
}
if ( ! cc->yield() ) {
cc.release();
// TODO should we assert or something?
break;
}
if ( !c->ok() ) {
break;
}
}
continue;
}
Record *r = c->_current();//游标当前所指向的记录
DiskLoc loc = c->currLoc();//游标当前所指向的记录所在地址
// TODO Maybe this is unnecessary since we have seenObjects
if ( c->getsetdup( loc ) ) {//判断当前记录是否是重复
c->advance();
continue;
}
BSONObj js(r);
BSONObj pattern = patternOrig;
if ( logop ) {//记录日志
BSONObjBuilder idPattern;
BSONElement id;
// NOTE: If the matching object lacks an id, we'll log
// with the original pattern. This isn't replay-safe.
// It might make sense to suppress the log instead
// if there's no id.
if ( js.getObjectID( id ) ) {
idPattern.append( id );
pattern = idPattern.obj();
}
else {
uassert( 10157 , "multi-update requires all modified objects to have an _id" , ! multi );
}
}
if ( profile )
ss << " nscanned:" << nscanned;
......
uassert( 10158 , "multi update only works with $ operators" , ! multi );
//查看更新记录操作的时间戳,本人猜测这么做可能因为mongodb会采用最后更新时间戳解决分布式系统
//一致性的问题,也就是通常使用的Last write wins准则,有关信息可参见这篇文章:
//http://blog.mongodb.org/post/520888030/on-distributed-consistency-part-5-many-writer
BSONElementManipulator::lookForTimestamps( updateobj );
checkNoMods( updateobj );
//更新记录
theDataFileMgr.updateRecord(ns, d, nsdt, r, loc , updateobj.objdata(), updateobj.objsize(), debug, god);
if ( logop ) {//记录日志操作
DEV if( god ) log() << "REALLY??" << endl; // god doesn't get logged, this would be bad.
logOp("u", ns, updateobj, &pattern );
}
return UpdateResult( 1 , 0 , 1 );//返回操作结果
}
if ( numModded )
return UpdateResult( 1 , 1 , numModded );
......
return UpdateResult( 0 , 0 , 0 );
}
上面的代码主要执行构造更新消息中的查询条件(selector)游标,并将“游标指向”的记录遍历出来与查询条件进行匹配,如果匹配命中,则进行更新。(有关游标的构造和继承实现体系,mongodb做的有些复杂,很难一句说清,我会在本系列后面另用篇幅进行说明)
注意上面代码段中的这行代码:
theDataFileMgr.updateRecord(ns, d, nsdt, r, loc , updateobj.objdata(), updateobj.objsize(), debug, god); 该方法会执行最终更新操作,其定义如下:
//pdfile.cpp 文件934行
const DiskLoc DataFileMgr::updateRecord(
const char *ns,
NamespaceDetails *d,
NamespaceDetailsTransient *nsdt,
Record *toupdate, const DiskLoc& dl,
const char *_buf, int _len, OpDebug& debug, bool god) {
StringBuilder& ss = debug.str;
dassert( toupdate == dl.rec() );
BSONObj objOld(toupdate);
BSONObj objNew(_buf);
DEV assert( objNew.objsize() == _len );
DEV assert( objNew.objdata() == _buf );
//如果_buf中不包含_id,但要更新的记录(toupdate)有_id
if( !objNew.hasElement("_id") && objOld.hasElement("_id") ) {
/* add back the old _id value if the update removes it. Note this implementation is slow
(copies entire object multiple times), but this shouldn't happen often, so going for simple
code, not speed.
*/
BSONObjBuilder b;
BSONElement e;
assert( objOld.getObjectID(e) );//获取对象objOld的ID并绑定到e
b.append(e); // 为了最好的性能,先放入_id
b.appendElements(objNew);
objNew = b.obj();
}
/*重复key检查*/
vector<IndexChanges> changes;
bool changedId = false;
//获取要修改的索引信息(包括要移除和添加的index key,并将结果返回给changes)
getIndexChanges(changes, *d, objNew, objOld, changedId);
//断言是否要修改_id索引
uassert( 13596 , str::stream() << "cannot change _id of a document old:" << objOld << " new:" << objNew , ! changedId );
dupCheck(changes, *d, dl);//重复key检查,如果重复则通过断言终止当前程序
//如果要更新的记录比最终要插入的记录尺寸小
if ( toupdate->netLength() < objNew.objsize() ) {
// 如不合适,则重新分配
uassert( 10003 , "failing update: objects in a capped ns cannot grow", !(d && d->capped));
d->paddingTooSmall();
if ( cc().database()->profile )
ss << " moved ";
//删除指定的记录(record),删除操作详见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/06/mongodb_delete_recode_source_code.html
deleteRecord(ns, toupdate, dl);
//插入新的BSONObj信息,插入操作详见我的这篇文章:
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html
return insert(ns, objNew.objdata(), objNew.objsize(), god);
}
nsdt->notifyOfWriteOp();
d->paddingFits();
/* 如果有要修改的索引 */
{
unsigned keyUpdates = 0;
int z = d->nIndexesBeingBuilt();//获取索引(包括正在构建)数
for ( int x = 0; x < z; x++ ) {
IndexDetails& idx = d->idx(x);
//遍历当前更新记录要修改(移除)的索引键信息
for ( unsigned i = 0; i < changes[x].removed.size(); i++ ) {
try {
//移除当前记录在索引b树中相应信息(索引键)
idx.head.btree()->unindex(idx.head, idx, *changes[x].removed[i], dl);
}
catch (AssertionException&) {
ss << " exception update unindex ";
problem() << " caught assertion update unindex " << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
}
}
assert( !dl.isNull() );
//获取指定名称(key)下的子对象
BSONObj idxKey = idx.info.obj().getObjectField("key");
Ordering ordering = Ordering::make(idxKey);//生成排序方式
keyUpdates += changes[x].added.size();
//遍历当前更新记录要修改(插入)的索引键信息
for ( unsigned i = 0; i < changes[x].added.size(); i++ ) {
try {
//之前做了dupCheck()操作,所以这里不用担心重复key的问题
//在b树中添加索引键信息,有关该方法的定义参见我的这篇文章
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html
idx.head.btree()->bt_insert(
idx.head,
dl, *changes[x].added[i], ordering, /*dupsAllowed*/true, idx);
}
catch (AssertionException& e) {
ss << " exception update index ";
problem() << " caught assertion update index " << idx.indexNamespace() << " " << e << endl;
}
}
}
if( keyUpdates && cc().database()->profile )
ss << '\n' << keyUpdates << " key updates ";
}
// update in place
int sz = objNew.objsize();
//将新修改的记录信息复制到旧记录(toupdate)所在位置
memcpy(getDur().writingPtr(toupdate->data, sz), objNew.objdata(), sz);
return dl;
}
上面代码段主要先对B树索引进行修改(这里采用先移除再重建方式),之后直接更新旧记录在内存中的数据,最终完成了记录的更新操作。
最后,用一张时序图回顾一下更新记录时mongodb服务端代码的执行流程:

好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了,在接下来的文章中,将会介绍Mongodb的游标(cursor)设计体系和实现方式。
参考链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/06/mongodb_delete_recode_source_code.html http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/02/2003335.html http://blog.mongodb.org/post/520888030/on-distributed-consistency-part-5-many-writer
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/08/mongodb_update_recode_source_code.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
微博: http://t.sina.com.cn/daizhj Tags: mongodb,c++,source code
相关文章推荐
- Mongodb源码分析--更新记录
- Mongodb源码分析--更新记录
- mongodb源码分析(十二)数据的更新
- Mongodb源码分析--删除记录
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--删除记录
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--删除记录
- Mongodb源码分析--删除记录
- Mongodb源码分析--删除记录
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb源码分析--插入记录及索引B树构建
- Mongodb 源码分析--Replication之OpLog
- Vue学习之源码分析--Vue.js异步更新DOM策略及nextTick(八)
- PostgreSQL存储引擎源码分析二(原创,不断更新)
- PostgreSQL存储引擎源码分析三(原创,不断更新)
- mongodb源码分析(十六)replication replset同步以及状态的切换
